Pin on horticulture careers

What Is The Relationship Between Soil Texture And Water?
Soil Composition and Crop Quality This chart reflects a tremendous amount of information available for your understanding of the composition of a healthy productive soil environment. It is based on scientific research accumulated over years of observation on productive soil types throughout many growing areas of the country. The approach to obtaining this insight on
Solved Soil Is Composed Of Particles That Are Categorized...
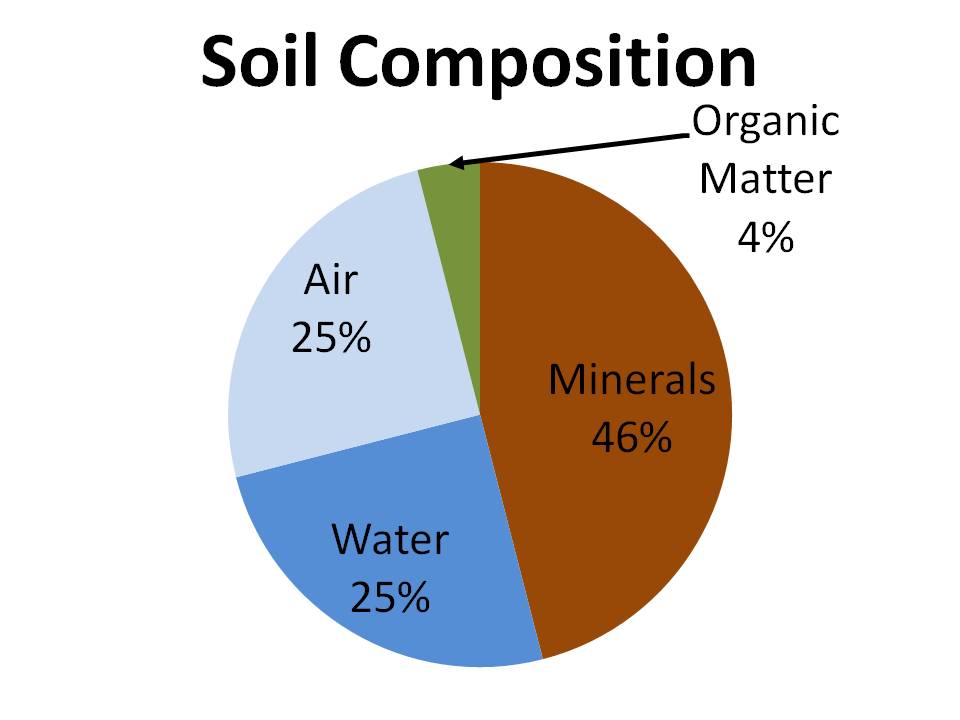
Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, air and water. Visit our site to learn about Soils, Plant Nutrition and Nutrient Management. | Chapter 4 of the Missouri Master Gardener Core Manual Manjula V. Nathan Soil Testing and Plant Diagnostic Service Laboratory Soil as a medium for plant growth can be described as a complex natural material derived from weathering of rocks and.
Soil Composition
The purpose of soil classification is to arrange various types of soils into groups according to their engineering properties. Particle Size: Individual solid particle in a soil can have different sizes and this characteristic of soil can have a significant effect on its engineering properties.

Soil Classification The Bigger Picture
You can calculate the required volume of soil by multiplying the grass yard area by the desired soil thickness. 153.5 yd² * 0.6 yd = 92.1 yd³. The last thing to do is assess the estimated weight of the required soil and its cost. The weight of the cargo may come in handy when transporting the soil.

Pin on horticulture careers
Soil - Texture, Structure, Composition: The two principal systems of soil classification in use today are the soil order system of the U.S. Soil Taxonomy and the soil group system, published as the World Reference Base for Soil Resources, developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Both of these systems are morphogenetic, in that they use structural.
Soil is the thin layer of material covering the earth’s surface
Overview of Soil Important Questions and Answers about Soil 33,617 From a general perspective, "soil" is a very broad term and refers to the loose layer of earth that covers the surface of the planet. The soil is the part of the earth's surface, which includes disintegrated rock, humus, inorganic and organic materials.
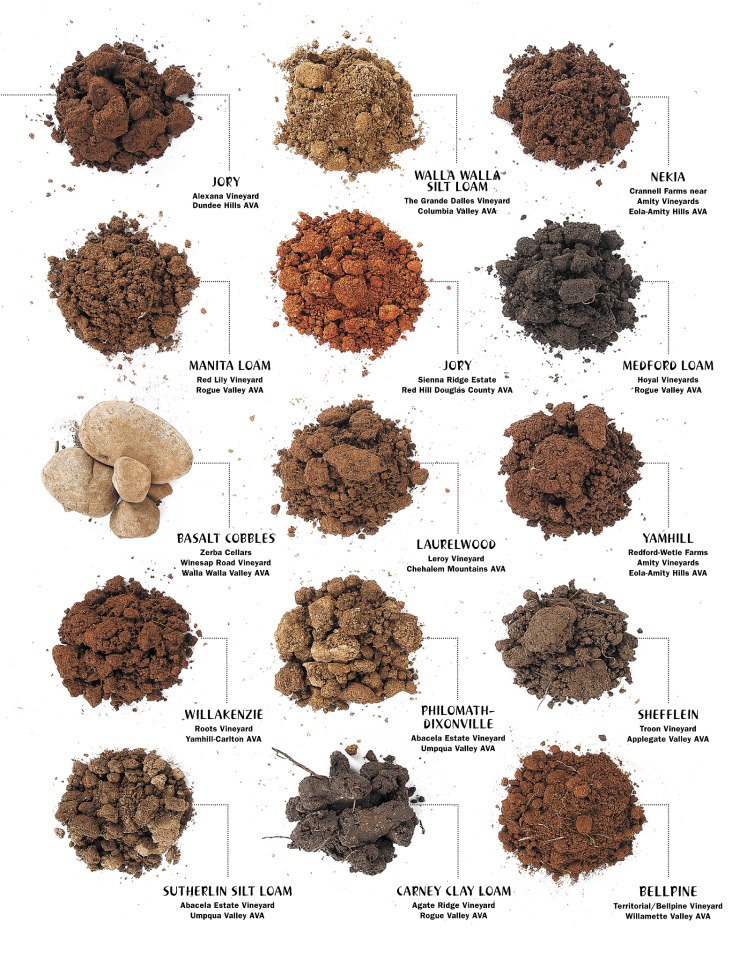

soil types DriverLayer Search Engine
Healthy soil also has a positive impact on water quality, decreasing nutrient runoff into streams and rivers. In addition, healthier soil tends to have a greater ability to hold water, which can give crops greater drought resilience. This chart appears in the May 2019 ERS report, Agricultural Resources and Environmental Indicators, 2019.
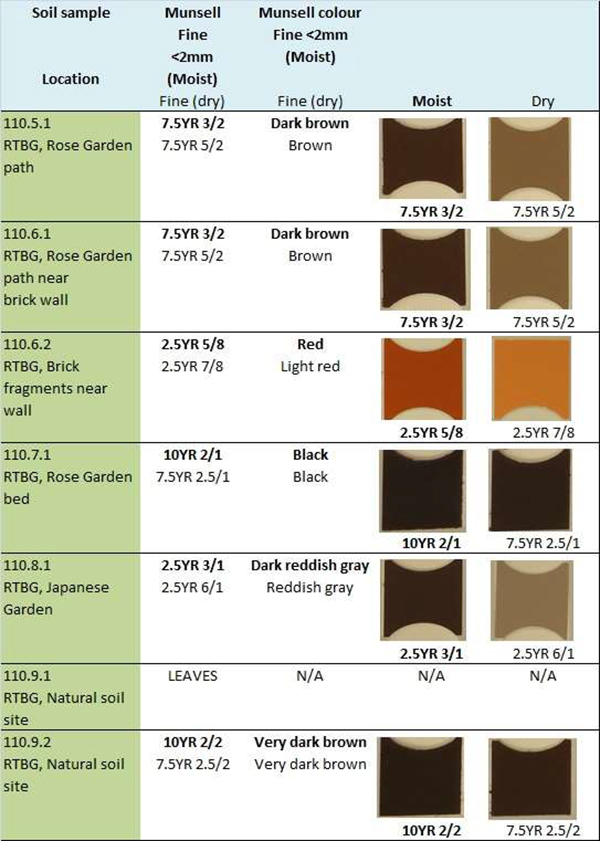

Using Soil Color Analysis for Forensic Application at a Crime Scene
Our focus will be on the fifth function. In this role, soil provides structural stability for plants and retains and relinquishes water and the nutrients necessary for plant growth. An ideal soil for plant growth contains 50% pore space and 50% solids, with the pore space filled with equal parts air and water.
Civil Engineering Community Soil Classification Systems
The second edition of Soil Taxonomy, A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys is the result of the collective experience and contributions of thousands of pedologists from around the worl. Keys to Soil Taxonomy Taxonomic keys for field classification. Official Soil Series Descriptions (OSD)
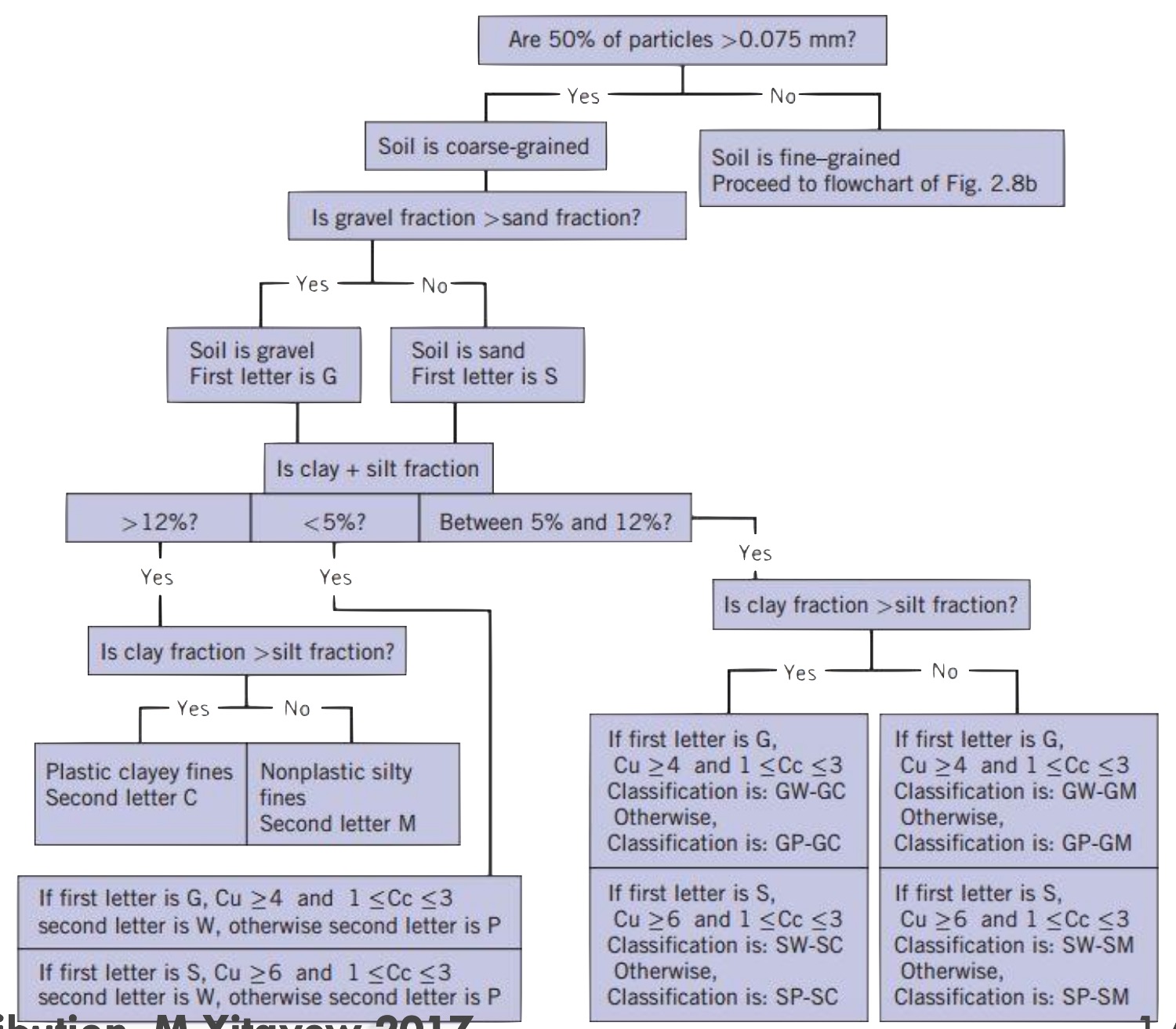
Soil Classification Flow Chart Images and Photos finder
Soil Classification Outline Overview Identify different soil types Understand the methods of testing the soil Understand the soil mechanics Understand the weight of the soil Review case studies Understanding workers rights Soil Types Stable Rock

Infographics
Soil surveys use Soil Taxonomy to provide: A connotative naming system that enables those users familiar with the nomenclature to remember selected properties of soils. A means for understanding the relationships among soils within a given area and in different areas. A means of communicating concepts of soils and soil properties.

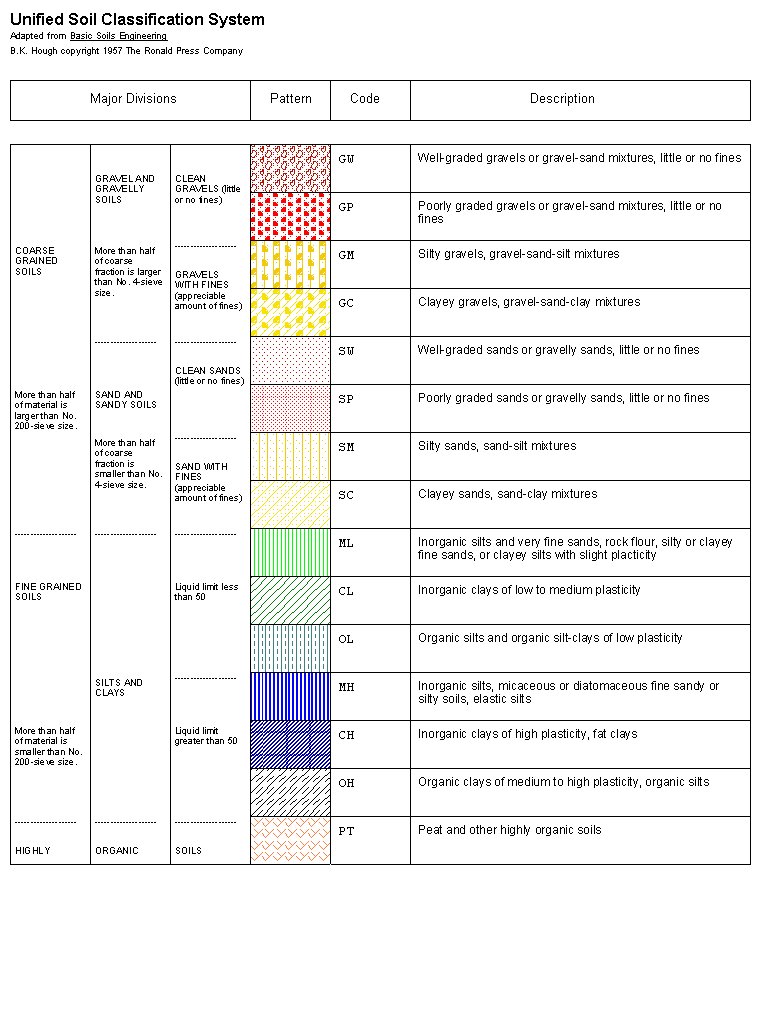
Unified Soil Classification System / Two commonly classification system
Soil is a natural resource and a living ecosystem (the "living skin of the earth"). Soils sustain all life on earth and filter and break down natural and man-made toxins. Soils provide water, nutrients, and support, along with oxygen for the plant's root growth. Soils have four main components: mineral particles (sand, silt, and clay), organic.
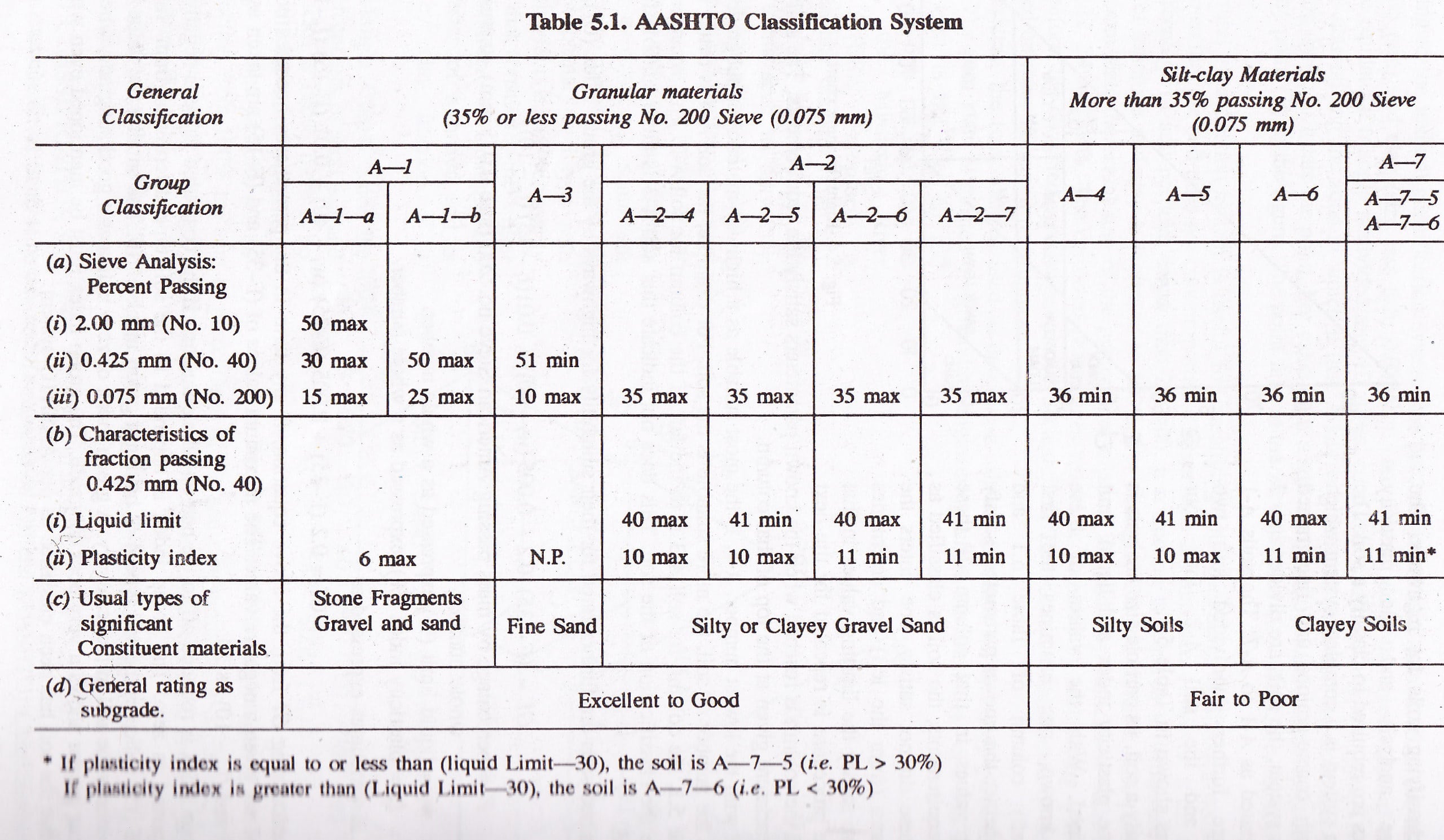
AASHTO Soil Classification System AASHTO Chart
The Digital General Soil Map of the United States or STATSGO2 is a broad-based inventory of soils and non-soil areas that occur in a repeatable pattern on the landscape and that can be cartographically shown at the scale mapped of 1:250,000 in the continental U.S., Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands and 1:1,000,000 in Alaska.
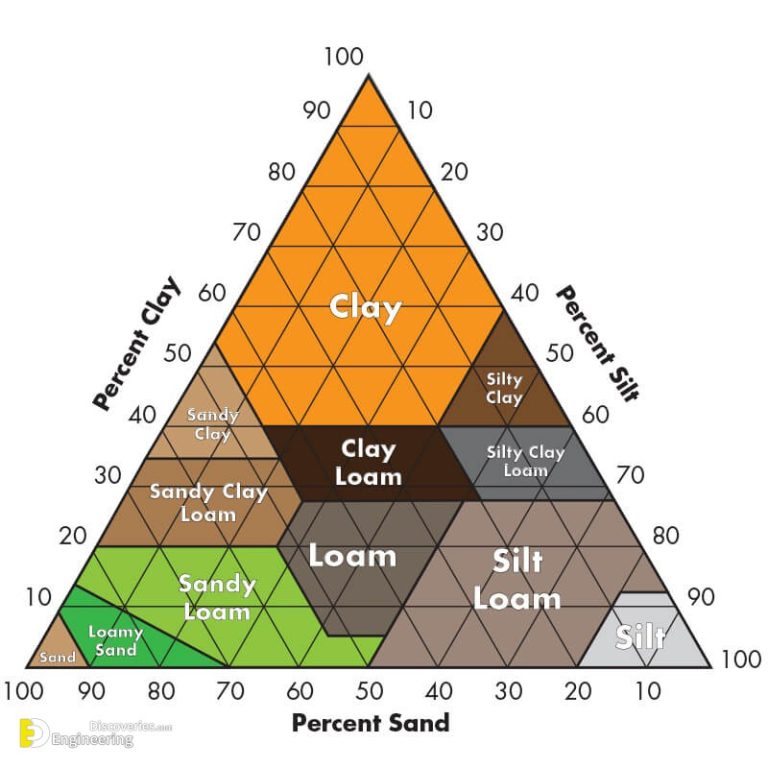
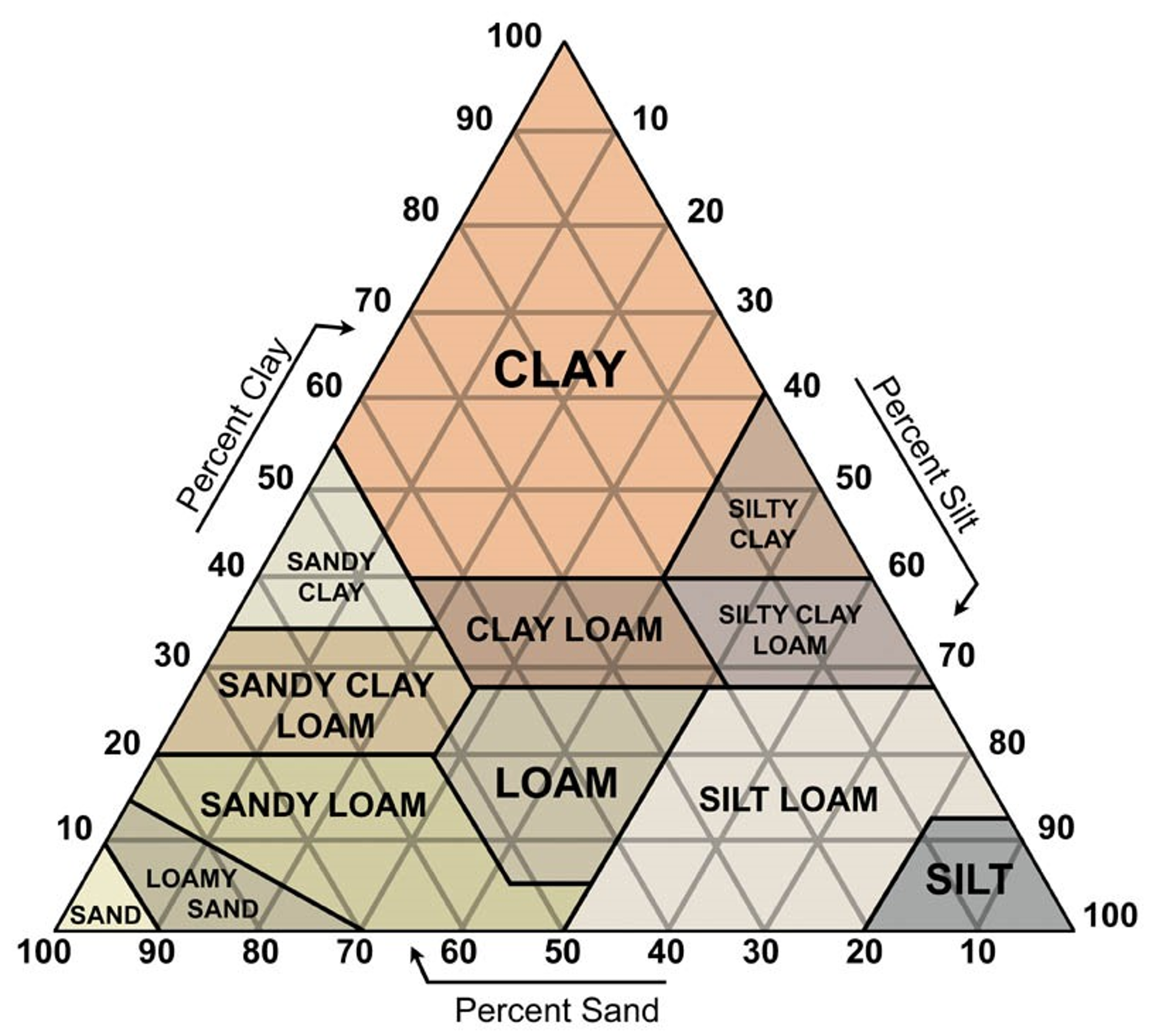
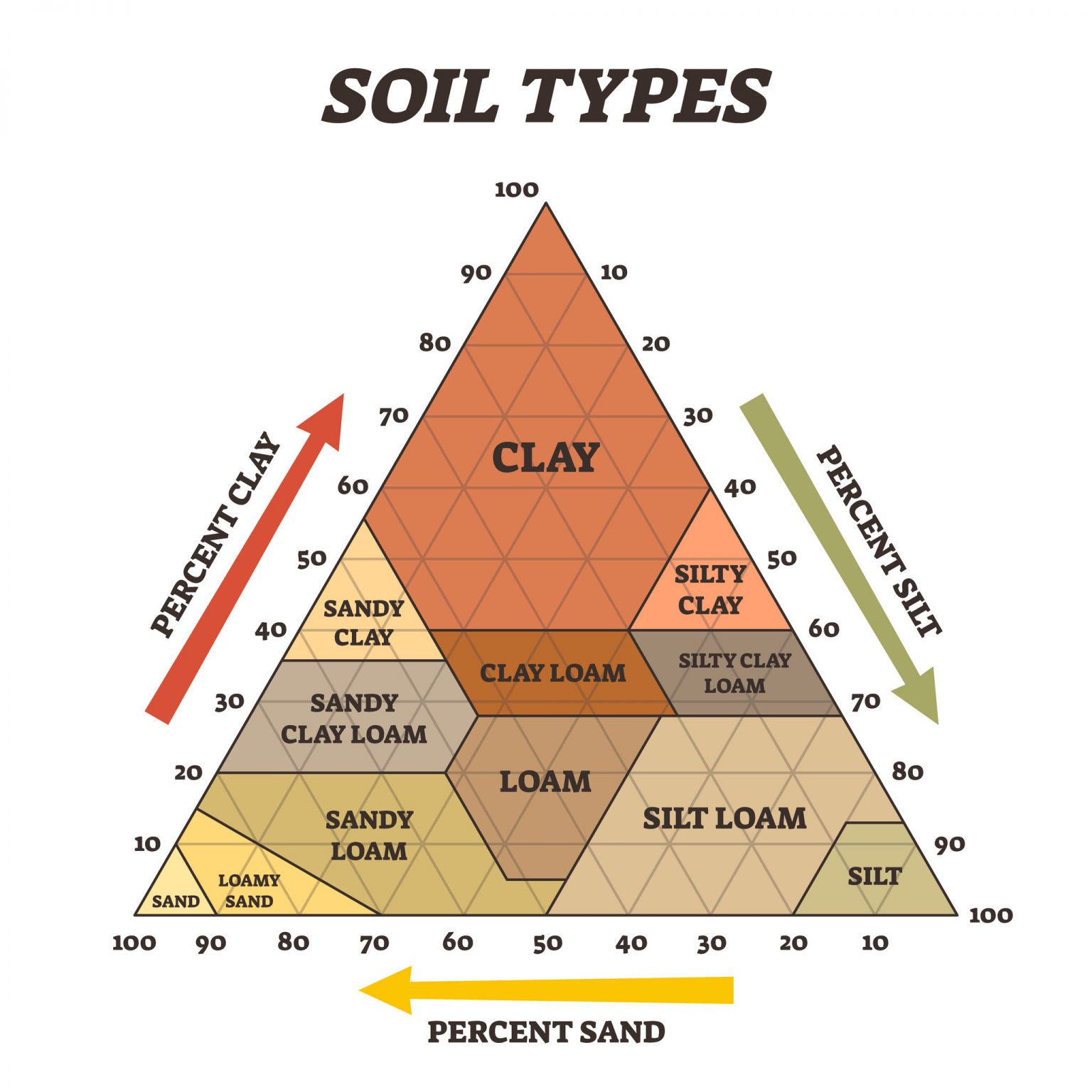
What Is Soil Texture? Classification System Of Soil Texture
• The Munsell Soil Color System is the standard to which we describe soil color. • Both the color and the patterns of color in the soil are important to note when describing soil color. The End ; Title: Slide 1 Author: jerry.daigle Created Date:
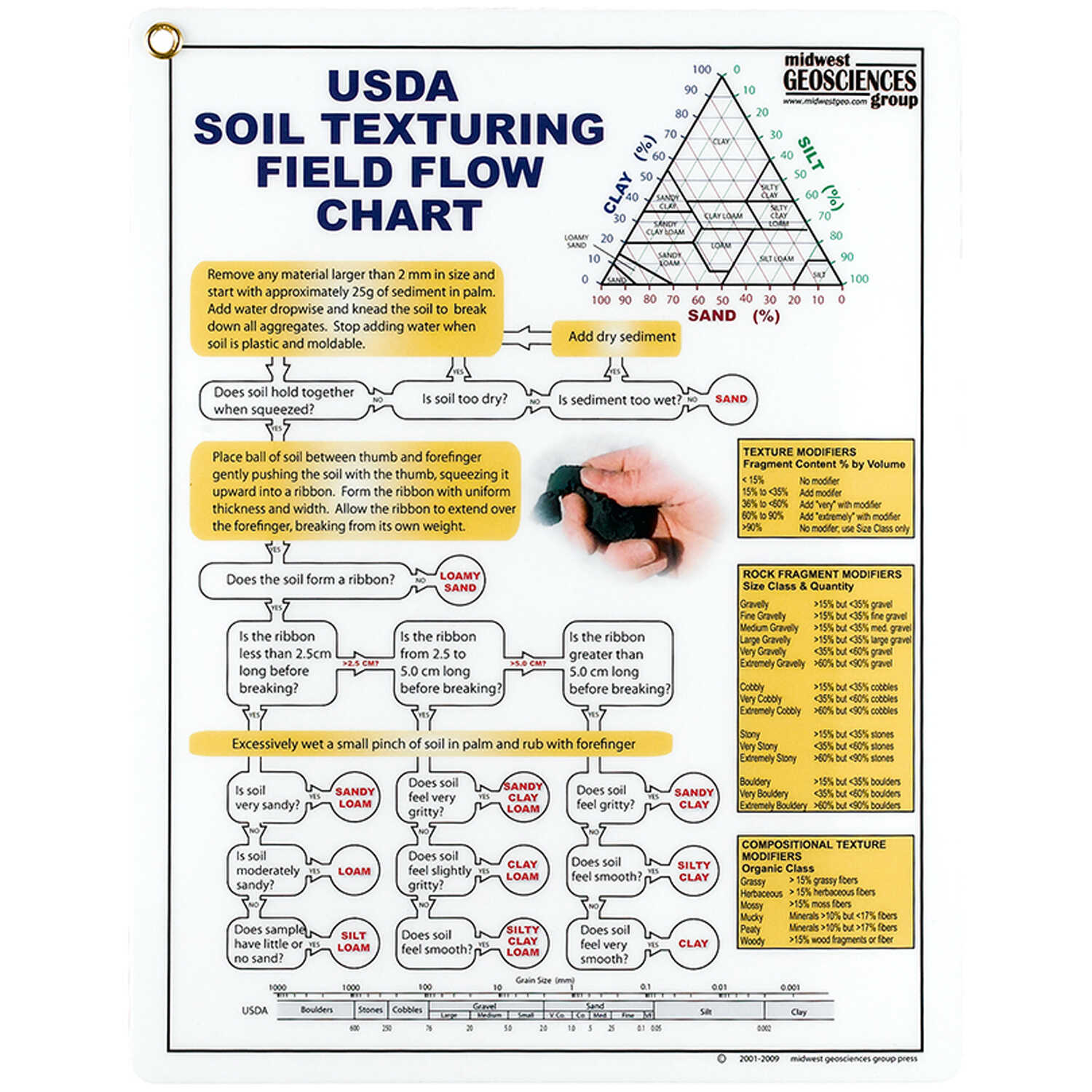
USDA Soil Texturing Field Flow Chart Forestry Suppliers, Inc.
The USCS has three major classification groups: (1) coarse-grained soils (e.g. sands and gravels ); (2) fine-grained soils (e.g. silts and clays ); and (3) highly organic soils (referred to as "peat"). The USCS further subdivides the three major soil classes for clarification.

Soil Texture Chart Soil Texture, Work Habits, Personal History
3.1 INTRODUCTION Soils can behave quite differently depending on their geotechnical characteristics. In coarse grained soils, where the grains are larger than 0.075 mm (or 75 µm), the engineering behaviour is influenced mainly by the relative proportions of the different sizes present, the shapes of the soil grains, and the density of packing.