DIRECTION Fil in the blanks with the correct word to complete the

Selective Cutting and Sustainable Forestry Plans Countryside
The removal of forest canopy cover post clear-cutting causes extreme changes in the biotic and abiotic environment. Controlled burning of clear cuts is also a common practice after timber harvests. However, because of limited data on clear-cutting, forest recovery after this widespread timber-harvesting practice is poorly understood.

Is weed or alcohol more addictive?
Difference Between Clear-Cutting And Deforestation. Clear-cutting is often mistaken for deforestation. Yet, clear-cutting and deforestation are two different terms. Clear-cutting can be regarded as deforestation only when forests are logged for agricultural use, with possible desertification as the most serious land degradation outcome.

What is the Difference Between Monohybrid Cross and Reciprocal Cross
Selective cutting is a term used in the management of forest land. Selective cutting and clear cutting both have a place in the proper management of timber growth. Protecting trees from deer is just one concern of forest landowners today. Trees are a renewable resource. Forests need to be managed and cared for properly as any natural resource.

62 Short Answer Similarities and Differences The social science lens
Selective cutting is a less ecologically sensitive approach to harvesting timber. Here's how Shultz explains it. Professional foresters are taught in school how to use a number of silvicultural systems, including the selection system, as a menu of alternatives for managing woodlands. Forestry professors are quick to point out that.

5.2 Clearcutting YouTube
Selective cutting, also called selective thinning, involves carefully choosing which trees to log while leaving the rest of the forest intact. This process allows for better yield and productivity over several decades. Each year provides trees for harvest, rather than having to wait a minimum of sixty years after a clear-cut.
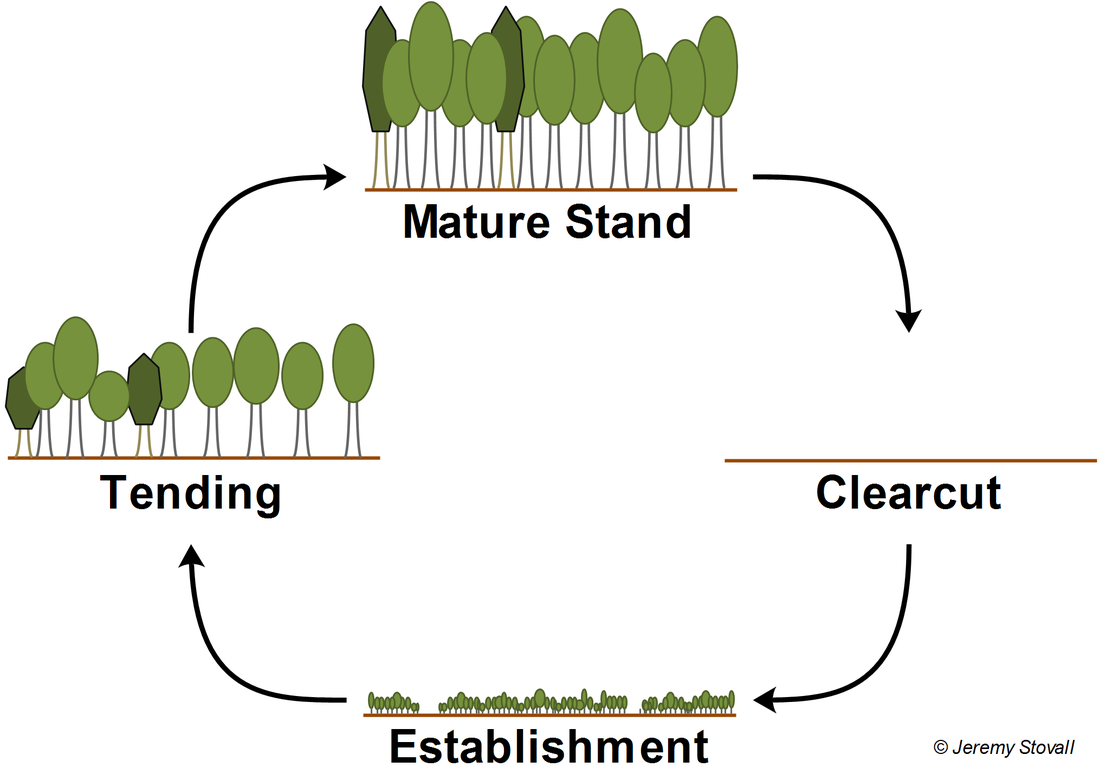
Methods of cutting Methods of cutting and replanting of forests
This article will provide an overview of clear cutting and selective cutting, highlighting their impacts on forests and the environment. Clear Cutting. Definition: Clear cutting is a forestry technique that involves the complete removal of all trees in a designated area. This method is often used for large-scale commercial operations.

SOLVEDWhat is the difference between a promoterproximal element and a
Clear Cutting. All the trees are cut at once. - Quicker, cheaper, safer. -Changes the ecosystem soil erosion loss of habitat, tree take a long time to grow back. Selective Cutting. Only cutting only certain trees down at once. - Slower, more expensive. - Less damaging to environment, tree growth can be managed.
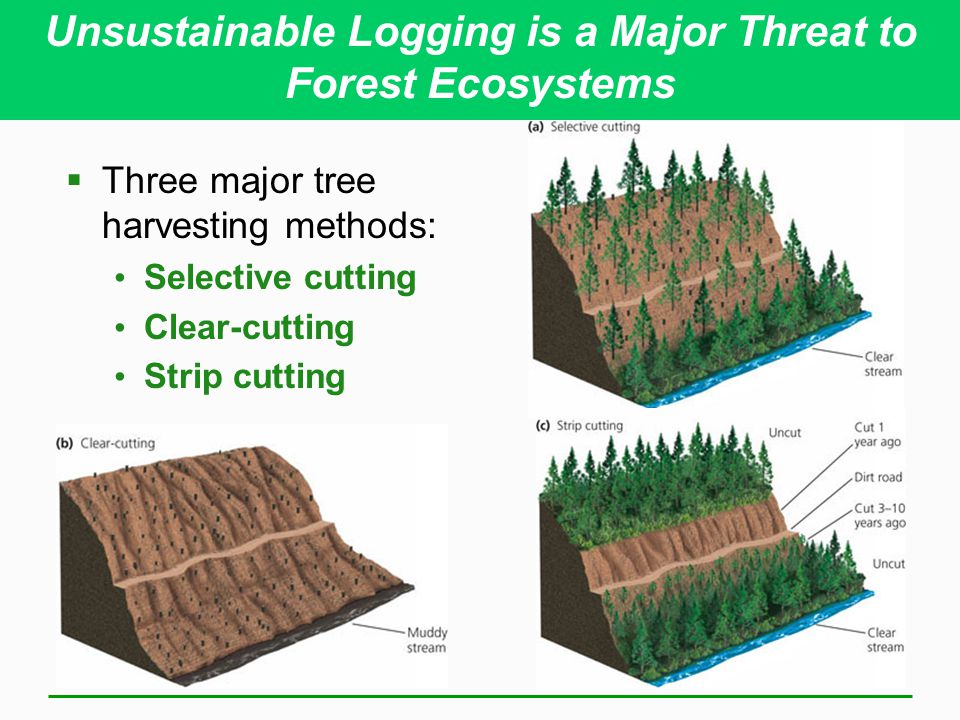
Methods of cutting Methods of cutting and replanting of forests
In Table 1, we present different environmentally ethical perspectives with a brief definition and examples relating these views to different forestry aims.Clear boundaries between clear-cutting, selective logging, and variable retention harvesting can be evidenced when different ethical points of view and alternatives in the human-nature relationships are considered.
What Are the Similarities Between Clear Cutting and Selective Cutting
Clear-cutting and selective logging have been widely employed to harvest tropical forests. Variation in harvesting methods is generally associated with different degrees of recovery and successional trajectories (Chazdon et al. 2009). Few studies have compared the impacts of these two harvesting approaches on tropical forest recovery, although.

DIRECTION Fil in the blanks with the correct word to complete the
Clear-cutting, the practice of cutting down most or all of the trees in a forest or a section of forest at the same time, usually in a uniform way. Clear-cutting is done to clear land for agriculture or ranching or simply to provide timber and other wood products. In some cases, clear-cutting may.

Logging Selective vs Clear Cut YouTube
A clear-cut increases soil erosion, water degradation, and increased silting in creeks, rivers, and reservoirs. Old-growth forests, which have been systematically clear-cut, are healthy ecosystems that have evolved over centuries to be more resistant to insects and disease.; Clear-cutting inhibits the sustainability of healthy, holistic forest ecosystems.
Similarities, Key Differences Between COVID19 and the Flu
Selective and clear-cut logged forests supported similar stem density of trees, but they were lower than that of the old-growth forest. Finally, the old-growth forest exhibited significantly higher basal area than the selectively logged forest, which in turn, had significantly higher basal area than the clear-cut logged forest..

Oral presentation for the exam Structure Research questions What
Selective Cutting. That's a good thing, right? It's what everybody wants for their woodlots, and what many loggers use to describe their work. But what does "selective cutting" really mean? Many foresters consider it a euphemism for exploitive cutting, often used to describe high grading, liquidation harvests, or diameter limit cutting.

Clearcut & Selective cut YouTube
With selective cutting, the property owner pays a company (like us), to cut the trees for them. In clear cutting, the logger pays the homeowner a percentage of the timber sale and pockets the rest. We get it — we'd rather get money than spend it, too! Many property owners think of it as a "quick buck" — they'll clear cut, plant and.

Selective cutting vs clearcutting long term perspective Download
Selective logging is the removal of selected trees within a forest based on criteria such as diameter, height or species. Remaining trees are left in the stand, as opposed to clearcutting where all trees are felled. This intervention is similar to several others that involve harvesting some, but not all, trees.

what are the similarities that the picture have? Brainly.ph
The individual tree selection method meets the needs of most high-forest, cavity-dwelling, closed canopy wildlife species. This method is least beneficial for wildlife species that use openings, edges and low browse. The visual resource is minimally affected by harvesting with the individual tree selection method.