What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
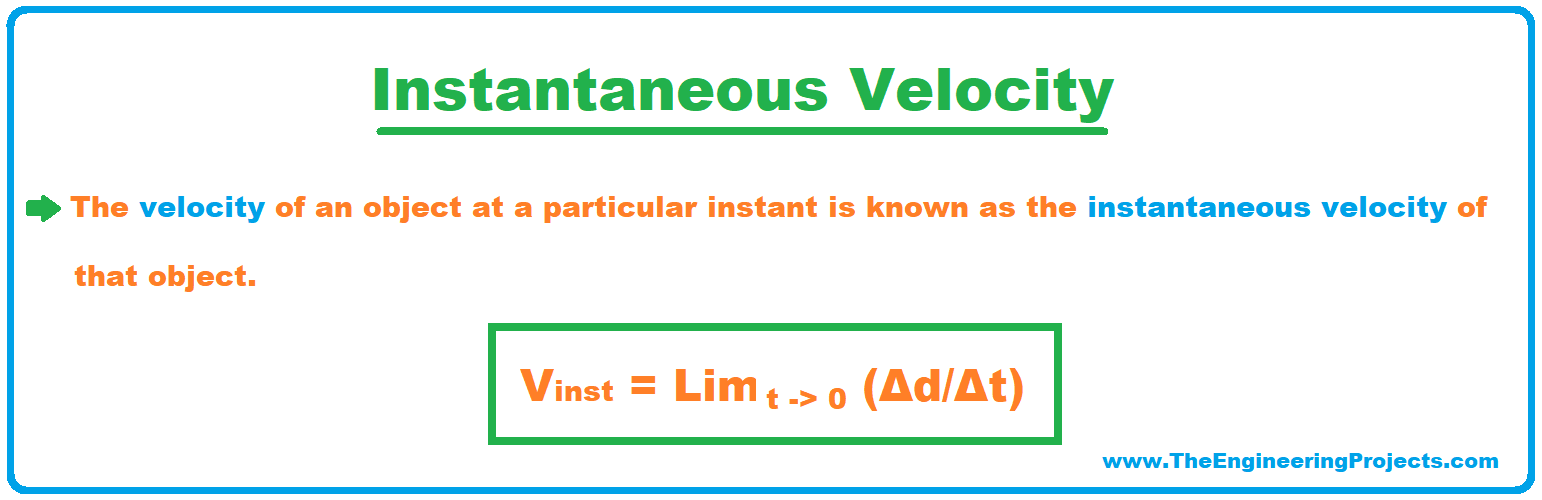
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
Physics Article SI Units List SI Units in Physics The answer to what is SI unit is that it is an abbreviation of the French word Système International. The International System Of Units (SI) is the metric system that is used universally as a standard for measurements.
Si Unit Of Speed Speed and Velocity SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes / These are
The SI unit for velocity is meters per second, or m/s. Sometimes derived units have their own names. Below is a table of some of the more important derived units in the SI system: Dimensionality Unit Definition; Force: Newtons N: kgms −2: Energy: Joules J: Nm = kgm 2 s −2: Power: Watts W:
Speed and Velocity SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes
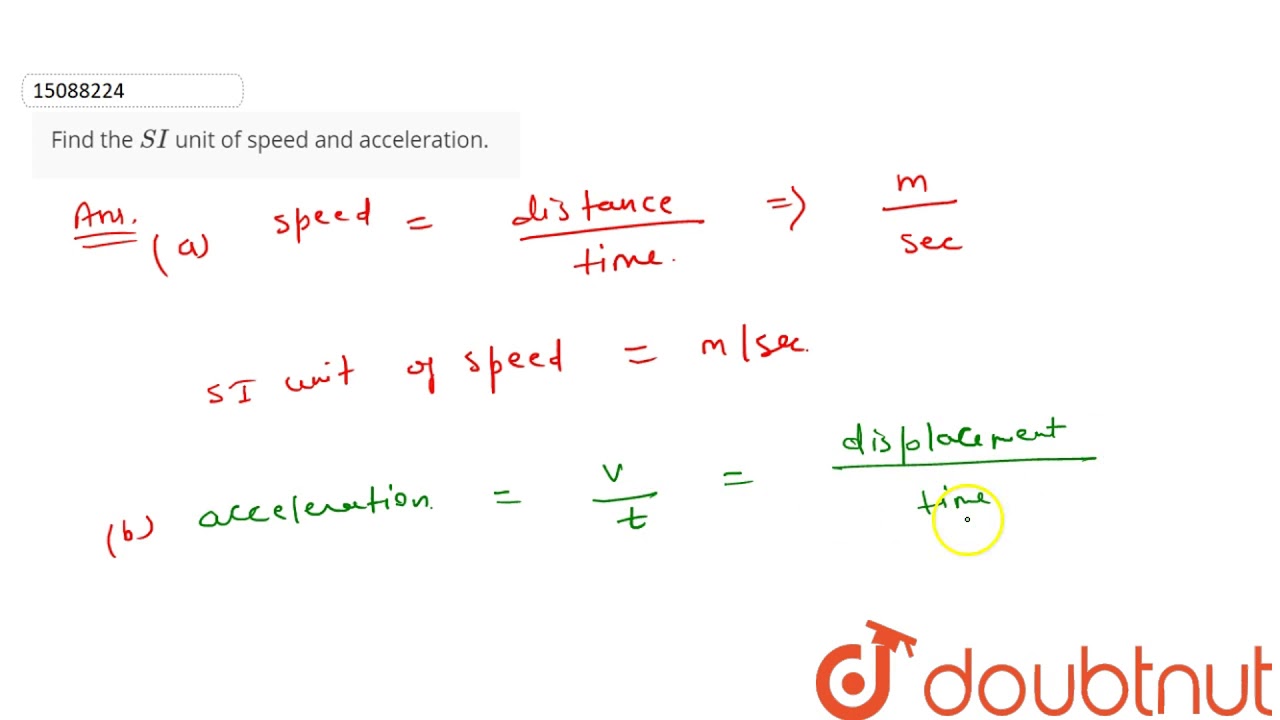
The following are some instances of derived SI units: Velocity v = m/s. Acceleration a = m/s 2. Force N = kgm/s 2. Energy J = Nm = kgm 2 /s 2. Power W = J/s . Pressure Pa = N/m 2.. Derive the units of velocity, acceleration, and force using them. Solution Velocity. Velocity is given by displacement over time.
Find the `SI` unit of speed and acceleration. YouTube
Because acceleration is velocity in m/s divided by time in s, the SI units for acceleration are \( m/s^2\), meters per second squared or meters per second per second, which literally means by how many meters per second the velocity changes every second. Recall that velocity is a vector—it has both magnitude and direction.
Area X Velocity
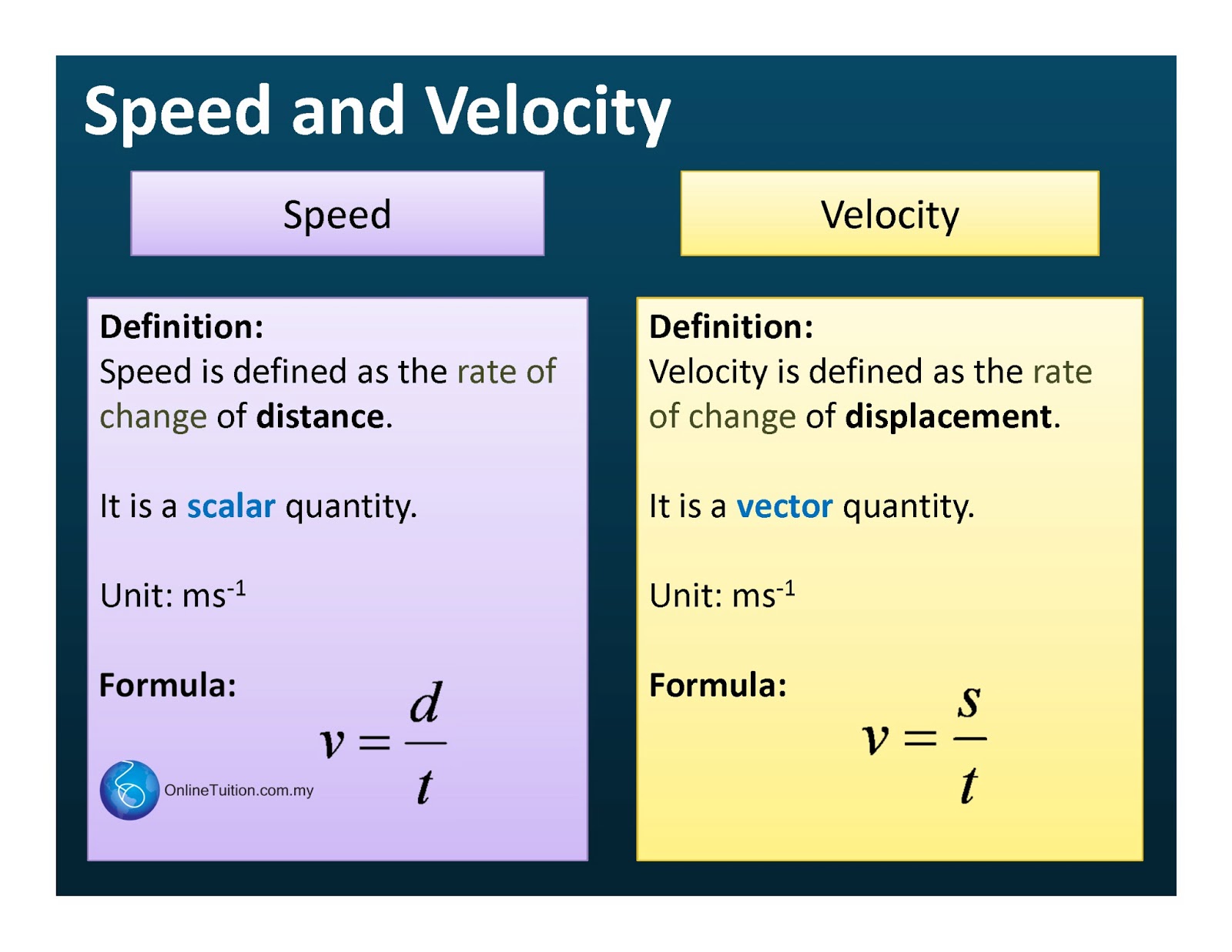
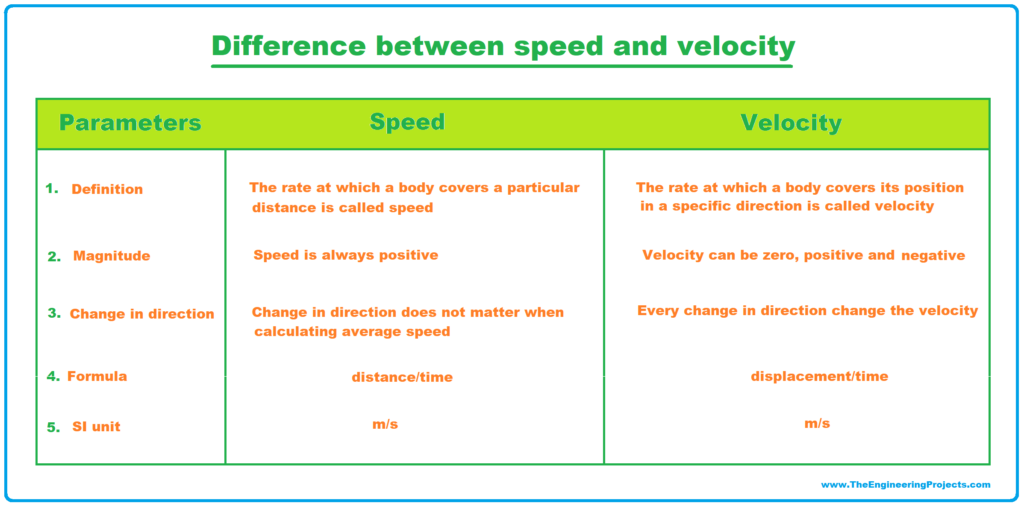
Speed is a scalar quantity and is defined as the rate of change of position of an object in any position and time. The formula for speed is S = d t S = d t , where s- The speed attained in m/s d- The total distance travelled t - The total time taken Distance:

Write the SI unit for the following (a)distance, (b) displacement, (c) speed, (d) velocity (e
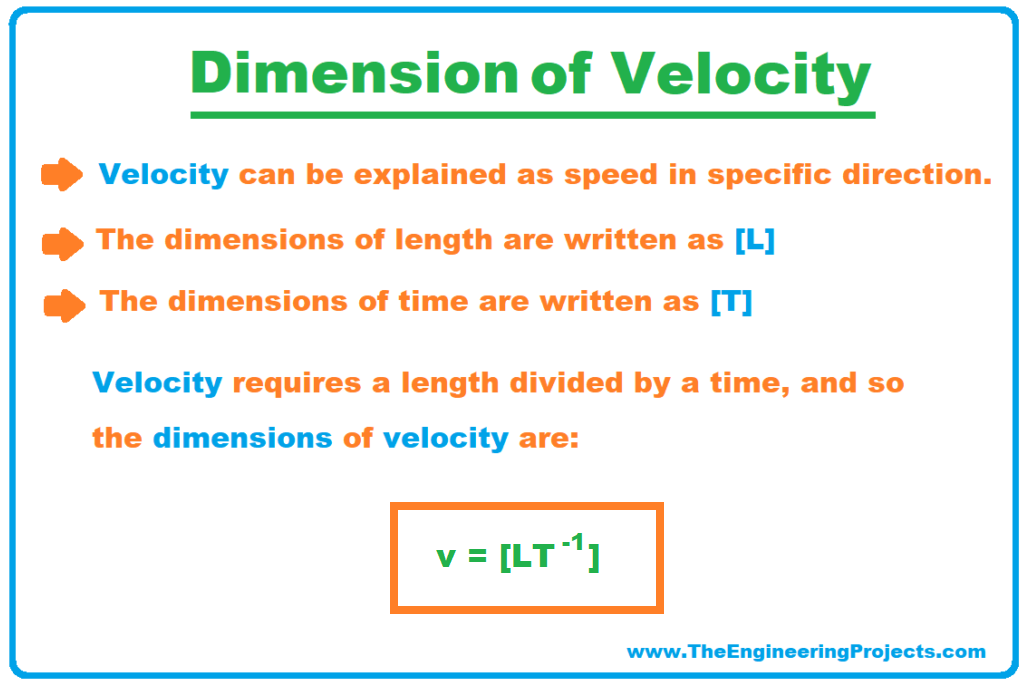
Units Since the derivative of the position with respect to time gives the change in position (in metres) divided by the change in time (in seconds ), velocity is measured in metres per second (m/s). Equation of motion Average velocity
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
We will take a look at what exactly velocity is, how it can be measured, what scale has System International (SI) defined to measure the velocity, how many forms of velocity do exist in our surroundings, and what are the real-life applications of this physical quantity?
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
SI units are gradually replacing Imperial and USCS units . The SI is maintained by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM, for Bureau International des Poids et Mesures) in Paris.. velocity (or speed) meters per second: m/s: m s -1 : viscosity, absolute or dynamic (often used symbol m ) Pascal second: Pa s: m -1 kg s -1 :

Si Unit Of Speed Speed and Velocity SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes / These are
Table 1.2 lists the metric prefixes and symbols used to denote various factors of 10 in SI units. For example, a centimeter is one-hundredth of a meter (in symbols, 1 cm = 10 -2 m) and a kilometer is a thousand meters (1 km = 10 3 m). Similarly, a megagram is a million grams (1 Mg = 10 6 g), a nanosecond is a billionth of a second (1 ns = 10.
Velocity Graphs
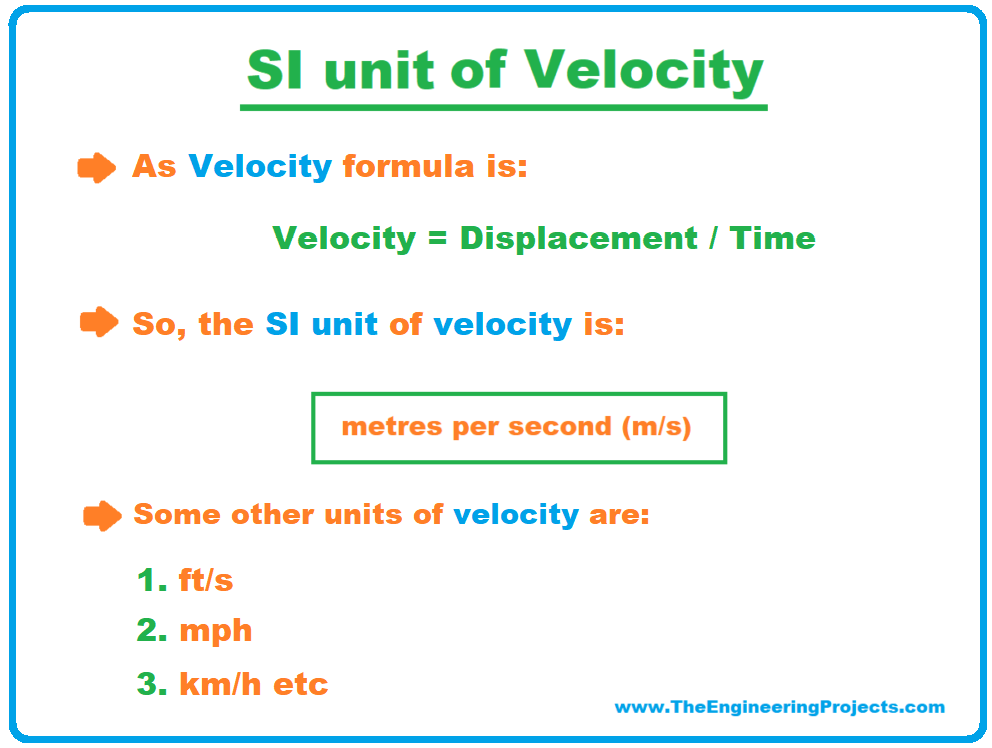
The SI unit of velocity is metre per second (m/s). Alternatively, the velocity magnitude can also be expressed in centimetres per second (cm/s). Some Other Velocity Units Some of the other units that identify velocity are: Kilometres per hour Knot (unit) Feet per minute Foot per second Metre per hour Miles per hour Inch per second Speed of light

Si Unit of Velocity ElizabethkruwCoffey
The speed of light in a vacuum is defined in the SI system to be 299,792,458 m/s (about a billion km/h). This is usually stated with a more reasonable precision as 3.00 × 10 8 m/s. The speed of light in a vacuum is assigned the symbol c (italic) when used in an equation and c (roman) when used as a unit.
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
The SI unit of velocity is metres per second (m/s). Alternatively, the velocity magnitude can also be expressed in centimetres per second (cm/s). READ SOMETHING ELSE Table of Contentsshow 1What are the 3 types of velocity? 2What is velocity vs acceleration? 3Who discovered velocity? 4How velocity is calculated? 5Can velocity be negative?

SI unit of velocity YouTube
Acceleration is the change in velocity divided by a period of time during which the change occurs. The SI units of velocity are m/s and the SI units for time are s, so the SI units for acceleration are m/s 2. Average acceleration is given by a¯ = Δv Δt = vf −v0 tf −t0. a ¯ = Δ v Δ t = v f − v 0 t f − t 0.
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The Engineering Projects
The International System of Units (SI) unit for velocity is meters per second or m s , but many other units such as km hr , mi hr (also written as mph), and cm s are commonly used. Suppose, for example, an airplane passenger took 5 seconds to move −4 meters, where the negative sign indicates that displacement is toward the back of the plane.

PPT Displacement and Velocity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6592660
The SI unit of time is the second (s), and the SI unit of speed is meters per second (m/s), but sometimes kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph) or other units of speed are used. When you describe an object's speed, you often describe the average over a time period.

Si Unit Of Velocity Ans Q 25 Explain coefficient of viscosity its units and / An object
The SI unit of velocity is metres per second (m/s). Alternatively, the velocity magnitude can also be expressed in centimetres per second (cm/s). Table of Contents show What are the SI units for Class 9? Length (l) Meter. m. Mass (M) Kilogram. kg. Time (T) Second. s. Electric current (I) Ampere. A. Thermodynamic temperature (Θ) Kelvin. K.