Barati Express adlı kullanıcının Green Energy panosundaki Pin Teknik

Closeup of an Auto Part for an Internal Combustion Engine. Gas Turbine Stock Photo Image of
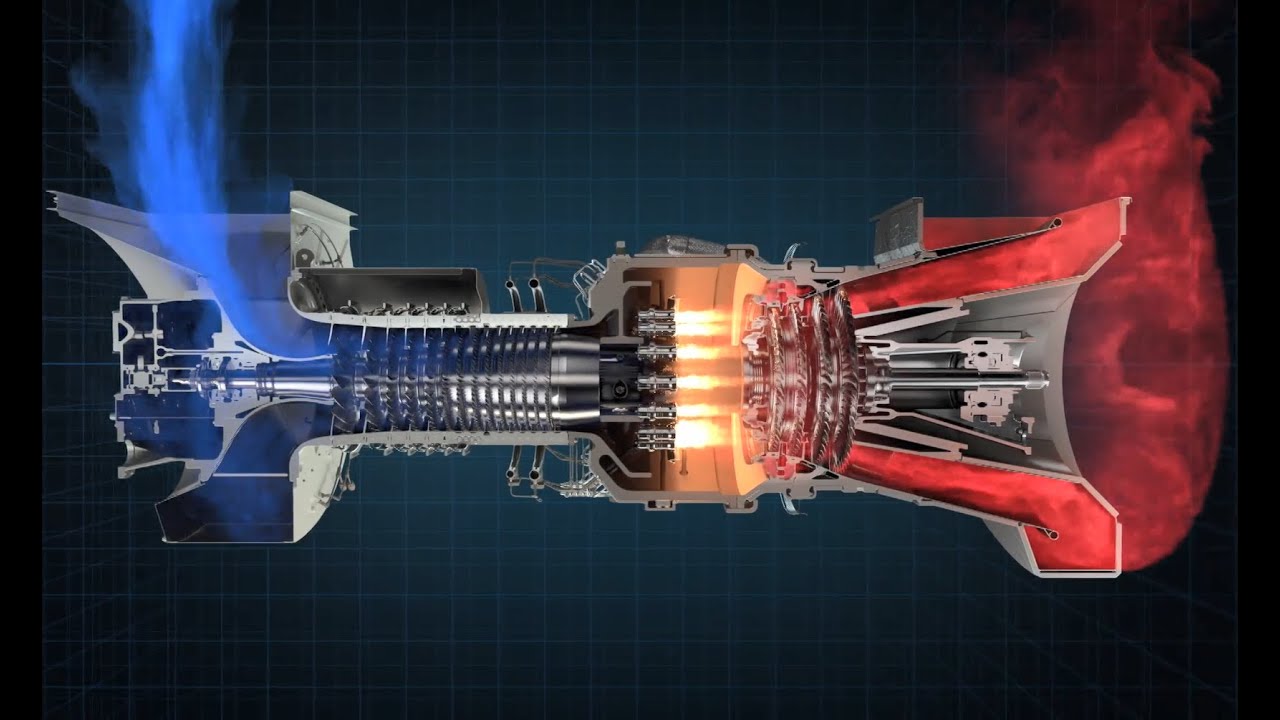
A gas turbine combustion system consists of the following regions and components: (1) diffuser (2) fuel nozzle (3) primary zone (4) intermediate zone (5) dilution zone. These regions are shown in Fig. 6.3, which is a schematic representation of a gas turbine combustion system. Sign in to download full-size image 6.3.

Material types used in different sections in an Alstom gas turbine... Download Scientific Diagram
In this video, I explained Advantages And Disadvantages Of Gas Turbines Over Internal Combustion Engine.Chapter: Thermal Power PlantPlaylist of Thermal Power.

Closeup of an Auto Part for an Internal Combustion Engine. Gas Turbine Stock Image Image of
Pistons vs turbines Figure 1. A diagram of a gas turbine engine. [3] An engine that uses a piston is called an intermittent combustion engine, whereas one that uses a turbine is called a continuous combustion engine. The difference in mechanics is obvious due to the names, but difference in use is less obvious.
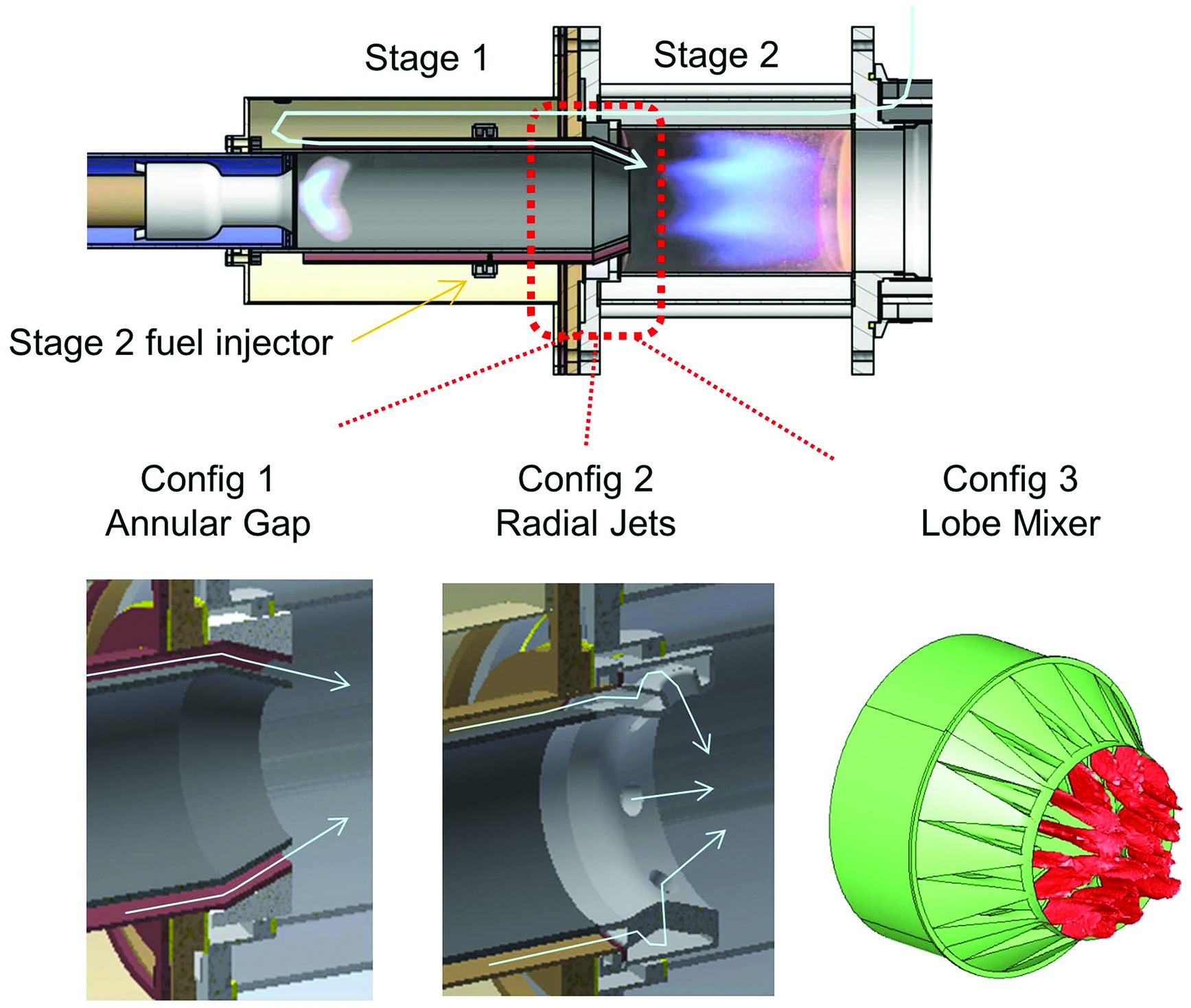
Staged combustion concept for gas turbines
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine, by its old name internal combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. [1] The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the direction of flow: a rotating gas compressor a combustor
Center for Environment, Commerce & Energy Natural Gas Combustion Turbines
CHAPTER 1 Review of Basic Principles (Pages: 4-44) Summary PDF Request permissions CHAPTER 2 Thermodynamics of Reactive Mixtures (Pages: 45-93) Summary PDF Request permissions Part II : Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines CHAPTER II Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (Pages: 95-98) First Page
The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Gas Engine Linquip
The internal combustion has taken on many different forms throughout its long, greater than 150-year history, but combustion has always been one of its few constants. Indeed, combustion is even in its name and helps differentiate it from other thermodynamic work devices such heat engines and fuel cells. Type.

Modeling of Engine Combustion Processes Thomson Lab
Abstract. The current article introduces a physics-based revolutionary technology that enables energy efficiency and environmental compatibility goals of future generation aircraft and power generation gas turbines (GTs). An ultrahigh efficiency GT technology (UHEGT) is developed, where the combustion process is no longer contained in isolation between the compressor and turbine, rather.
GASOLINE INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE HISTORY Wroc?awski Informator Wroc?aw
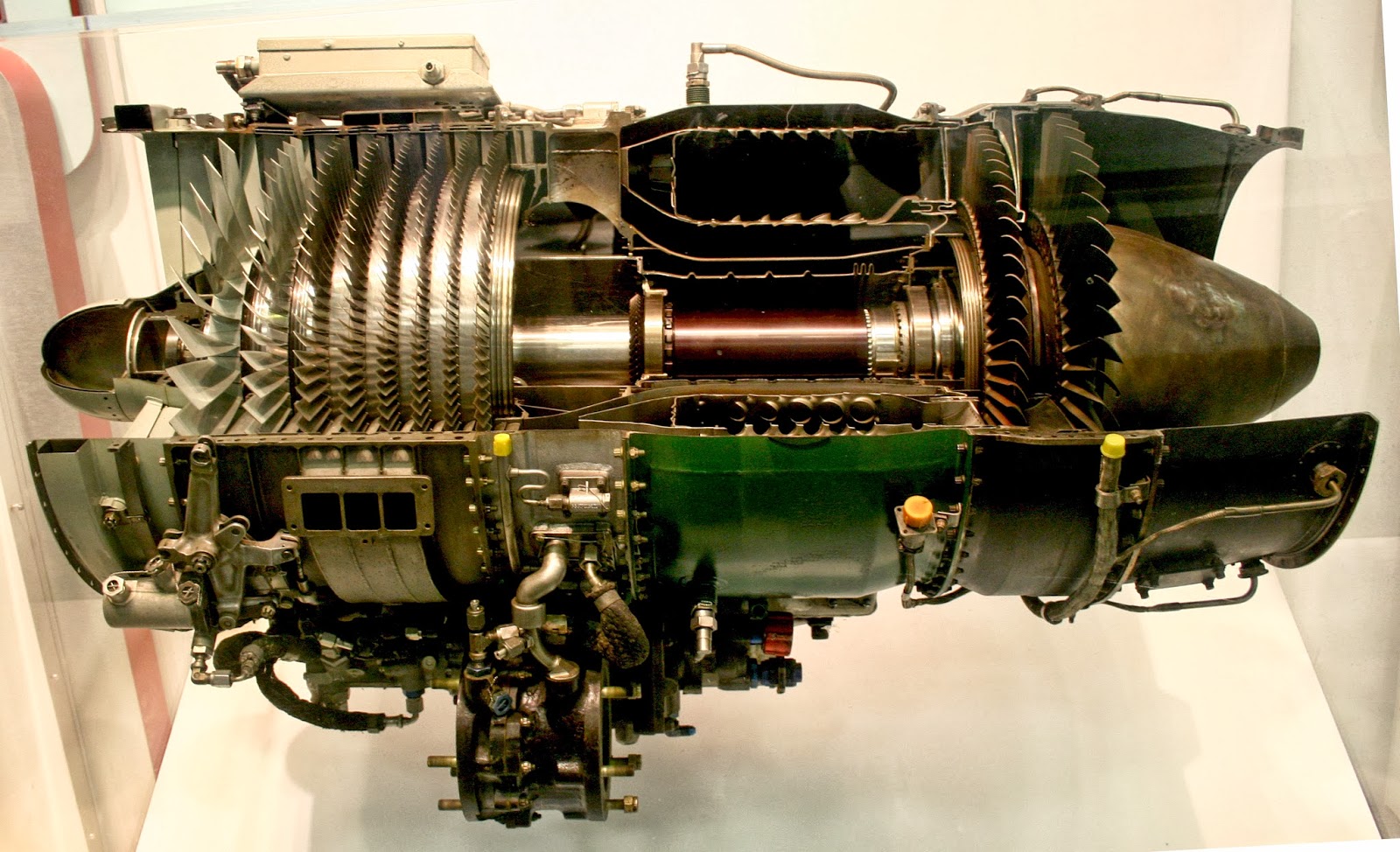
gas-turbine engine, any internal- combustion engine employing a gas as the working fluid used to turn a turbine. The term also is conventionally used to describe a complete internal-combustion engine consisting of at least a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. General characteristics

Combustion section transition pieces that direct hot gasses onto the turbine blades of a
In 1791, John Barber developed the gas turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel, and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens built the first American internal combustion engine.
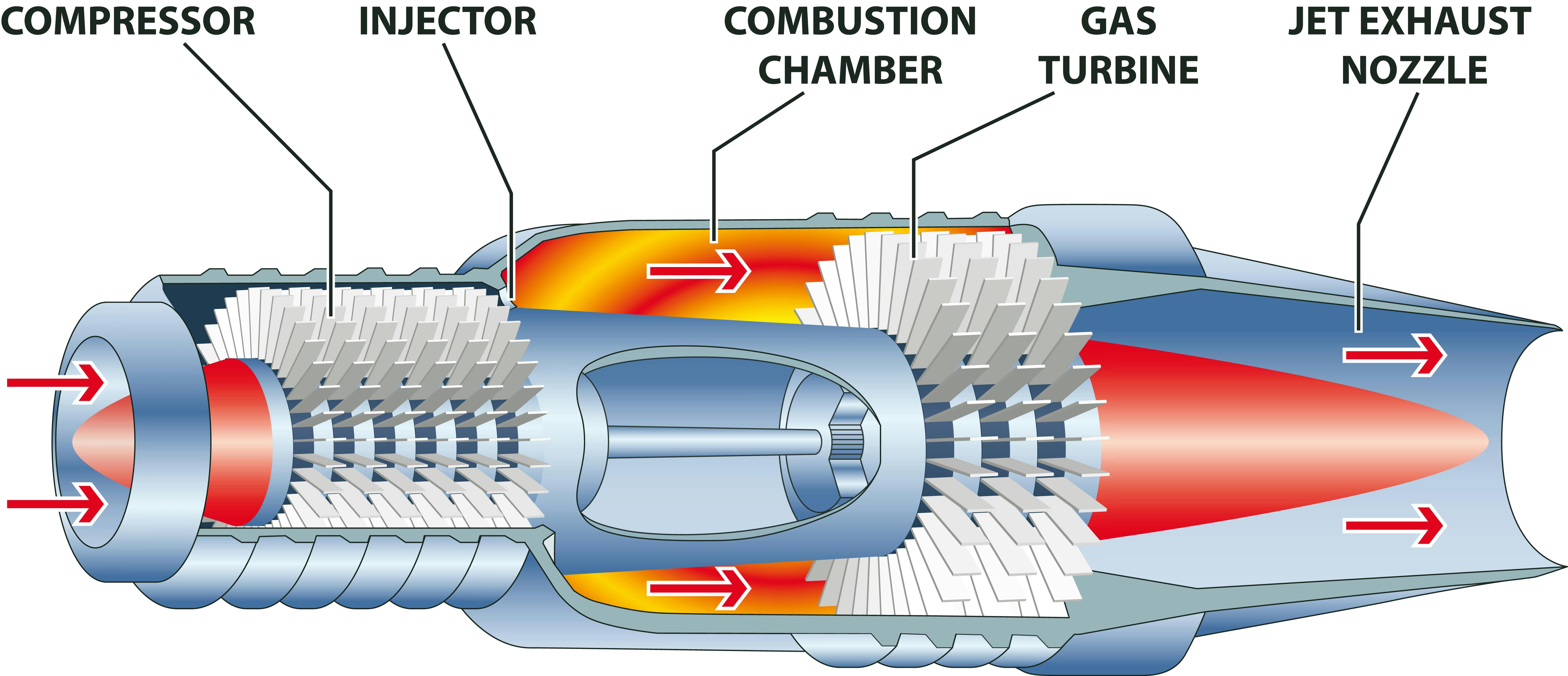
Jet Engine Major Components How Do They Work? Xometry
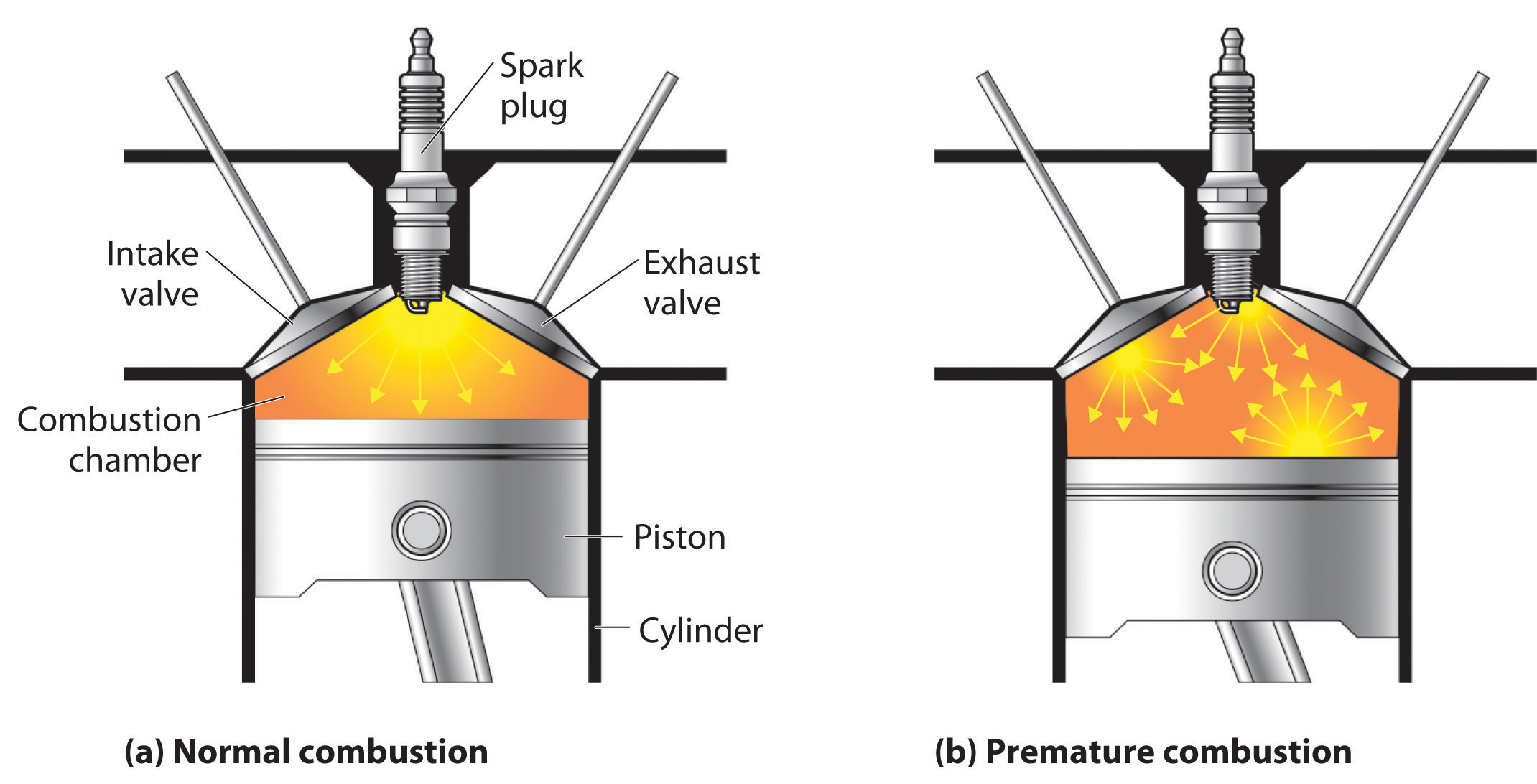
The basic principle of the airplane turbine engine is identical to any and all engines that extract energy from chemical fuel. The basic 4 steps for any internal combustion engine are: Intake of air (and possibly fuel). Compression of the air (and possibly fuel). Combustion, where fuel is injected (if it was not drawn in with the intake air.

Closeup of an Auto Part for an Internal Combustion Engine. Gas Turbine Stock Image Image of
An internal combustion engine is a type of heat engine that is widely used in various applications, particularly in transportation. This engine acts as the primary power source for automobiles, motorcycles, airplanes, boats, and many other machines.

[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Gas Turbine Power Production System
A Gas Turbine is a type of engine that converts fuel into mechanical energy by combustion in a turbine. In a gas turbine, fuel is mixed with air and burned in a combustion chamber. The hot exhaust gases are then passed through a turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity or mechanical energy.

Barati Express adlı kullanıcının Green Energy panosundaki Pin Teknik
Gas turbines are a type of internal combustion (IC) engine in which burning of an air-fuel mixture produces hot gases that spin a turbine to produce power. It is the production of hot.

ETN Hytrogen Gas Turbines 03 Hydrogen Combustion Turbine Logic
Internal combustion ( gasoline, diesel and gas turbine - Brayton cycle engines) and External combustion engines ( steam piston, steam turbine, and the Stirling cycle engine). Each of these engines has thermal efficiency characteristics that are unique to it.

What Is a Combustion Turbine? (with pictures)
phenomenon known as "turbine combustor lean blowout." As the CT generators accelerated in response to the frequency excursion, the direct-coupled turbine compressors forced more air into their associated combustion chambers at the same time as the governor speed control function reduced fuel input in response to the increase in speed.
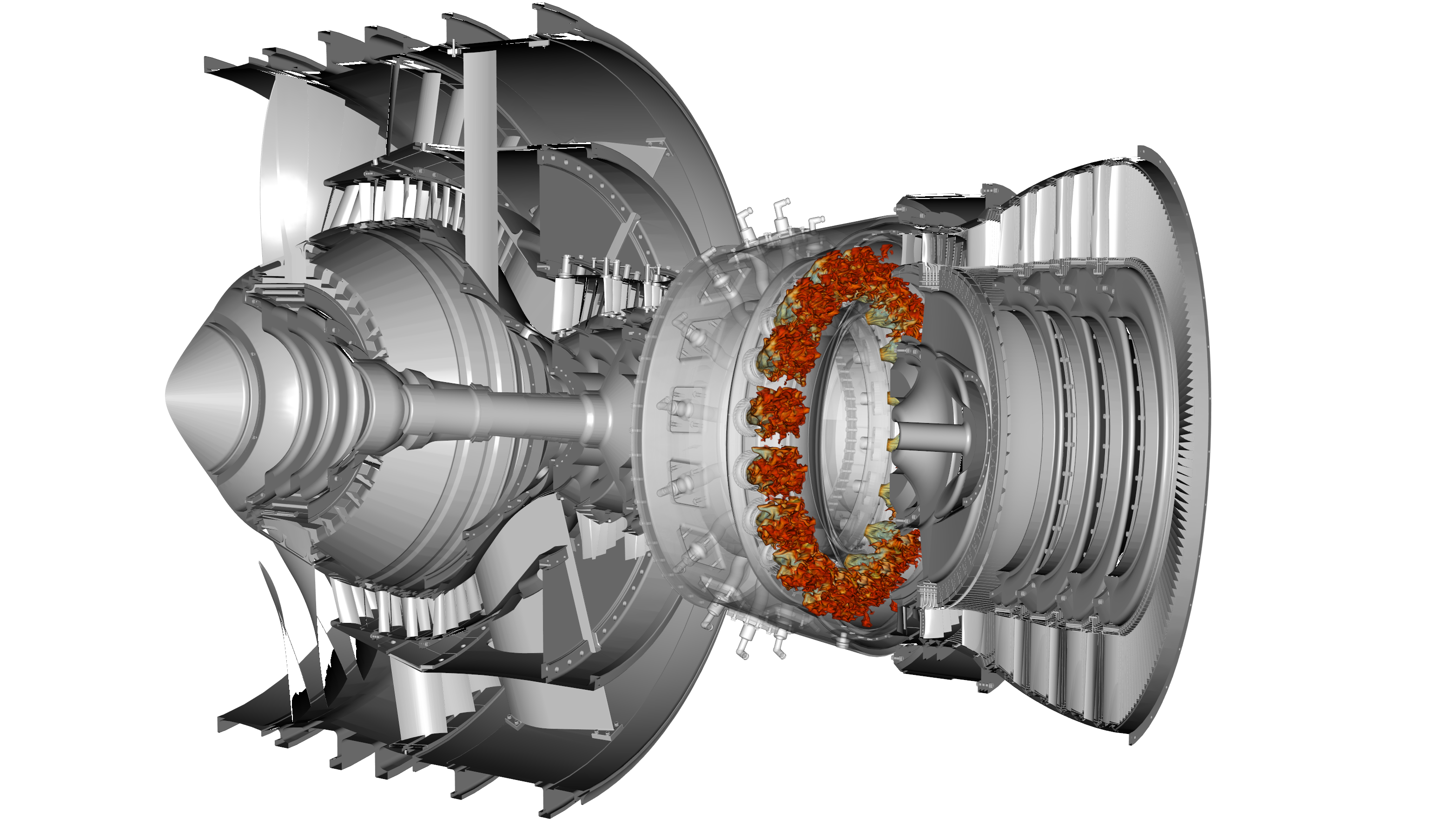
Combustion Siemens Software
Gas turbines have continuous combustion compared to reciprocating IC engines, which have intermittent combustion. This article covers a complete guide to understanding the Difference between a Combustion Engine and a Gas Turbine. How A Gas Turbine Performs?