Thoracic cavity Thoracic cavity, Anatomy, Thoracic duct
6.2 Review of Basic Concepts Nursing Pharmacology
thorax body cavity thoracic cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity (the body's largest hollow space) by a muscular and membranous partition, the diaphragm.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11160/lungs-in-situ_english__1_.jpg)
33 Label The Structures Of The Thoracic Cavity Labels For Your Ideas
The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature - all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. The thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture located inferiorly.

Thoracic cage Skeletal system anatomy, Basic anatomy and physiology
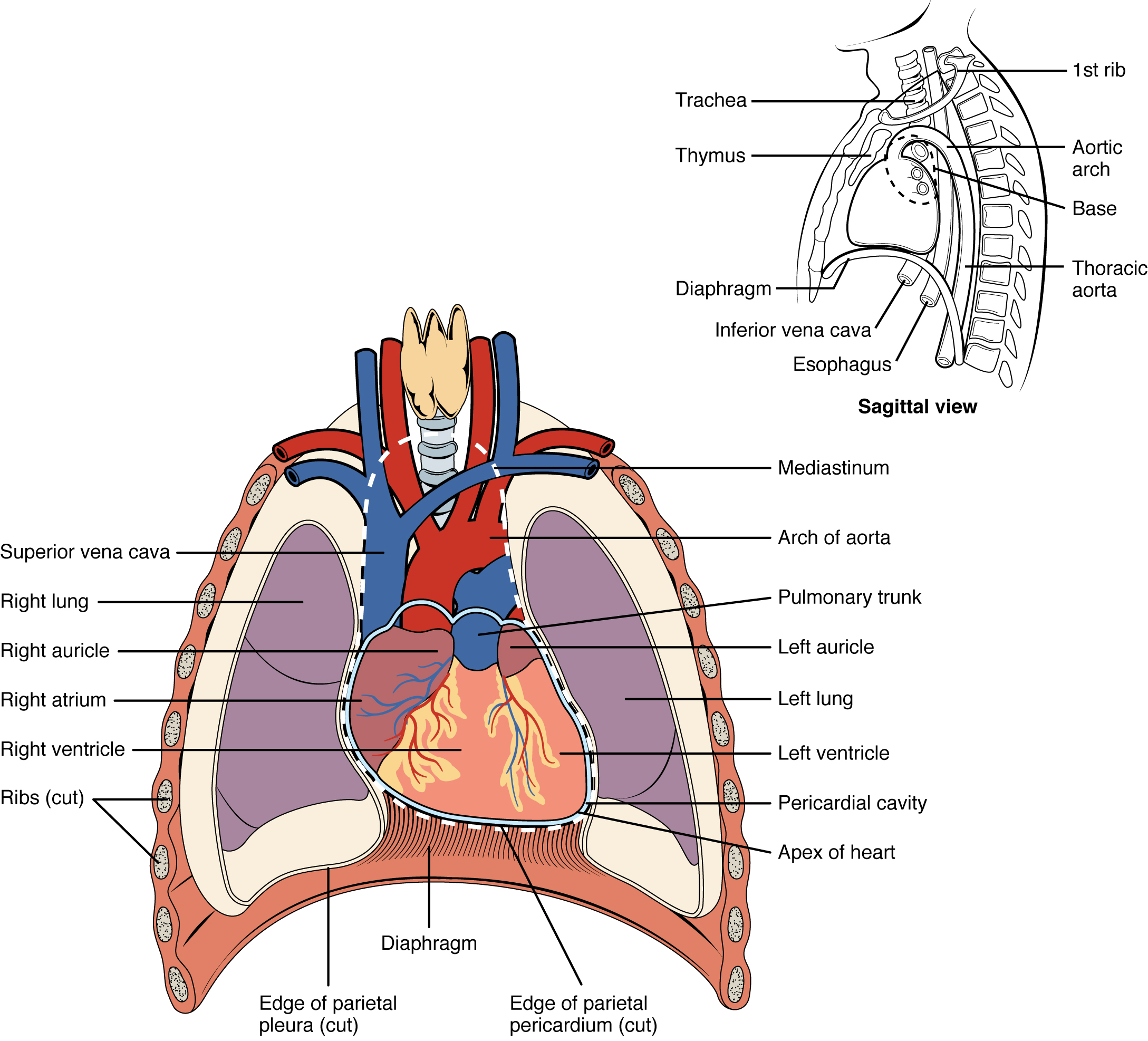
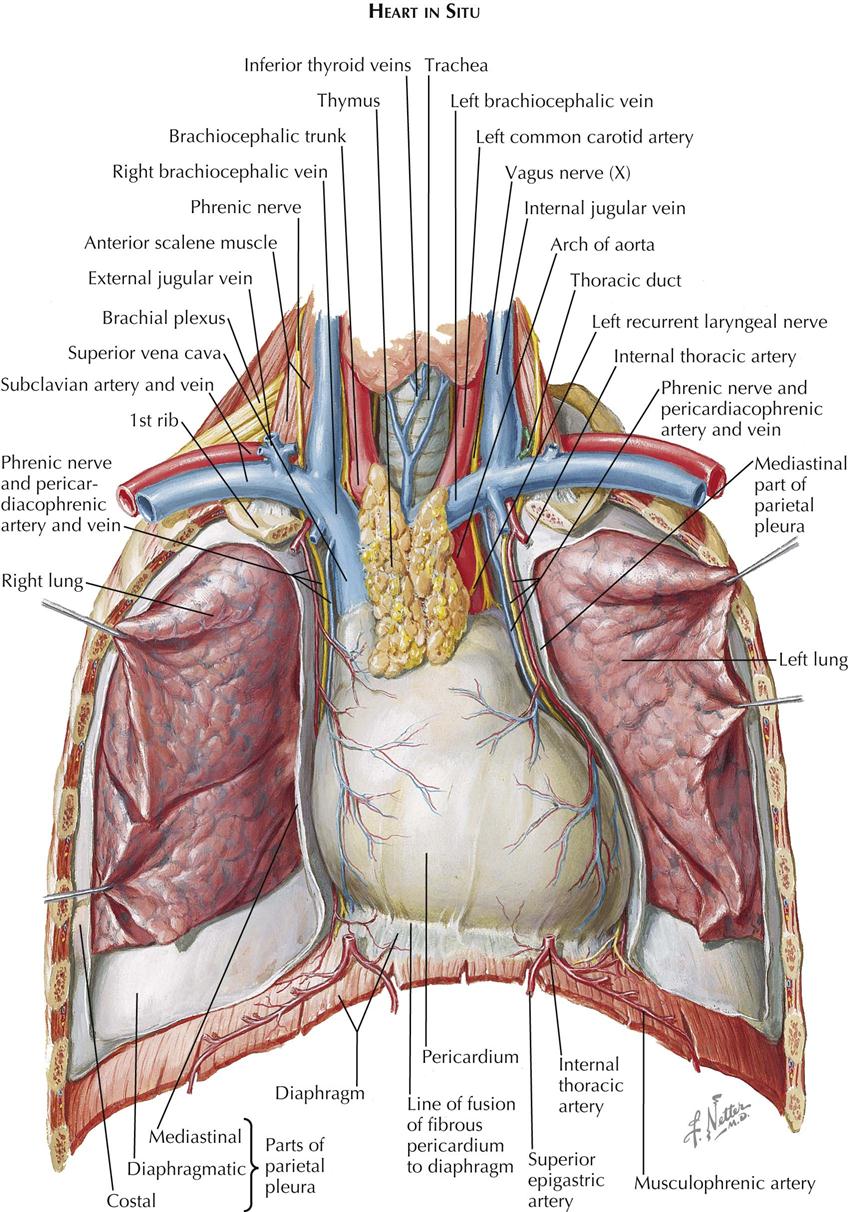
Your thoracic cavity is a space in your chest that contains organs, blood vessels, nerves and other important body structures. It's divided into three main parts: right pleural cavity, left pleural cavity and mediastinum. The five organs in your thoracic cavity are your heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea and thymus.

Thoracic cavity Thoracic cavity, Anatomy, Thoracic duct
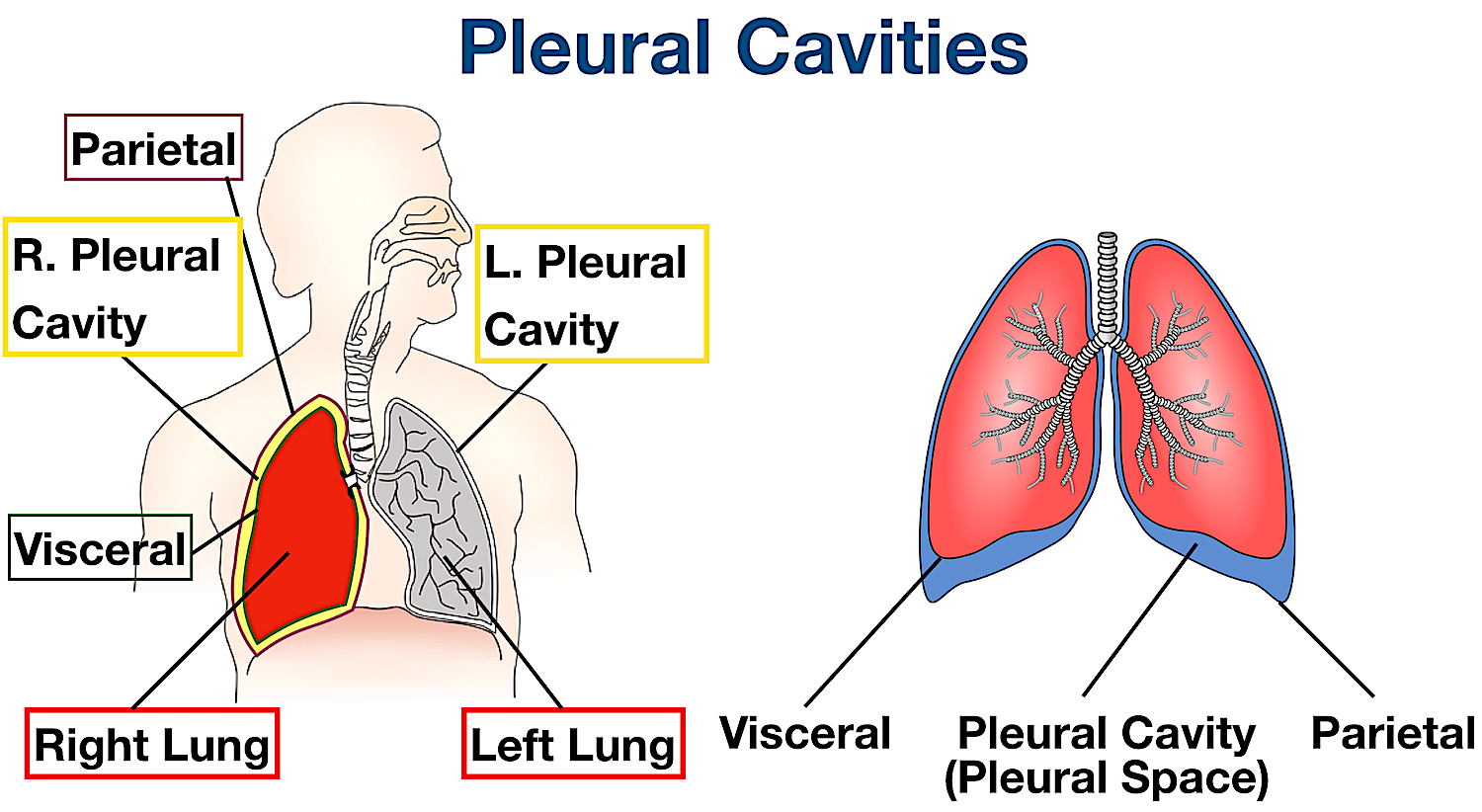
Anatomical Position and Relations. The lungs lie either side of the mediastinum, within the thoracic cavity. Each lung is surrounded by a pleural cavity, which is formed by the visceral and parietal pleura.. They are suspended from the mediastinum by the lung root - a collection of structures entering and leaving the lungs. The medial surfaces of both lungs lie in close proximity to several.
1. Anatomy Thoracic Key
The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. These muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. Other muscles that do not make up the thoracic wall, but attach to it include the pectoralis major and minor.

visceral pleura Planes, Sections, and Cavities Cavities, Thoracic
The thoracic wall consists of a bony framework held together by twelve thoracic vertebrae posteriorly, giving rise to ribs that encircle the lateral and anterior thoracic cavity. The first nine ribs curve around the lateral thoracic wall and connect to the manubrium and sternum. Ribs 10 to 12 are relatively short and attach to the costal margins of the ribs just above them. Ribs 10 to 12, due.
45 label thoracic cavity
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. Thoracic Cage. The thoracic cage is formed by the (a) sternum and (b) 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The ribs are classified as true ribs (1-7) and.

anterior view of a human thoracic cage. A&P Pinterest
Definition. The aspect of the pleura that covers the external surface of the lung. Location. The thoracic cavity can be subdivided into. 1. mediastinum. 2. left and right pleural cavities. 3. pericardial cavity. Sign up and see the remaining cards. It's free!

The Thoracic Cage and Pectoral Girdle, Anterior View anatomy images
Unit 1 Lab Homework 5.0 (3 reviews) Label the regions of the body. Click the card to flip 👆 Left Down: Cervical Axillary Cubital Antebrachial Crural Right Down: Deltoid Brachial Inguinal Femoral Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 13 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by tylerdylan1995 Students also viewed

Human Anatomy Chest Cavity Anatomy Of Chest Bones Human Anatomy Diagram
The sternum is the elongated bony structure that anchors the anterior thoracic cage. It consists of three parts: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The manubrium is the wider, superior portion of the sternum. The top of the manubrium has a shallow, U-shaped border called the jugular (suprasternal) notch.

Body Cavities Diagram Visual Diagram
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. Figure 7.32 Thoracic Cage The thoracic cage is formed by the (a) sternum and (b) 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The ribs are classified as true ribs (1.

Thoracic Cavity Definition & Organs of Chest Cavity Biology Dictionary
Correctly label the following structures related to the position of the heart in the thorax. Correctly label the following anatomical features of the thoracic cavity. Correctly label the following parts of the pericardium and the heart walls.

Human Anatomy Drawing, Human Body Anatomy, Human Anatomy And Physiology
The thoracic duct is the largest lymphatic vessel in the human body. Around 75% of the lymph from the entire body (aside from the right upper limb, right breast, right lung and right side of the head and neck) passes through the thoracic duct.. The cells of the immune system circulate through the lymphatic system.Also, large molecular products of digestion, like fats, first need to be absorbed.

The thoracic cage, an anterior view. Thoracic cage, Anatomy and
Location of the Heart. The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. Figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. Within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium.

Thoracic Cavity by Cryssari on DeviantArt
The thorax is the area of the body situated between the neck and the abdomen. The thorax itself can be split up into various areas that contain important structures.. The thorax is bound by bony structures including the 12 pairs of ribs and thoracic vertebrae, whilst also being supported by many ligaments and muscles.. The muscles of the thorax are also important for the vital actions of.

Thorax Anterior view of human body Biology Forums Gallery Human
Structure and Function Thoracic Wall The thoracic wall is formed by 12 ribs, 12 thoracic vertebrae, cartilage, sternum, and five muscles. [1] The thoracic wall functions in movement, respiration, and protection of the thoracic cavity. [3] [4] The thoracic vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs compose the posterior thoracic wall. [4]