Myelinated Motor Neurons Function, Location & Types

Motor Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
NIH HHS USA.gov While the term "motor neuron" evokes the idea that there is only one type of neuron that conducts movement, this is far from the truth.
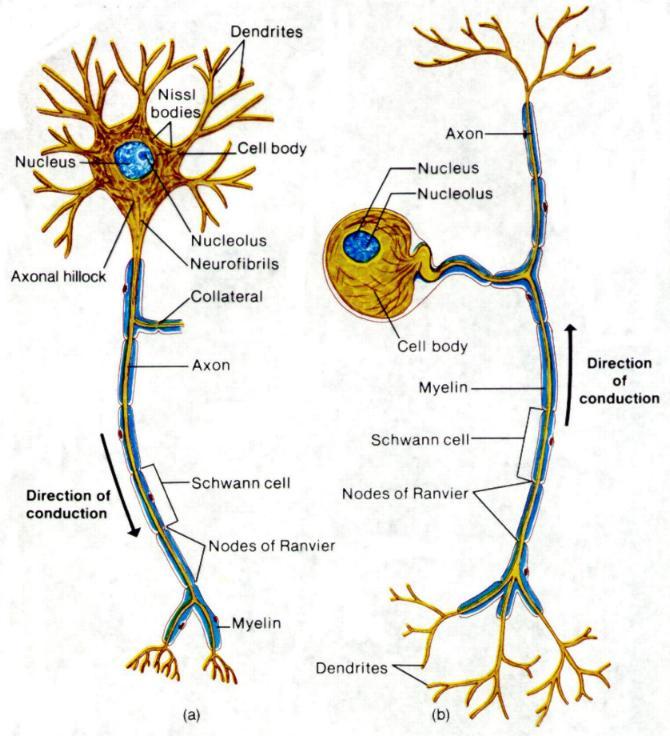
Neurones Anjung Sains Makmal 3
Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally-based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo-unipolar neurons. These cells coordinate bodily functions and movement so quickly, we don't even notice it happening. 9 Sources. By Kevin James Cyr.

Neuroanatomy, Motor Neuron StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf
Essentially, motor neurons, also known as motoneurons, are made up of a variety of intricate, finely tuned circuits found throughout the body that innervate effector muscles and glands to enable both voluntary and involuntary motions. Two motor neurons come together to form a two-neuron circuit.

Picture Of A Neuron Labeled Luxury Motor Neuron Detailed Accurate
Motor neurons get information from other neurons and convey commands to your muscles, organs and glands.

Motor neurons of the somatic nervous system pikolyourself
At its simplest, the neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract. The activation of many muscle fibers together causes muscles to contract, which in turn can produce movement.

Figure 7 4 Structure Of A Typical Motor Neuron Bangmuin Image Josh
A motor neuron is basically a nerve cell whose function is to respond to sensory stimulation by producing the required muscular movement. Motor neurons are located in the spinal cord, and their axon protrudes outside to the muscle fibers.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
Neuron Anatomy, Nerve Impulses, and Classifications
A single oligodendrocyte can extend to up to 50 axons, wrapping around approximately 1 mm of each and forming the myelin sheath; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can only wrap around 1 axon. ( 27 votes) Upvote Flag

Motor Neuron Disease Neurological Issues Herbal Care Products
Neuron Structure. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. The main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Somatic Motor Neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated.
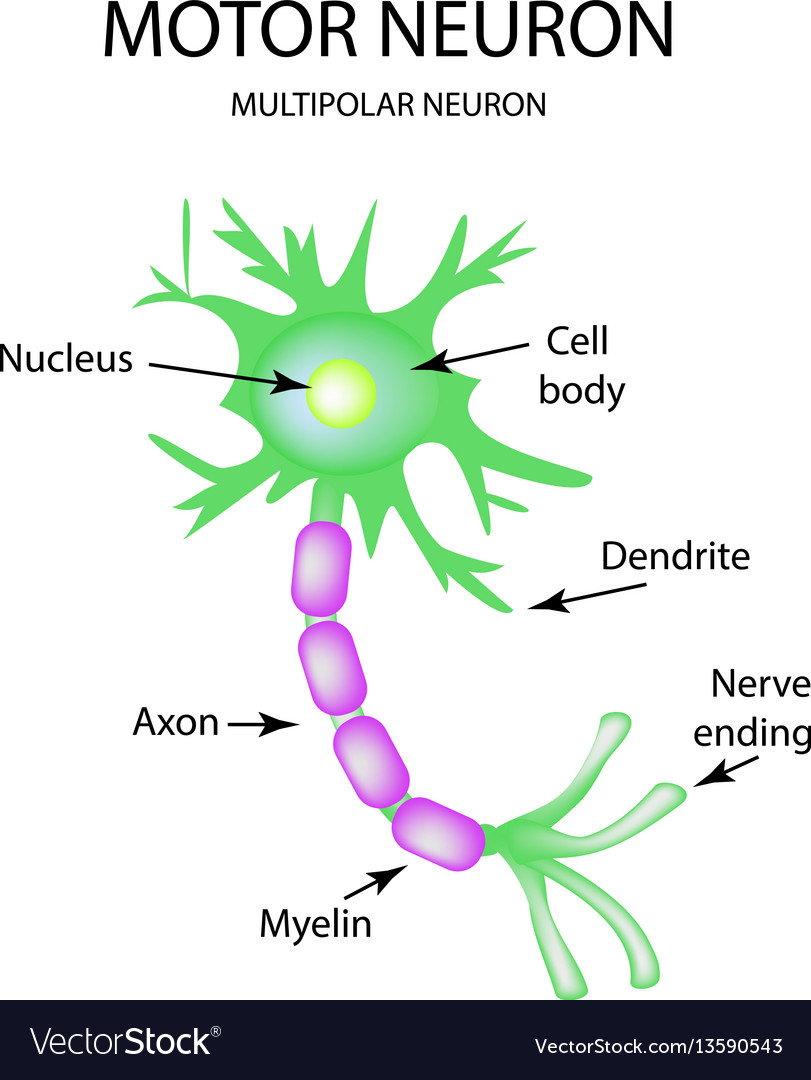
The structure of the motor neuron infographics on Vector Image
Motor neurones are cells in the brain and spinal cord that allow us to move, speak, swallow and breathe by sending commands from the brain to the muscles that carry out these functions. Their nerve fibers are the longest in the body, a single axon can stretch from the base of the spinal cord all the way to the toes.

Neuron Diagram Straight from a Scientist
Figure 14.28 Corticospinal Tract The major descending tract that controls skeletal muscle movements is the corticospinal tract. It is composed of two neurons, the upper motor neuron and the lower motor neuron. The upper motor neuron has its cell body in the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe and synapses on the lower motor neuron, which is in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and.

FileNeuron1.jpg Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Author Calli McMurray Source BrainFacts/SfN Motor neurons carry movement instructions from the brain and spinal cord to muscles throughout the body. Their nerve fibers are the longest in the body — a single axon can stretch from the base of the spinal cord all the way to the toes. Brain Bytes showcase essential facts about neuroscience.

Structure of a motor neuron. Anatomy of a typical human neuron
A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. When these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. This is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. Motor Neuron Overview

Myelinated Motor Neurons Function, Location & Types
Motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. They release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to muscle movement.

The Nervous System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
Well-Labelled Diagram of Motor Neuron A motor neuron is a nerve cell that functions to transmit signals from the central area of the nervous system to an effector site such as muscles or glands. A motor neuron can be broadly seen as consisting of three parts - cell body, axon and dendrites.
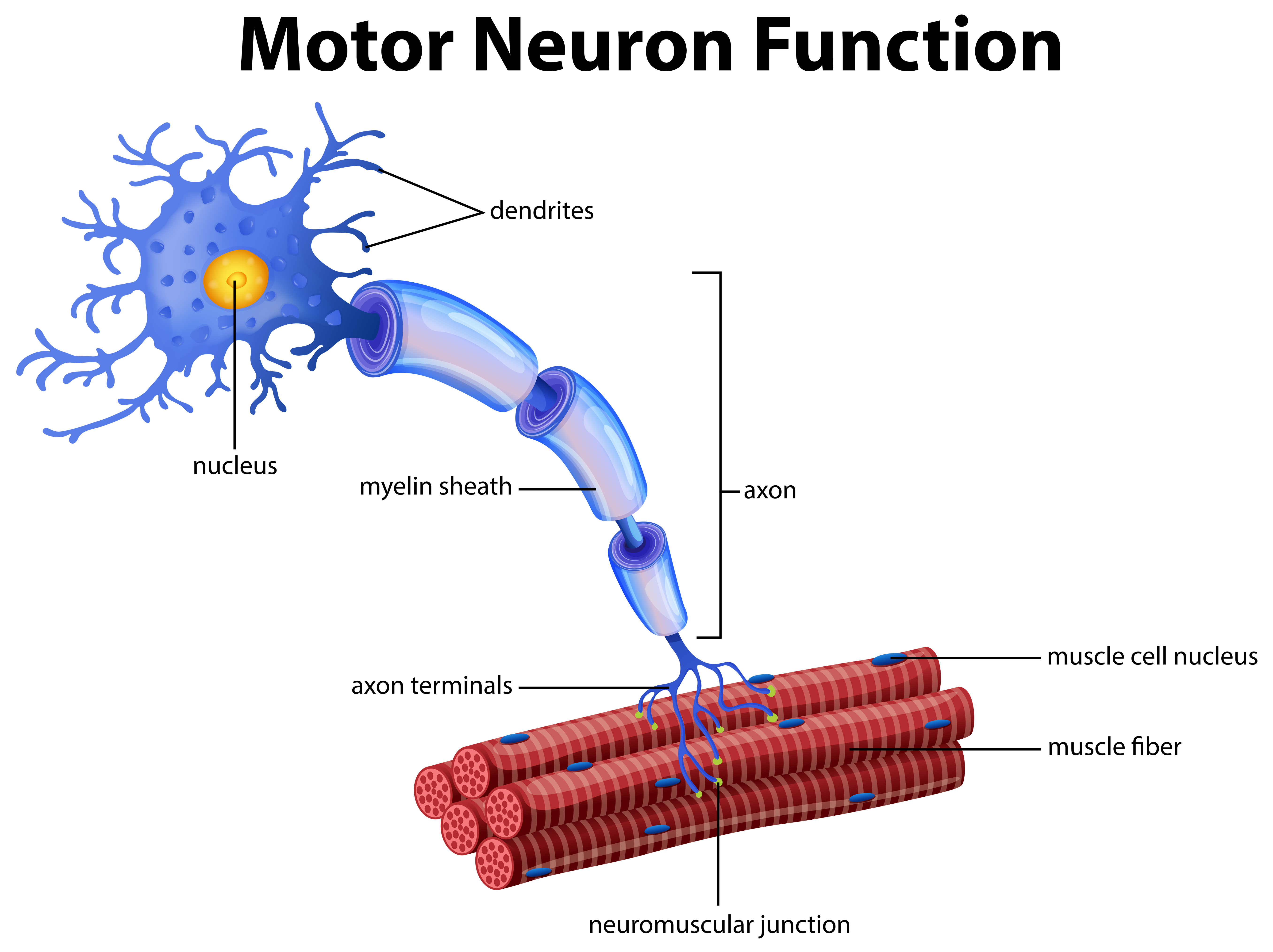
A Vector of Motor Neuron Function 296405 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Structure Motor neurons are usually made up of large and myelinated alpha-efferent axons. They arise from motor neuron cell bodies in the anterior horns of the gray matter within the spinal cord. Their terminal branches are short unmyelinated twigs which travel through the endomysium to form part of the neuromuscular junction.

Draw A Neuron And Label Its Parts Q10 A Draw The Structure Of Neuron
The target of the upper motor neuron is the dendrites of the lower motor neuron in the gray matter of the spinal cord. (8) The axon of the lower motor neuron emerges from the spinal cord in a nerve and connects to a muscle through a neuromuscular junction to cause contraction of the target muscle.