KS3 Physics Forces and Motion DistanceTime Graphs Teaching Resources
DistanceTime Graphs
Distance vs Time Graphs | Velocity & Speed Motion Graphs | Physics Explained Tadashi Science 27 subscribers Subscribe 0 30 views 2 months ago Motion - 1D Check out our channel for.

KS3 Physics Forces and Motion DistanceTime Graphs Teaching Resources
There are three types of motion graphs that you will come across in the average high school physics course - position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs, and acceleration vs time graphs. An example of each one can be seen below. The position vs time graph (on the left) shows how far away something is relative to an observer.

Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
The slope of a velocity graph represents the acceleration of the object. So, the value of the slope at a particular time represents the acceleration of the object at that instant. The slope of a velocity graph will be given by the following formula: slope = rise run = v 2 − v 1 t 2 − t 1 = Δ v Δ t v ( m / s) t ( s) r i s e r u n t 1 t 2 v 1 v 2
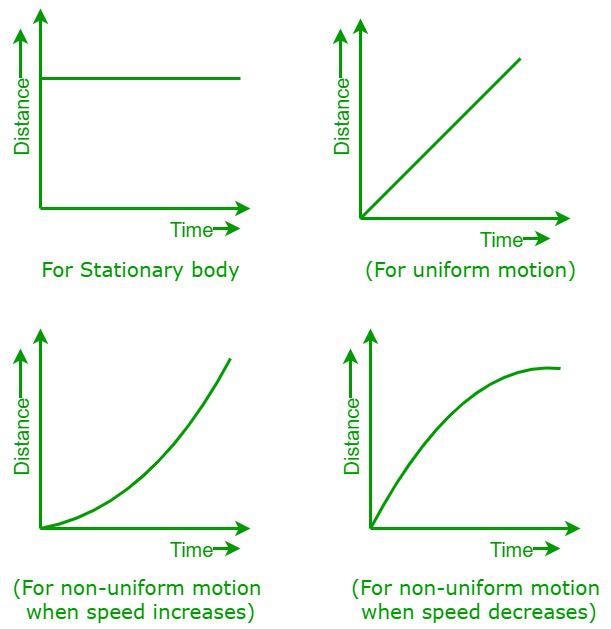
Distance Time Graph for Uniform and NonUniform Motion Teachoo
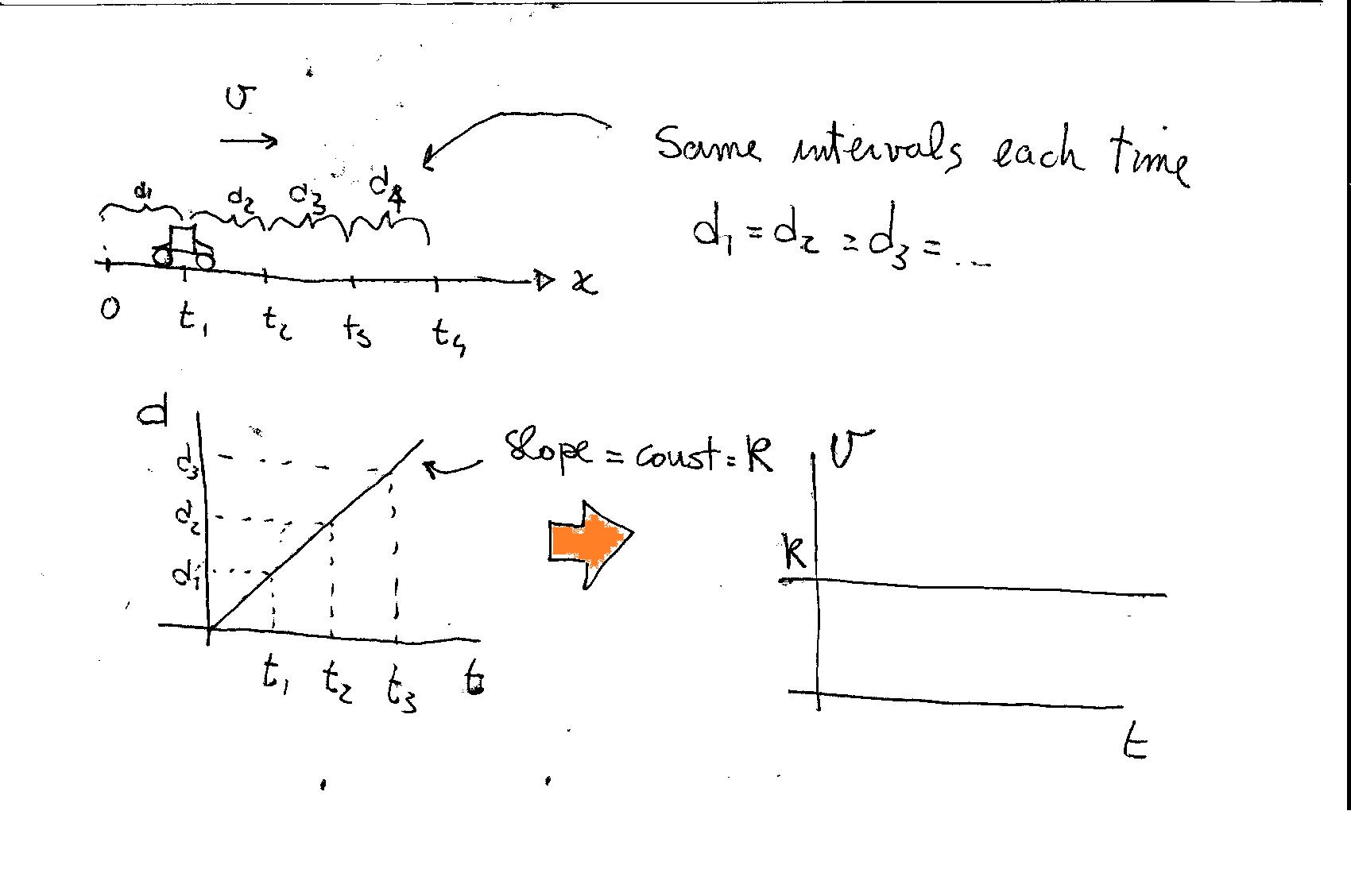
The two graphs are connected because the speed vs time is a graph of the slopes obtained from the distance vs time graph: For example: 1) consider a particle moving with constant speed: The distance vs time graph is a linear function while the speed vs time is a constant; 2) consider a particle moving with varying speed (constant acceleration):.
What is how does a motion graph of distance vs time differ from a graph of speed vs time? Socratic
David explains how to read a position vs. time graph. He then explains how to use the graph to determine the following quantities: displacement, distance, av.

Distance versus time curve for the free fall motion experiment. Download Scientific Diagram
Answers. Download this page, PMO1.2 Linear motion: Graphs (PDF 1480KB) Linear motion refers to the motion of an object in a straight line. Describing these motions require some technical terms such as displacement, distance, velocity, speed and acceleration.
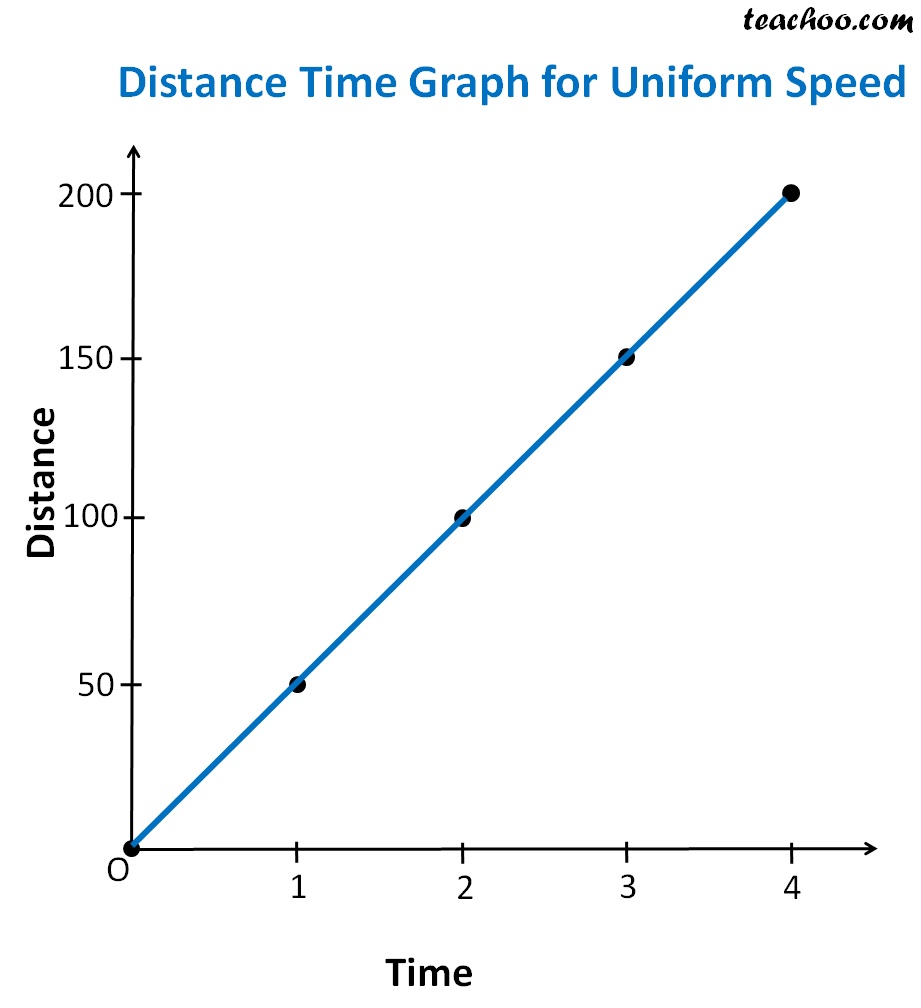
Distance Time Graph For Uniform Motion With Example
Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. The three graphs of motion a high school physics student needs to know are: Position vs. time graph (x vs. t) Velocity vs. time graph (v vs. t) Acceleration vs. time graph (a vs. t)

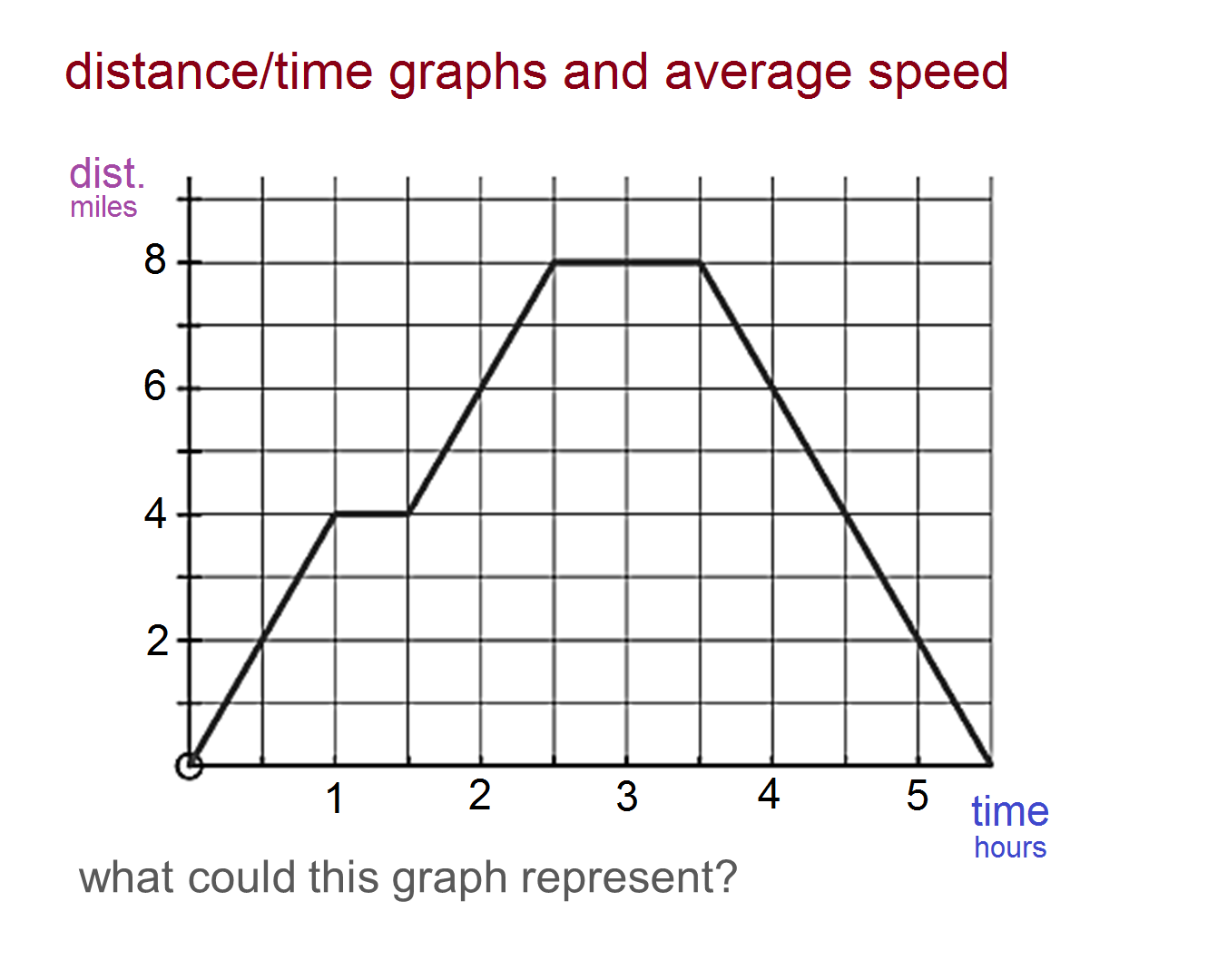
Two students were asked to plot a distancetime graph for the motion described by Table A and
Select the correct answer and click on the "Finish" button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz Start Quiz Read about distance time graph and velocity time graph. Learn the concepts of motion graphs for uniformly accelerated motion and more by registering with BYJU'S
Distance Time Graphs
Motion Graphs. Constant acceleration motion can be characterized by motion equations and by motion graphs. The graphs of distance, velocity and acceleration as functions of time below were calculated for one-dimensional motion using the motion equations in a spreadsheet. The acceleration does change, but it is constant within a given time.
PPT Motion in one dimension PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2463862
Motion Graphs. Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion is a change in position measured by distance and time. Speed tells us the rate at which an object moves. Velocity tells the speed and direction of a moving object.
Graphical Representation of Motion Class 7, Motion and Time, Science
Activity 1: Making distance vs. time graphs for different walking speeds and directions Start at the 1⁄2 meter mark and make a distance versus time graph, walking away from the sensor slowly and steadily (at constant speed). Sketch your graph on the axes to the right.
PPT Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4816796
What is displacement? Calculating average velocity or speed Solving for time Displacement from time and velocity example Instantaneous speed and velocity What is velocity? Position vs. time graphs What are position vs. time graphs? Average velocity and average speed from graphs Instantaneous velocity and instantaneous speed from graphs Science >

Reading Kinematics Graphs Mini Physics Learn Physics
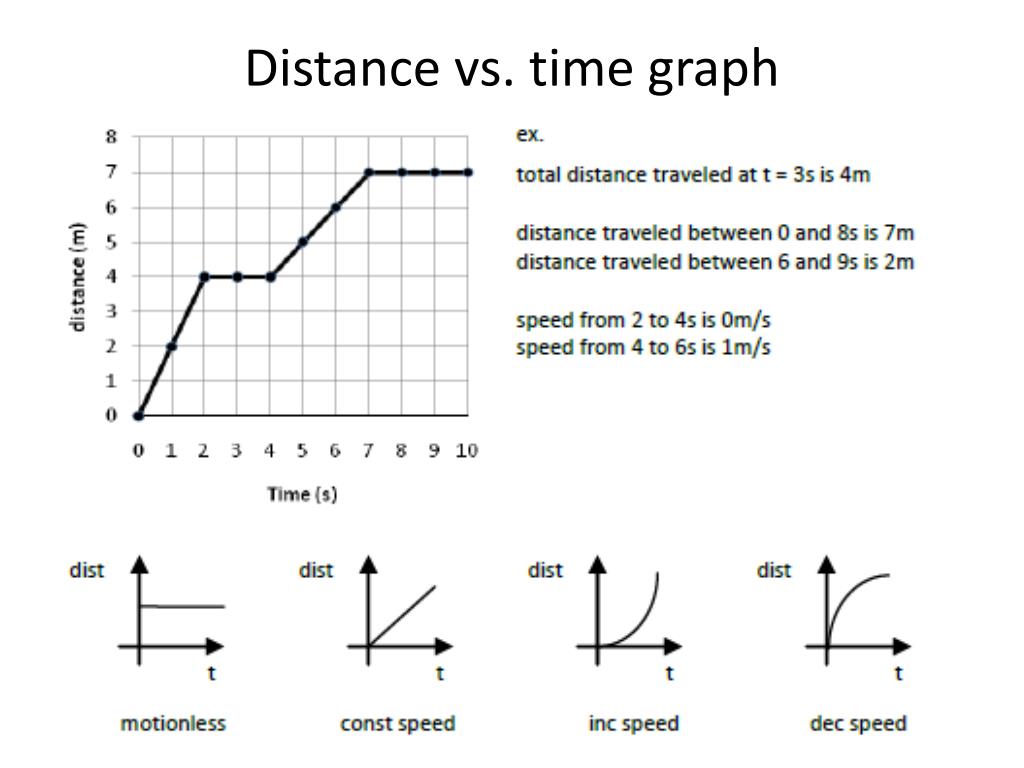
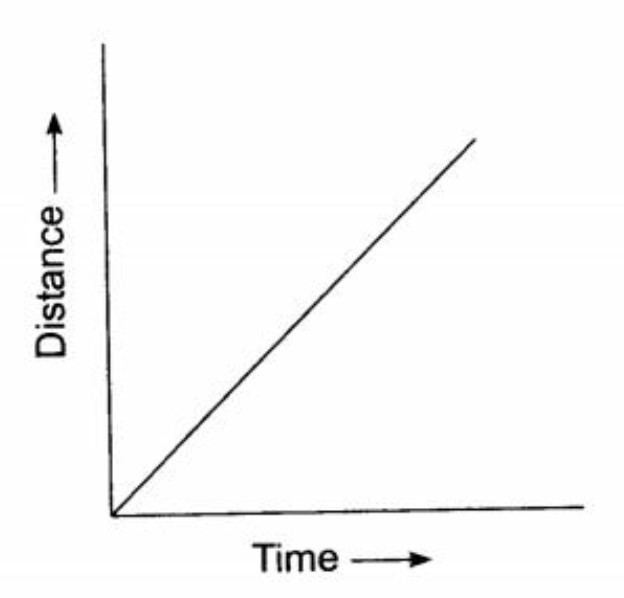
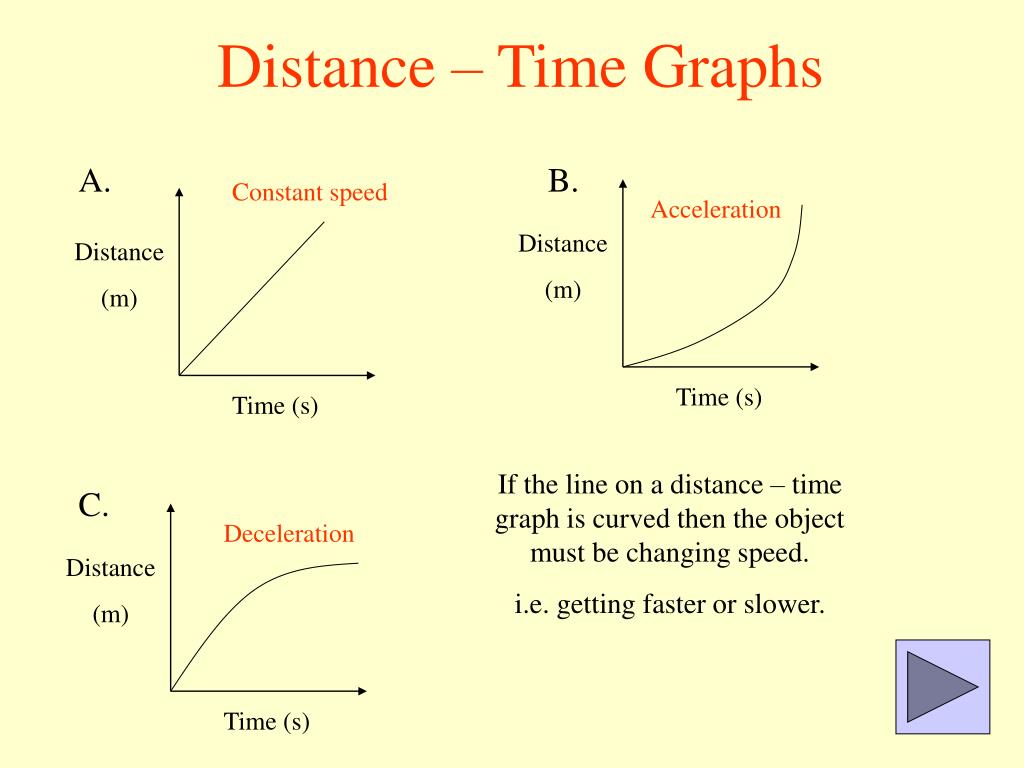
It is a simple line graph that denotes distance versus time findings on the graph. Distance is plotted on the Y-axis. Time is plotted on the X-axis. Note: Curved lines on a distance-time graph indicate that the speed is changing. You may also want to check out these topics given below! Graphs Velocity-Time Graph Linear Graph
MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching distance/time graphs and average speed
Motion Graphs - Distance vs Time Keipert Labs 6.43K subscribers Subscribe 302 views 6 years ago Moving In this episode of Keipert Labs, we'll go over how we can use graphs to describe the.
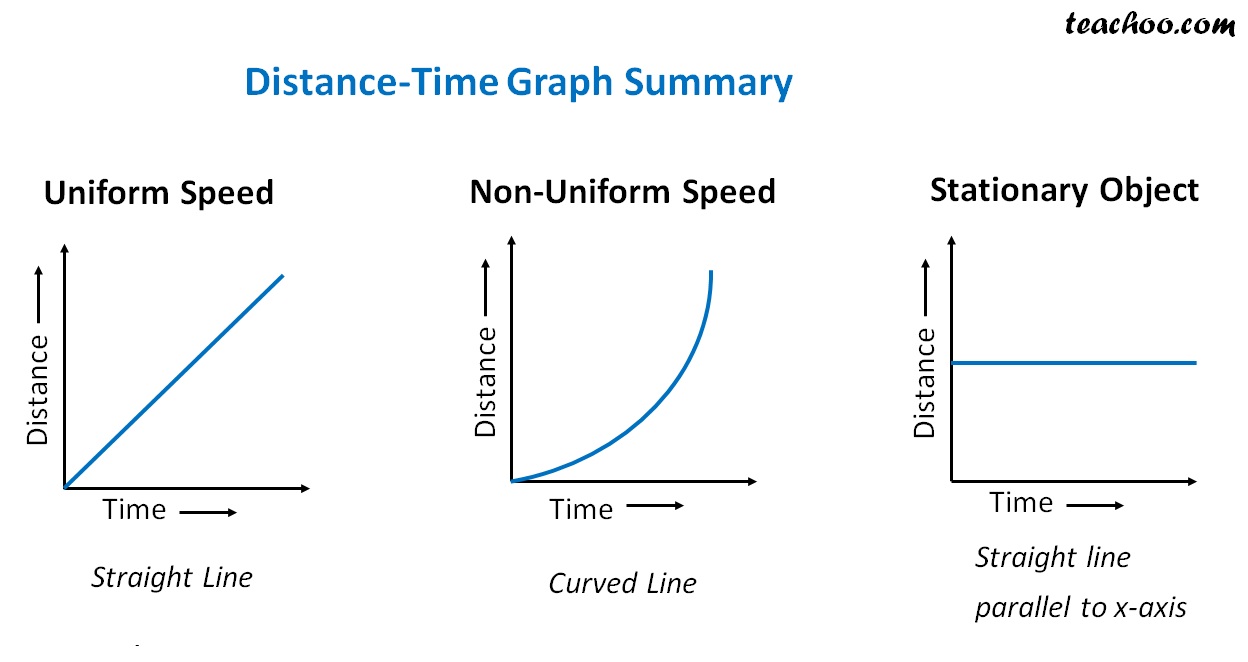
Distance Time Graph for Uniform and NonUniform Motion Teachoo
Constant acceleration motion can be represented in motion graphs which represent velocity, acceleration, and distance as functions of time. These graphs are useful for calculating information about motion using the slopes of the curves in each plot.

MOTION 06 DISTANCETIME GRAPH GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF MOTION CLASS 9 ONLINE PHYSICS
On a distance-time graph a diagonal straight line means CONSTANT SPEED. (This will be different on the speed time graph.) On a distance-time graph a curved upwards line means ACCELERATION and a line that returns down to the baseline means RETURNING BACK to the original starting point (0 line on the graph). Again, different on the speed time.