3. With help of a neat labelled diagram, describe structure of

3. With help of a neat labelled diagram, describe structure of
Genes are part of cell structures called chromosomes. In multicellular organisms, chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell. Each of these chromosomes contains one, long molecule of DNA, or d eoxyribo n ucleic a cid. A gene is a specific stretch of this DNA molecule.
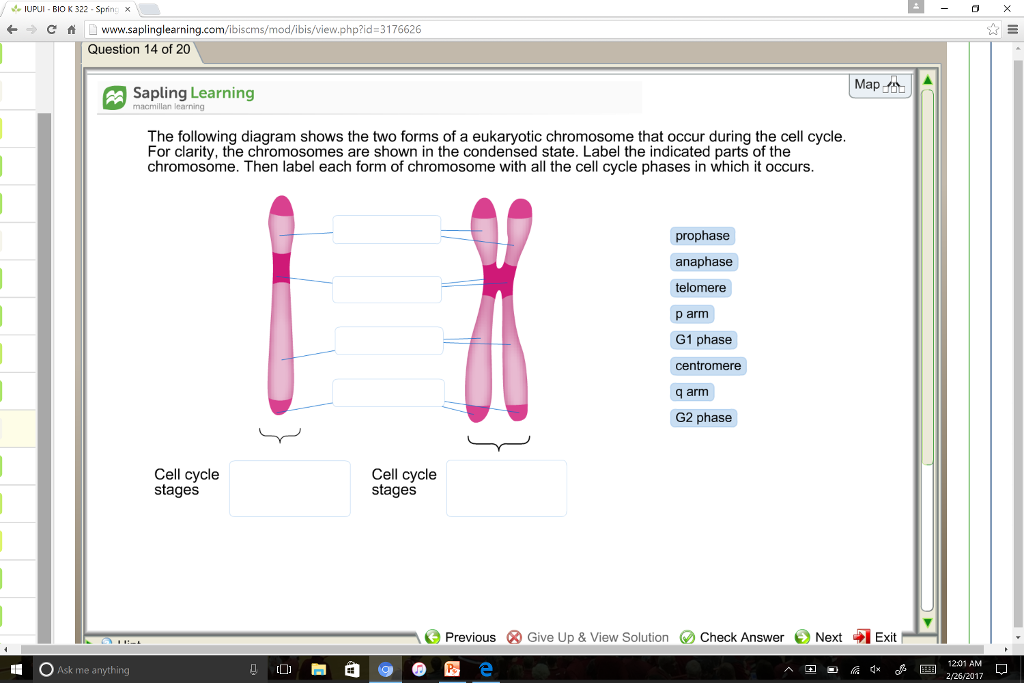
Solved The Following Diagram Shows The Two Forms Of A Euk...
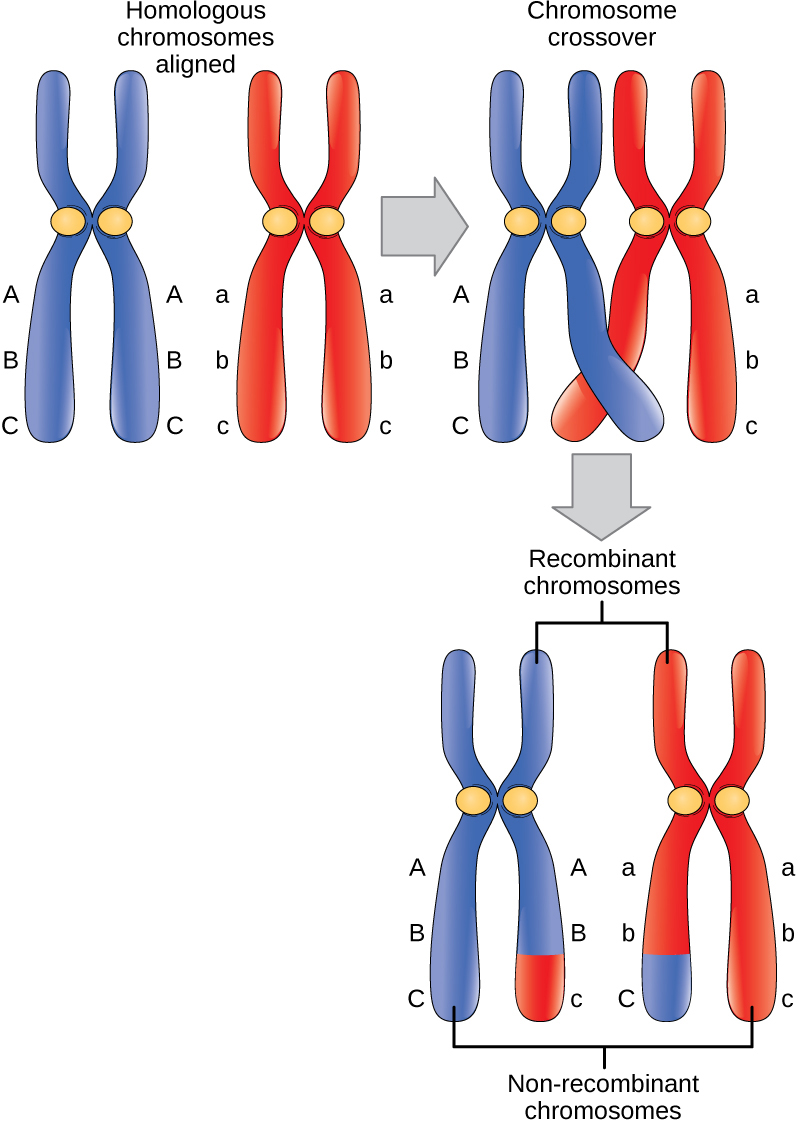
The 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the X and Y chromosomes; see below). Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n ).
7.2 Meiosis Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Students label a simple diagram of a chromosome showing the centromere, chromatid, DNA, and the location of the chromosome within the nucleus of a cell.
Types of Abnormalities in Embryos
The nonliving viruses have chromosomes consisting of either DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid); this material is very tightly packed into the viral head. Among organisms with prokaryotic cells (i.e., bacteria and blue-green algae ), chromosomes consist entirely of DNA.
Chromatid is(a) One half of chromosome(b) Haploid chromosome(c
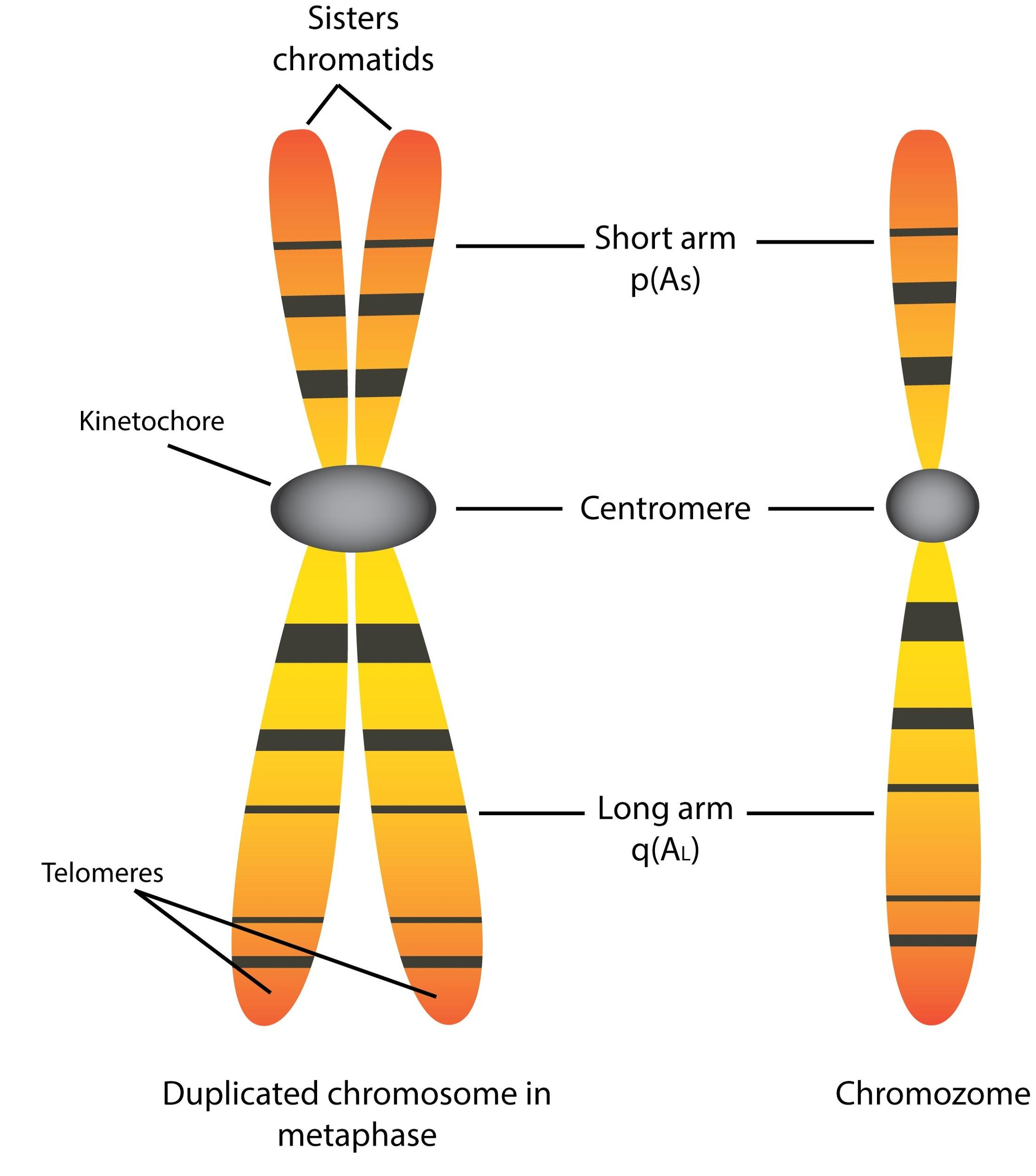
Chromatids are identical copies of a chromosome formed during DNA replication. They remain connected at the centromere until they separate during cell division, ensuring the accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells (Adlung, 2022). Figure 1: Basic schematic diagram of a chromosome, with labeled parts.

At The Beginning Of Cell Division Each Chromosome Consists Of Two
Part # 1. Pellicle and Matrix: A membrane which surrounds each chromosome is said as pellicle. A jelly substance present inside the membrane is called as matrix. Presumably the matrix and sheath are considered as non-genetic material.
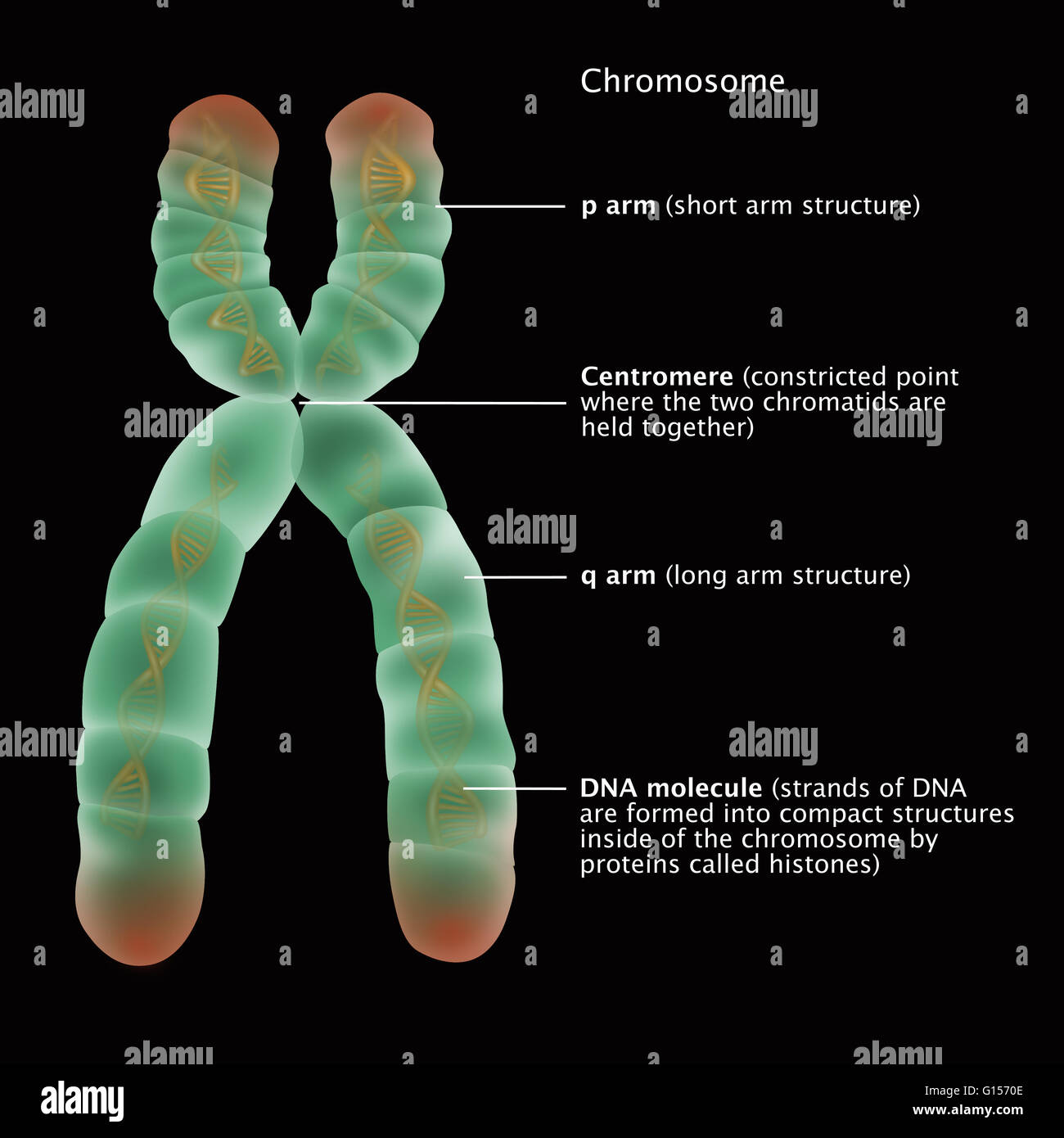
Illustration of the detailed structure of a chromosome. The p arm
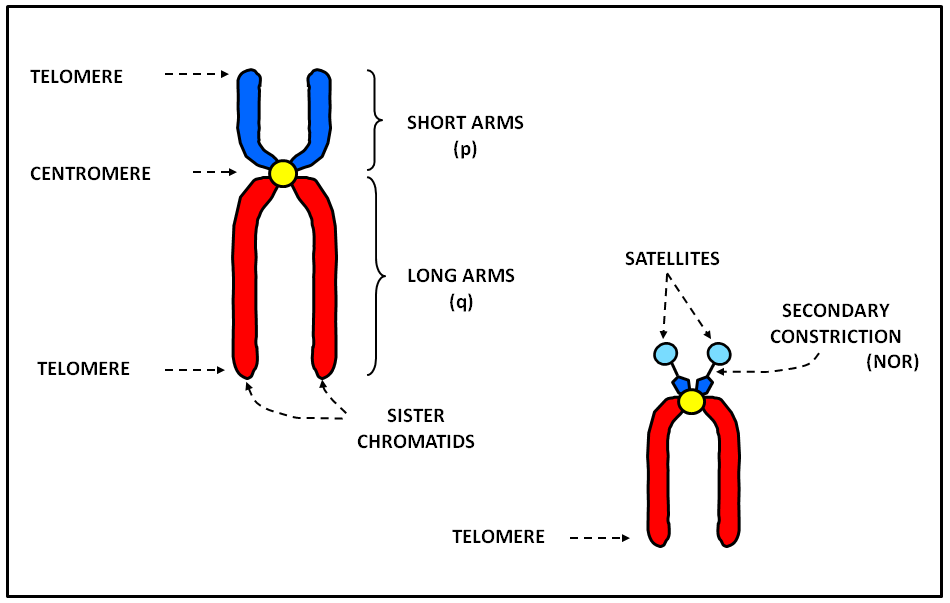
What are Chromosomes? Structure of a Chromosome Pellicle Matrix Chromonemata Centromere Secondary Constriction or Nucleolar Organiser Telomeres Types of Chromosomes A. Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes B. On the Basis of Number of Centromeres C. On the Basis of Location of Centromere Prokaryotic Chromosomes Eukaryotic Chromosomes a. Nucleosomes

Chromosomes Introduction, Structure & Types A Level Biology Notes
Google Classroom DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.

Labeled Chromosome
Instructor Greg Chin Understand what chromosomes are and learn about their structure, types, and parts. Learn the difference between homologous and heterologous chromosomes. Updated:.
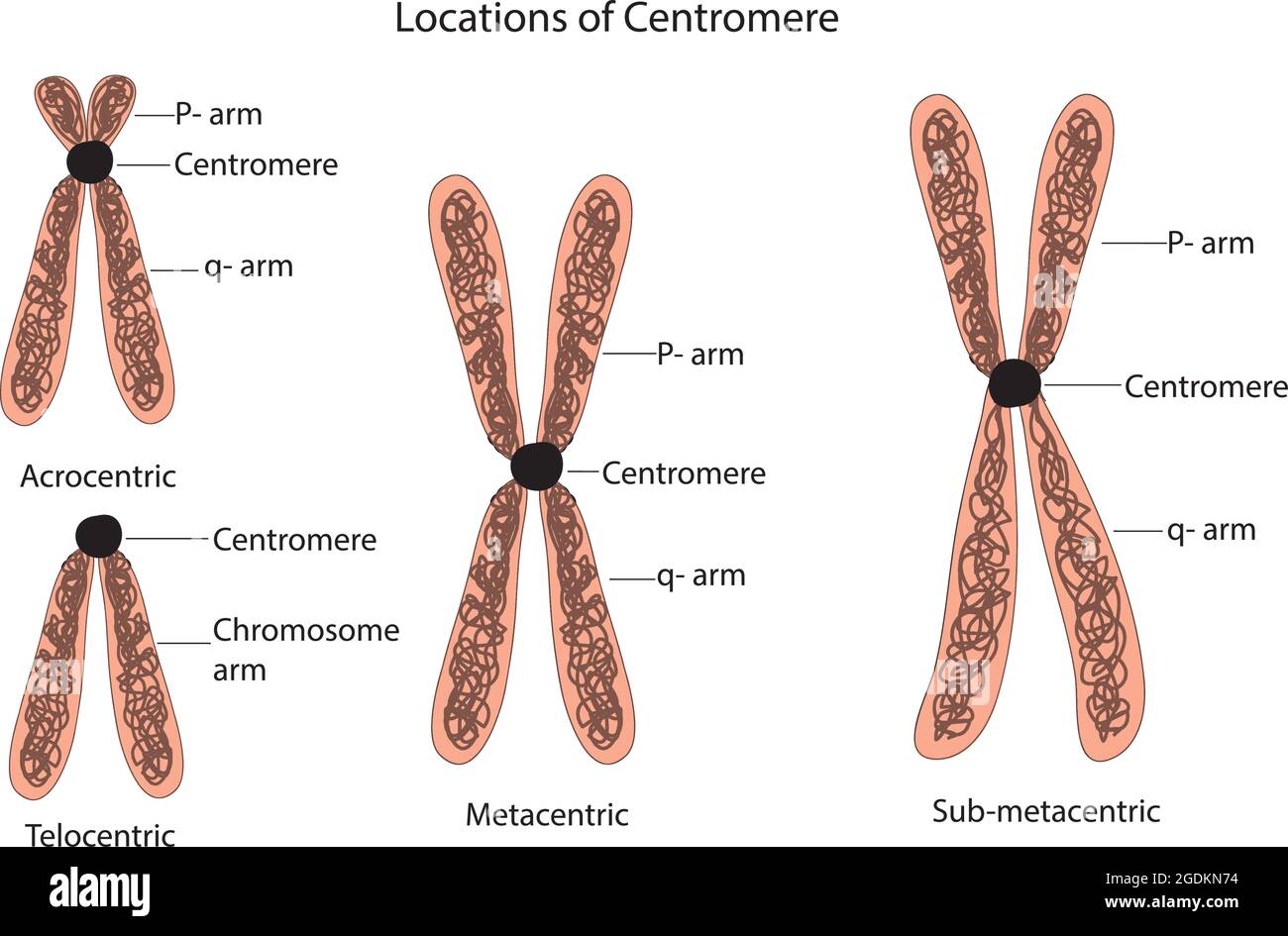
classification of chromosomes centromere, chromosome classifications
The short arm of the chromosome is labeled the "p arm." The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the "q arm." The location of the centromere on each chromosome gives the chromosome its characteristic shape, and can be used to help describe the location of specific genes. DNA and histone proteins are packaged into structures called chromosomes.

Chromosome structure Chromosome, Chromosome structure, Structural biology
Chromosome number. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one homologous.
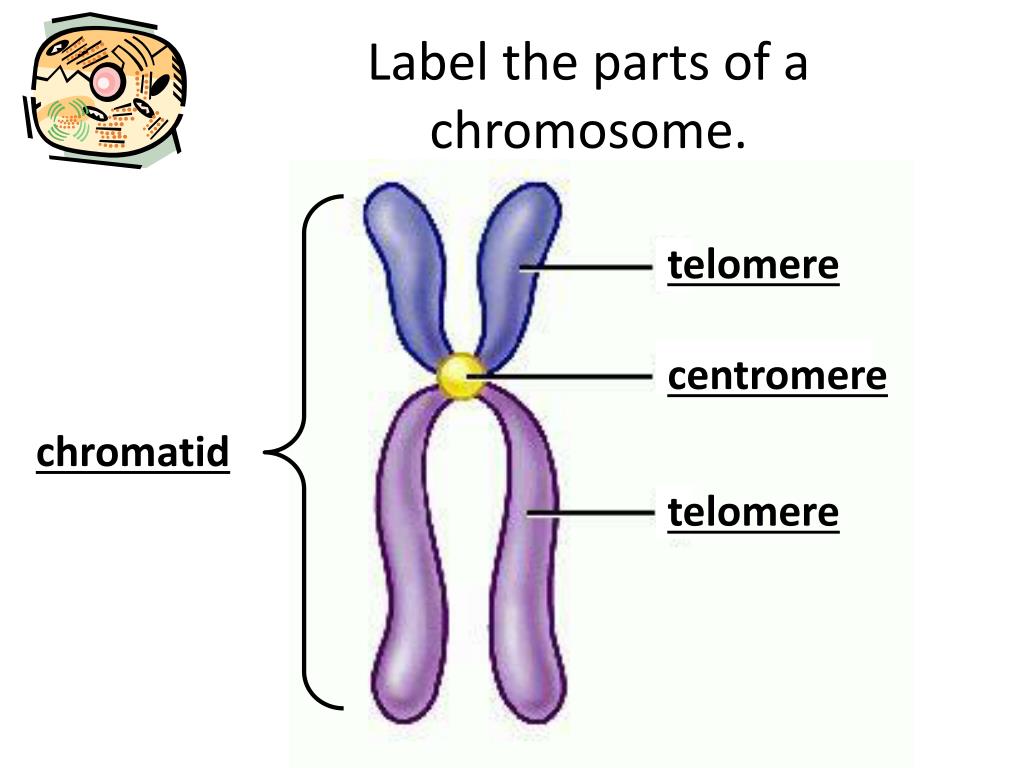
31 Label The Parts Of The Chromosome Labels Design Ideas 2020
< Prev Next > Chromosome Map Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.

Doubt Solutions Maths, Science, CBSE, NCERT, IIT JEE, NEET
Structure: A chromosome has generally 8 parts; Centromere or primary constriction or kinetochore, chromatids, chromatin, secondary constriction, telomere, chromomere, chromonema, and matrix. Centromere or Kinetochore: It is the primary constriction at the center to which the chromatids or spindle fibers are attached.

What are homologous chromosomes? Biology Stack Exchange
Chromosome Definition. A chromosome is a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure. During interphase of the cell cycle, the chromosome exists in a loose structure, so proteins can be translated from the DNA and the DNA can be replicated. During mitosis and meiosis, the chromosome.
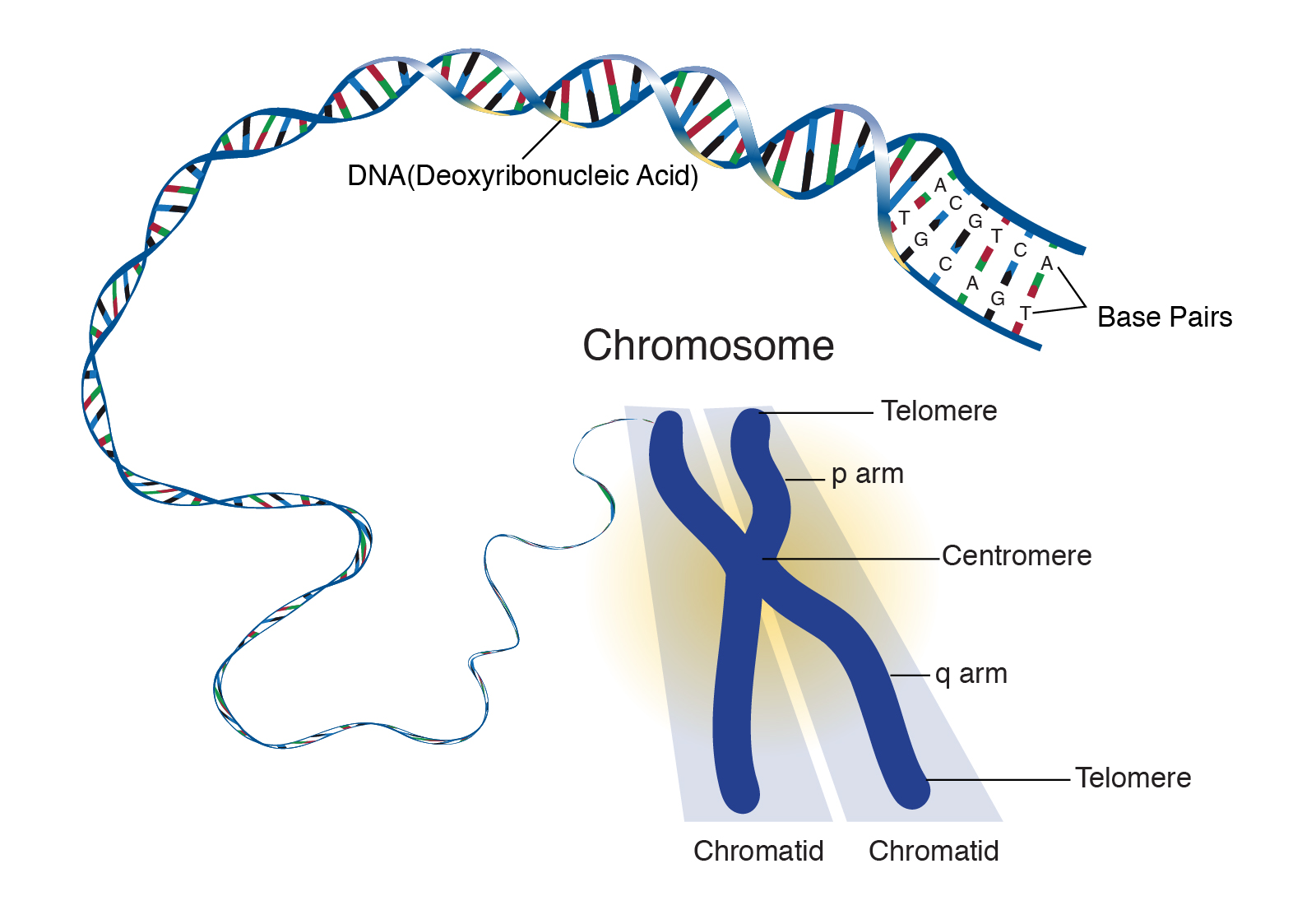
Chromosome
June 3, 2019 in Cell Biology, Genetics, Worksheets by Shannan Muskopf centromere, chromatid, chromosome, DNA, label, nucleus, practice, structure A diagram of a chromosomein the nucleus of the cell. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus.
Structure and types of the eukaryotic chromosomes WikiLectures
Chromosomes are components of a cell nucleus that are capable of self-reproduction. These chromosomes play an important role in mutation, variation, heredity, and the evolutionary development of a species. Moreover, the chromosome number is constant for a particular species. Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged as 23 pairs.