Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medical, antrum 91450550
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11880/stomach-mucosa-and-muscular-layers_english.jpg)
Stomach Anatomy, function, blood supply and innervation Kenhub
Anatomy of the Stomach. The stomach is an organ of the digestive system. It is an expanded section of the digestive tube between the esophagus and small intestine. Its characteristic shape is well known. The right side of the stomach is called the greater curvature and the left the lesser curvature. The most distal and narrow section of the.
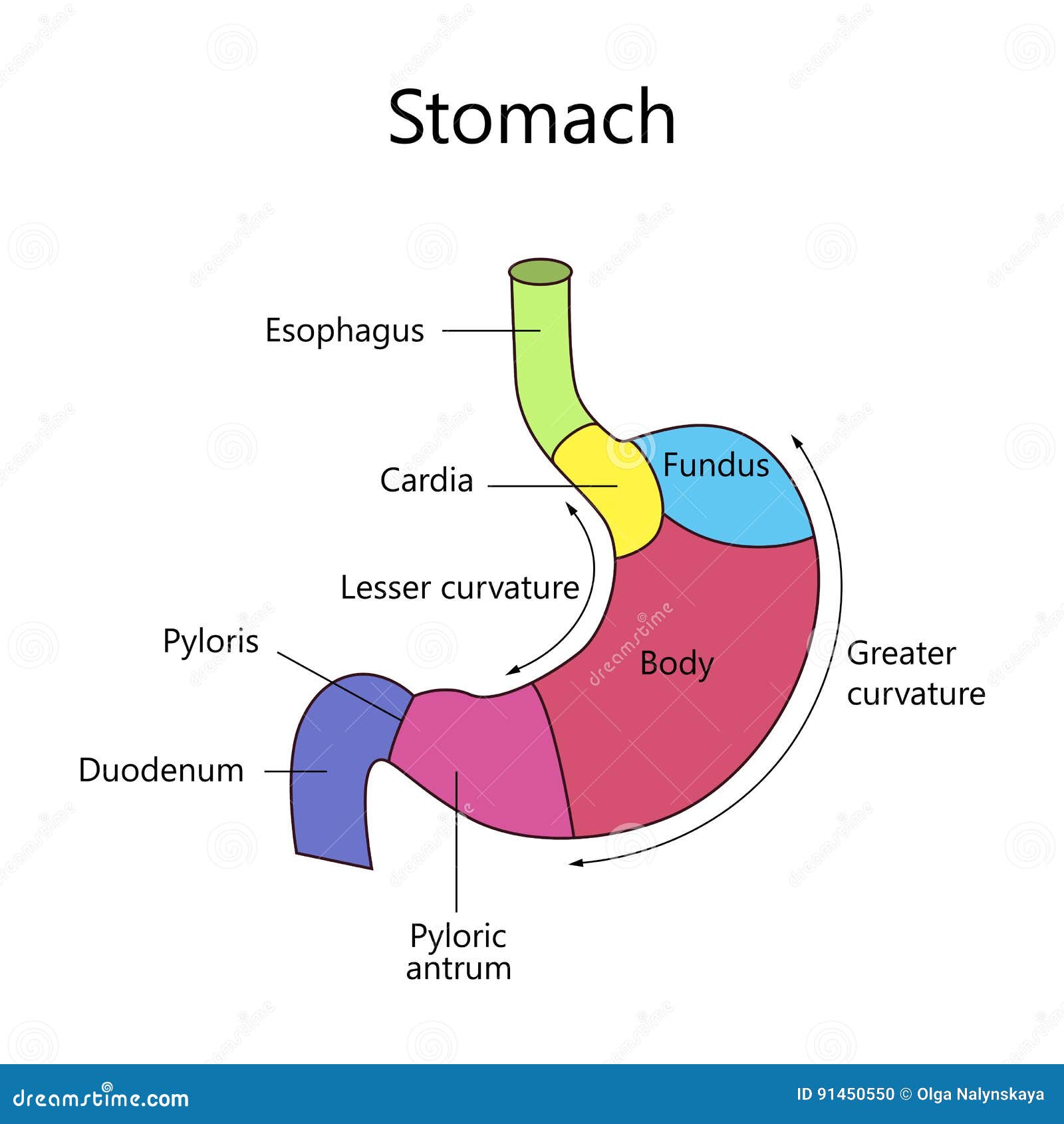
Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medical, antrum 91450550
Label on a diagram the four main regions of the stomach, its curvatures, and its sphincter Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself Describe the mechanical and chemical digestion of food entering the stomach
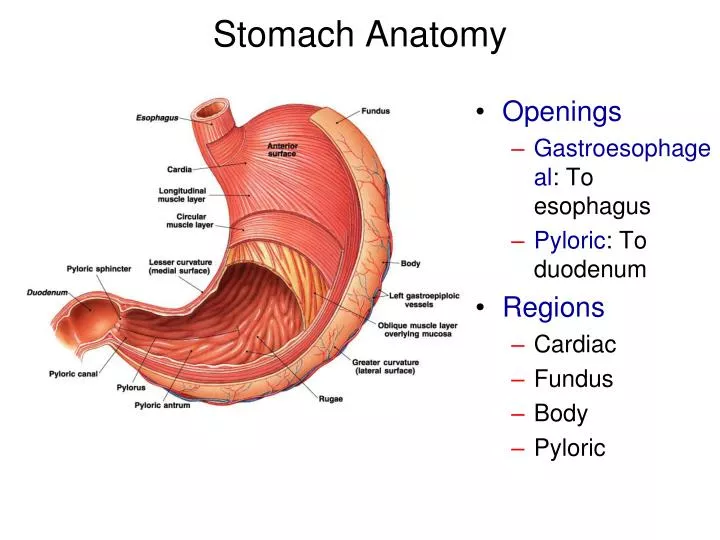
PPT Stomach Anatomy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1940155
The stomach is a sac-like organ with strong muscular walls. In addition to holding food, it serves as the mixer and grinder of food. The stomach secretes acid and powerful enzymes that continue.
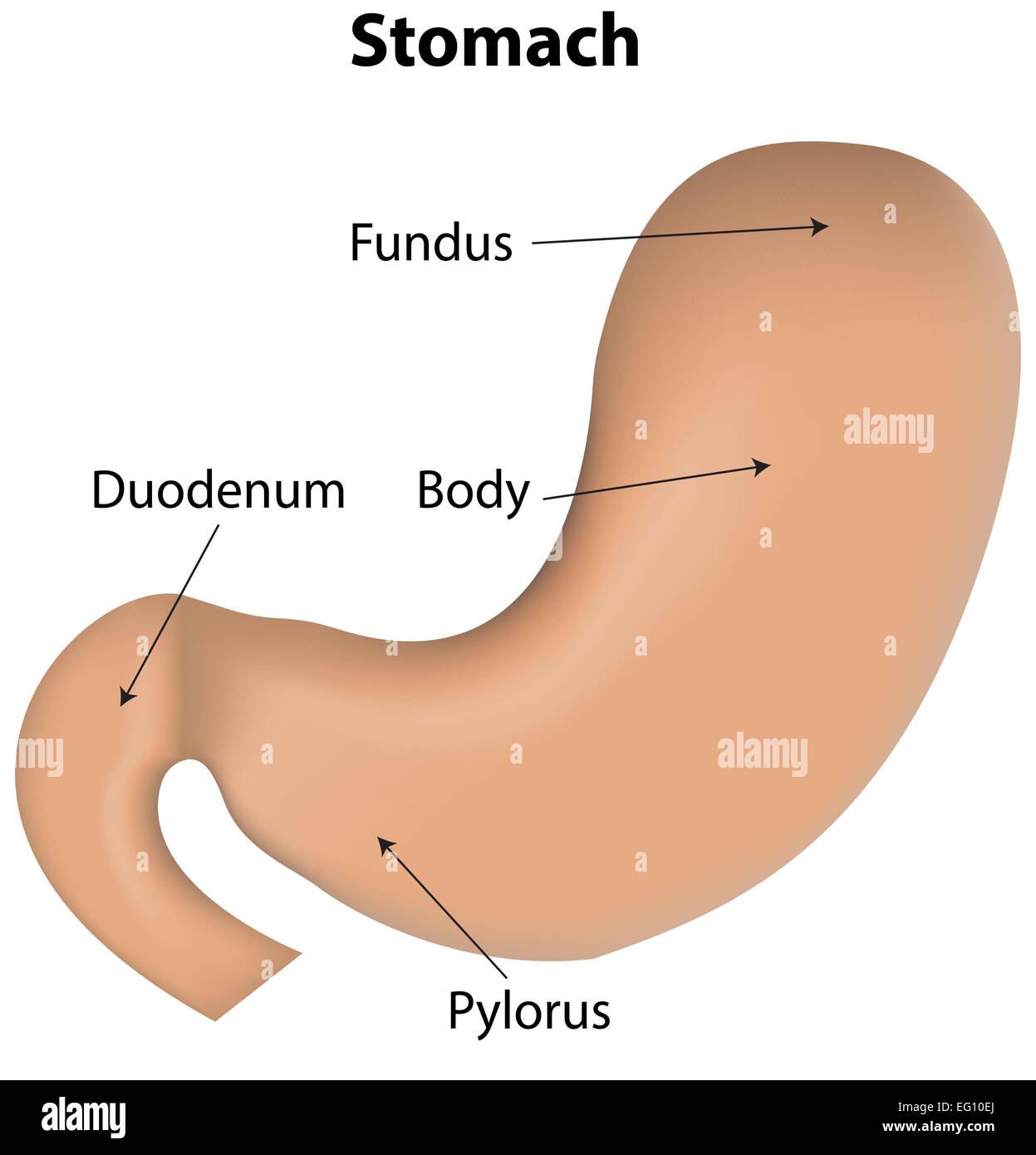
Stomach Labeled Diagram Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
ISSN 2534-5079. This e-Anatomy illustrates the gross anatomy of the digestive system. We focused especially on the diagrams of the abdominal digestive system (oesophagus is described on the modules about the thorax and oral cavity/pharynx on the ENT modules). 84 anatomical diagrams and histological images with over 300 labeled anatomical parts.

Overview of the Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology II
Start studying LABEL THE STOMACH. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

Physiology of the stomach Human anatomy and physiology, Human anatomy picture, Anatomy and
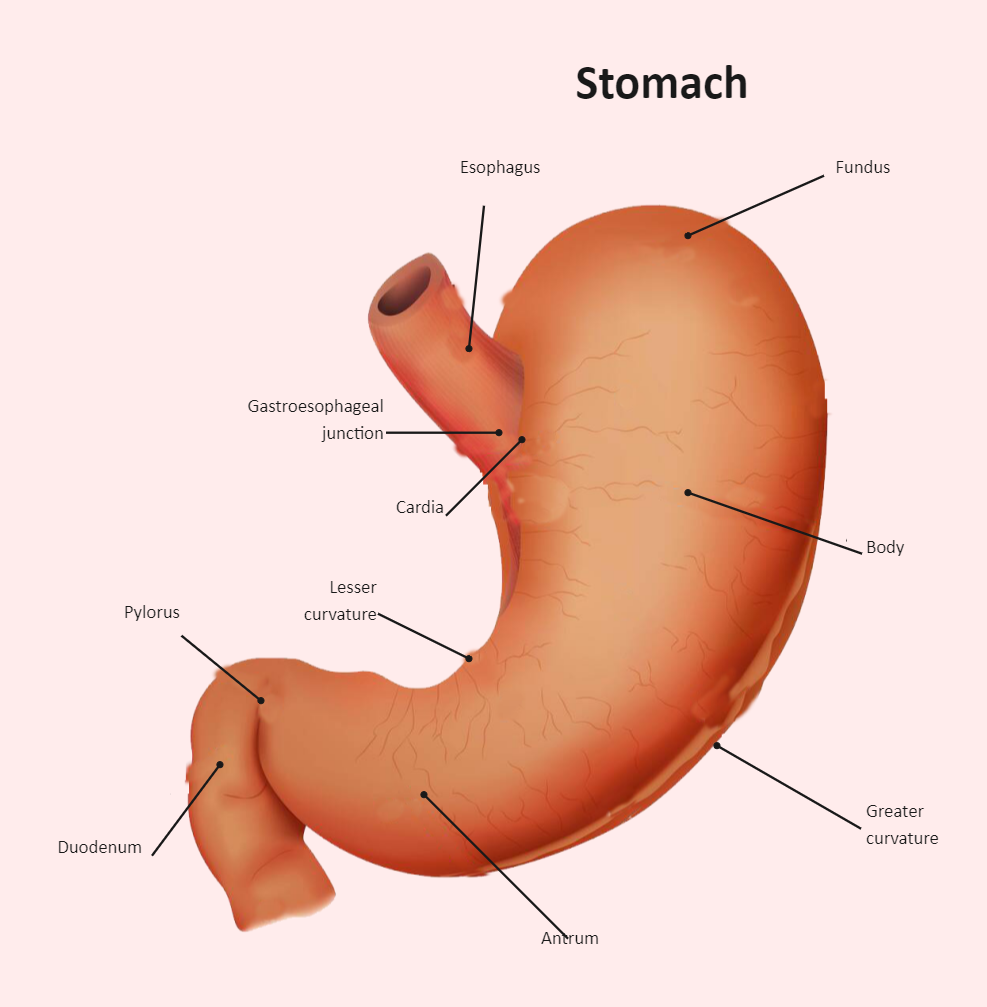
There are four main regions in the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus (Figure 21.4.1 21.4. 1 ). The cardia (or cardiac region) is the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach and through which food passes into the stomach. Located inferior to the diaphragm, above and to the left of the cardia, is the dome-shaped fundus.

stomach model Google Search Anatomy models labeled, Anatomy models, Human anatomy and physiology
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a collection of organs that allow for food to be swallowed, digested, absorbed, and removed from the body. The organs that make up the GI tract are the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The GI tract is one part of the digestive system.
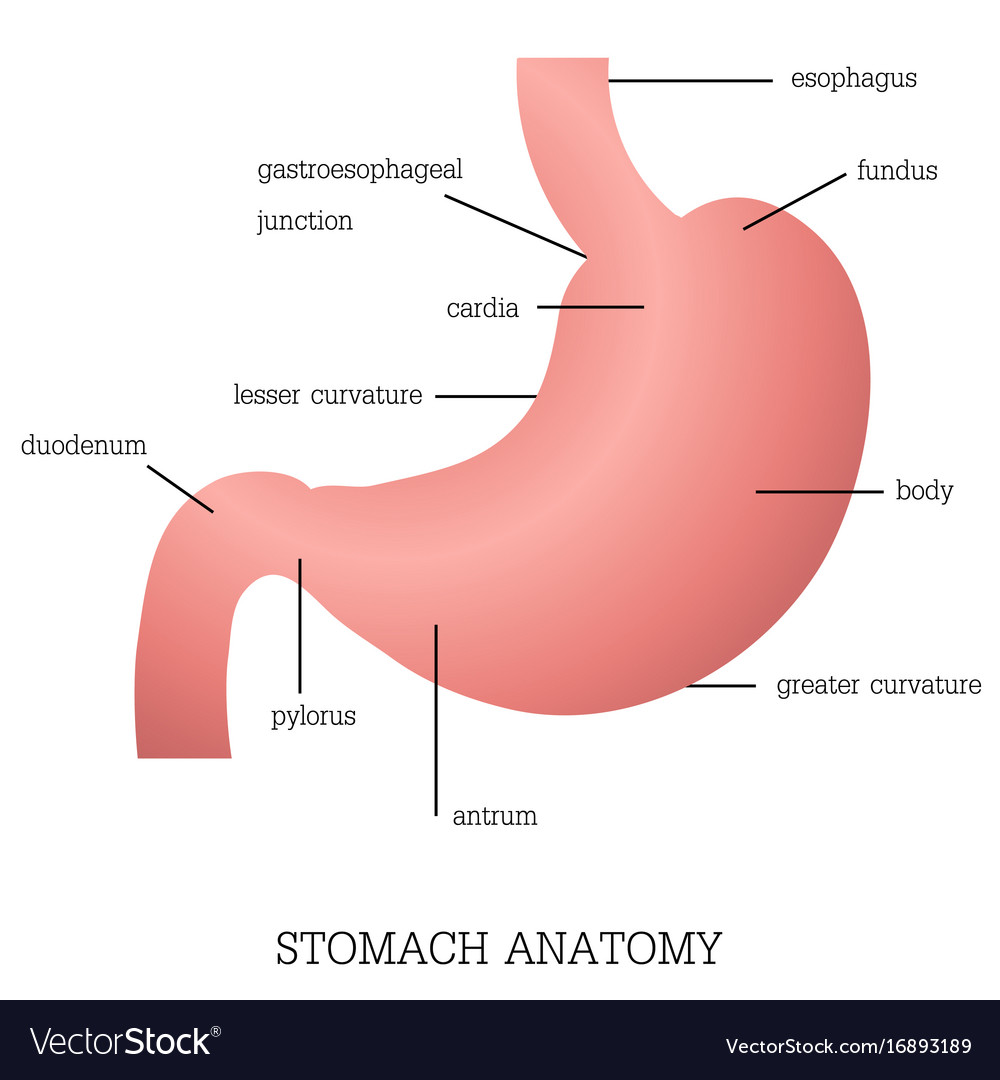
Structure and function of stomach anatomy system Vector Image
Label on a diagram the four main regions of the stomach, its curvatures, and its sphincter Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself Describe the mechanical and chemical digestion of food entering the stomach

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
The stomach is lined by a mucous membrane that contains glands (with chief cells) that secrete gastric juices. Two smooth muscle valves, or sphincters, keep the contents of the stomach contained: the cardiac or esophageal sphincter and the pyloric sphincter. The arteries supplying the stomach are the left gastric, the right gastric, and the.

Simple stomach diagram Stomach structure Stomach Anatomy Stomach diagram, Digestive system
23.4 The Stomach Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the functional anatomy of the stomach Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself

Anatomy 501 > Sorrells > Flashcards > Stomach, Spleen, and Small Intestine StudyBlue
The pylorus is surrounded by a thick circular muscular wall that is normally tonically constricted, forming a functional (if not anatomically discrete) pyloric sphincter that controls the movement of chyme. 22.6B: Microscopic Anatomy of the Stomach is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
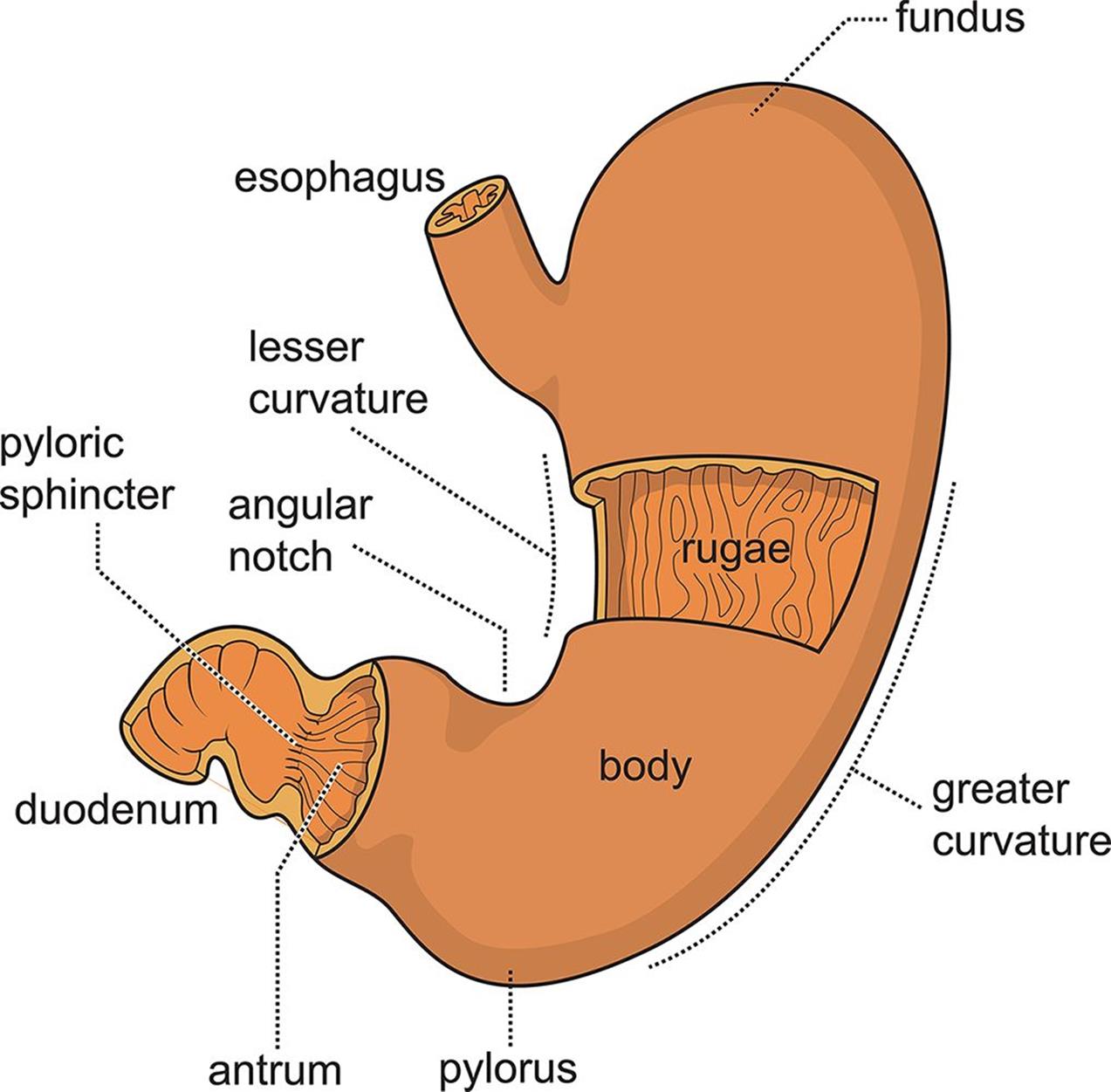
Figure 9.2. Anatomy of the Stomach
The stomach is a key part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, sitting between the esophagus and duodenum. Its functions are to mix food with stomach acid and break food down into smaller particles using chemical and mechanical digestion. The stomach can perform these roles due to the layers of the stomach wall.
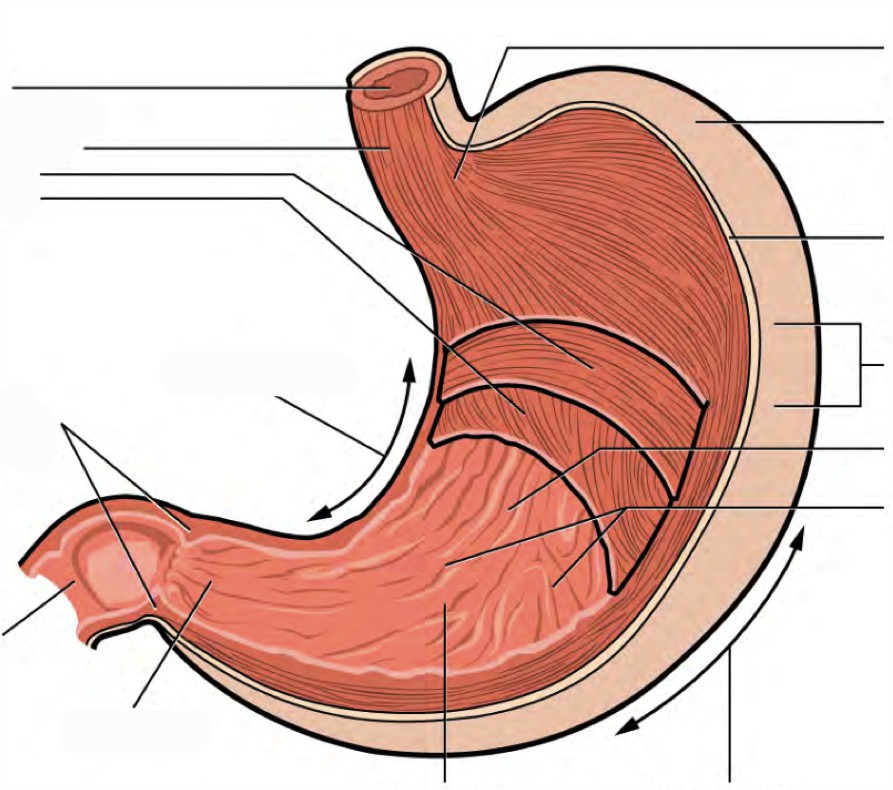
PreLab 8 Human Anatomy Lab Manual
The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food. Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus .
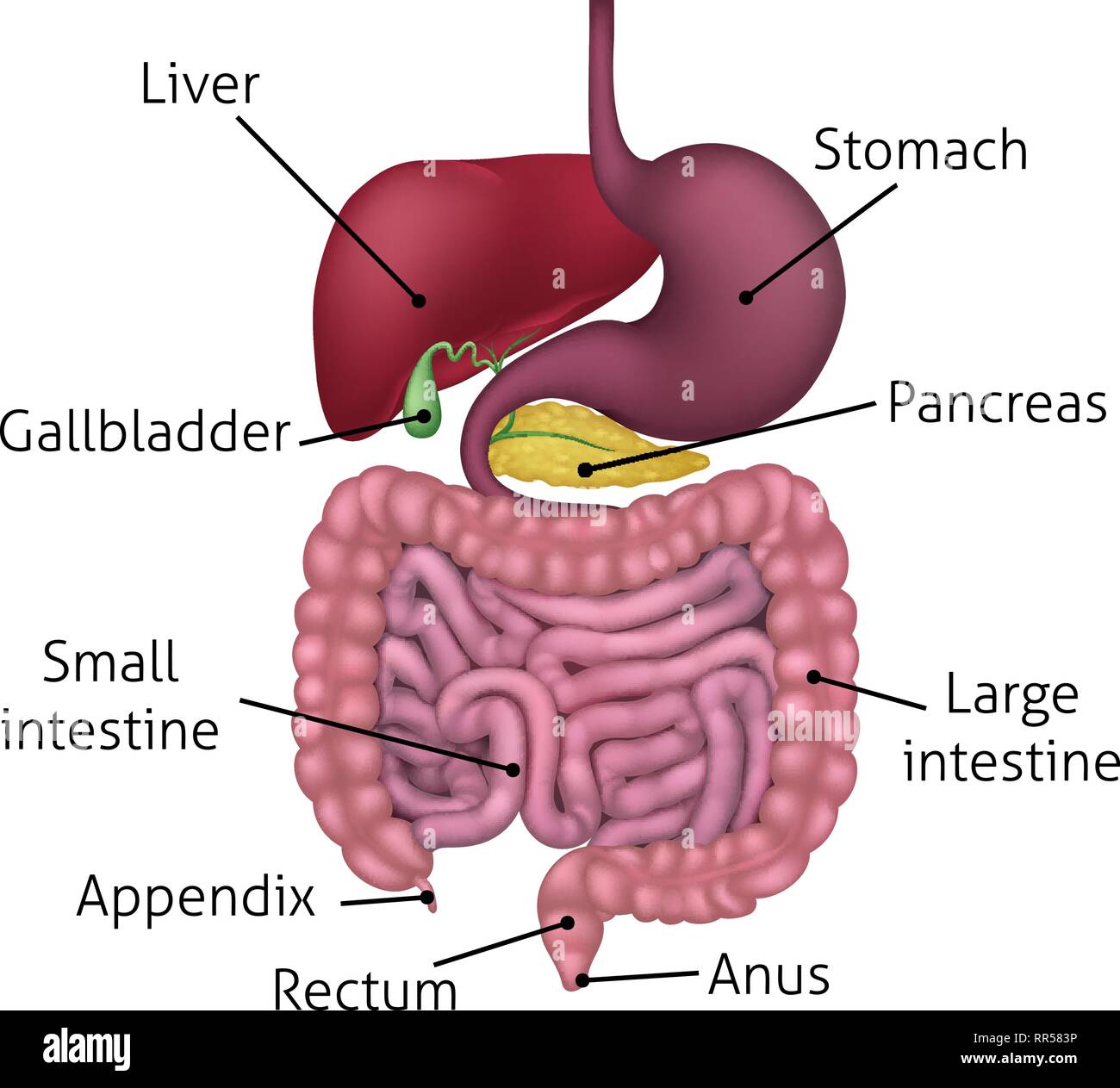
Gastrointestinal Digestive System and Labels Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
Diagram Stomach Gallbladder Liver Pancreas Small intestine Large intestine How they interact Common problems Summary The stomach is located in the upper part of the abdomen. The digestive.
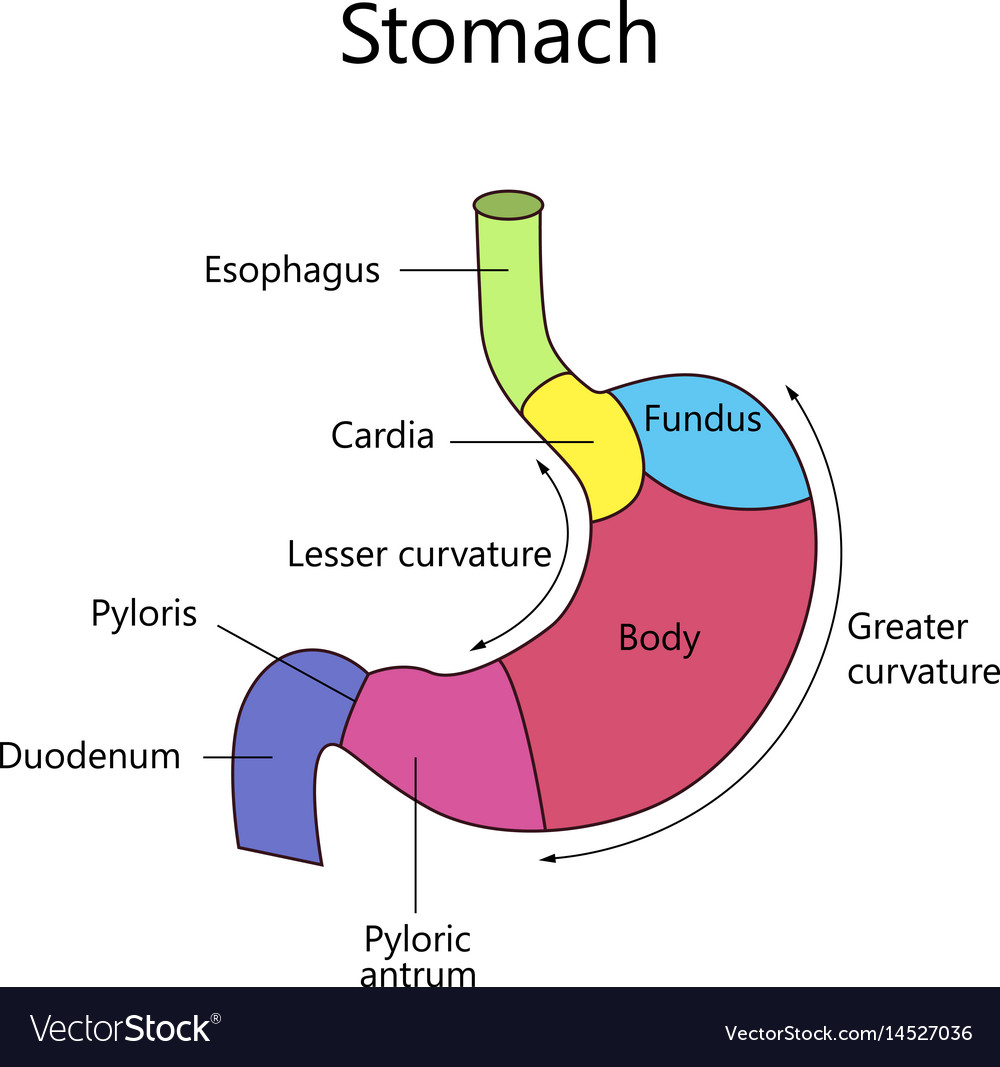
Internal structure human stomach Royalty Free Vector Image
The stomach's main roles: Food storage Acidic breakdown of swallowed food Sends mixture on to the next phase in the small intestine Structure of the Stomach The archaic illustration depicts the different regions of the stomach
Stomach Diagram Labeled EdrawMax Template
Stomach Stomach Your stomach is a muscular organ that digests food. It is part of your gastrointestinal (GI) tract. When your stomach receives food, it contracts and produces acids and enzymes that break down food. When your stomach has broken down food, it passes it to your small intestine.