(1 point) The vector equation r (u,v) = u cOS vi + u … SolvedLib

Pertamina RU V Balikpapan Dukung Kesiapan Menghadapi Nataru Pertamina
The problem of tracking with very long range radars is studied in this paper. First, the measurement conversion from a radar's r-u-v coordinate system to the Cartesian coordinate system is discussed.

R.U.V. Rover Utility Vehicle Overview Utility vehicles, Lego space, Classic space
If r(u;v) is the parameterization of a surface, then the surface unit normal is de-ned n = r u r v jjr u r vjj The vector n is also normal to the surface. surf3 Moreover, n is often considered to be a function n(u;v) which assigns a normal unit vector to each point on the surface. EXAMPLE 4 Find the surface unit normal and the equation of
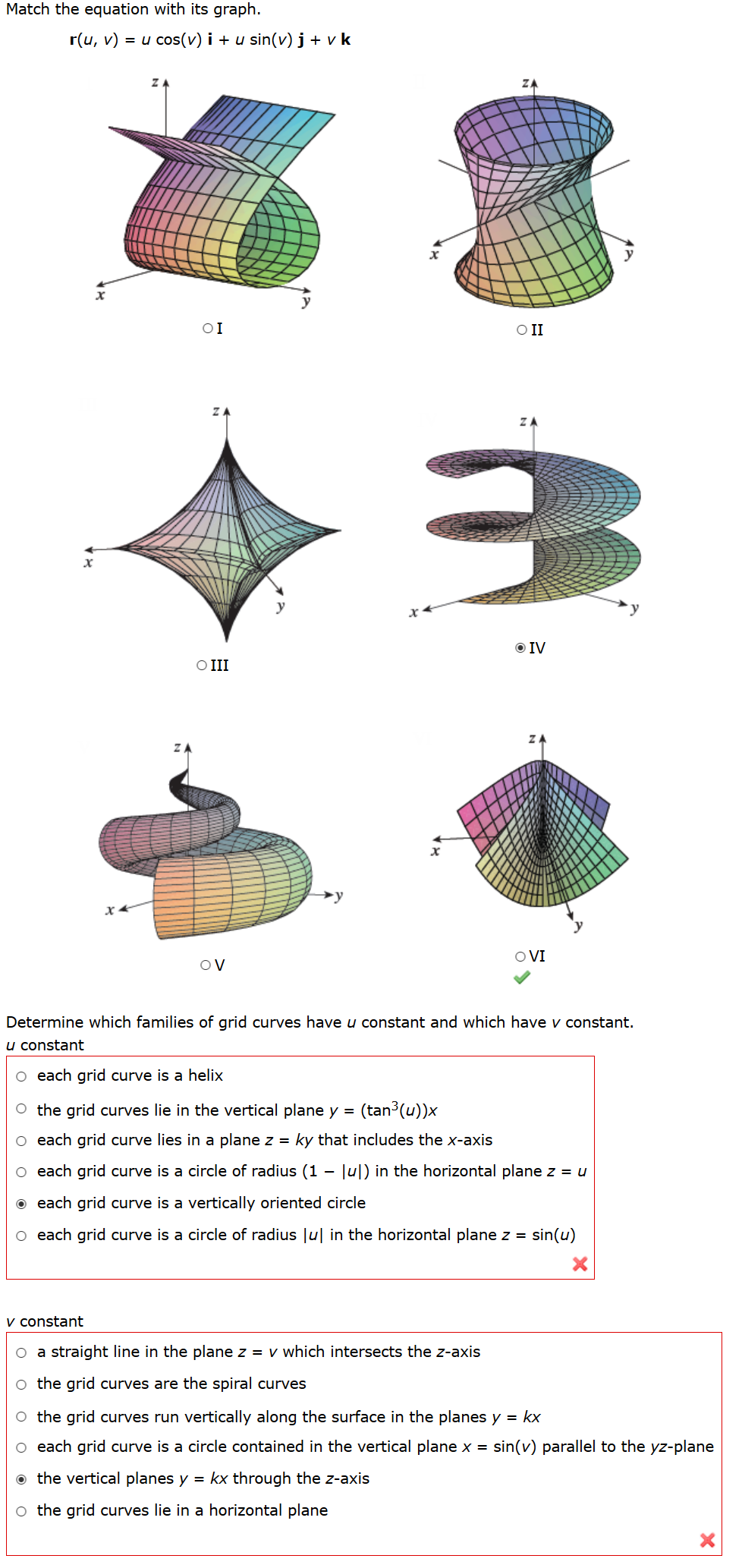
Solved Match the equation with its graph. r(u, v) = u cos(v)
De nition 1. A parametrization is a function from a domain D in the uv plane into R3, written as ~r(u; v) = hx(u; v); y(u; v); z(u; v)i where x = x(u; v), y = y(u; v) and z = z(u; v) are real valued continuous functions (usually di erentiable, and often with additional assumptions). Those three real valued functions are called parametric equations.

M.r.u.v
Mit der R+V-Auslandsreise-Krankenversicherung gehen Sie auf Reisen kein Risiko ein. Auch im Skiurlaub. Ab 10,80 EUR pro Jahr. Zur Auslandsreise-Krankenversicherung Beitrag berechnen Hardwareversicherung Schutz für Computer und Co. Der Top-Elektronikschutz für alle PCs, Laptops, Spielekonsolen inklusive Originalzubehör und nachgerüstetem Zubehör.

Solved Find the fundamental vector product for r(u, v) =
Figure 16.6.6: The simplest parameterization of the graph of a function is ⇀ r(x, y) = x, y, f(x, y) . Let's now generalize the notions of smoothness and regularity to a parametric surface. Recall that curve parameterization ⇀ r(t), a ≤ t ≤ b is regular (or smooth) if ⇀ r ′ (t) ≠ ⇀ 0 for all t in [a, b].

(1 point) The vector equation r (u,v) = u cOS vi + u … SolvedLib
The tangent plane at a regular point is the affine plane in R 3 spanned by these vectors and passing through the point r(u, v) on the surface determined by the parameters. Any tangent vector can be uniquely decomposed into a linear combination of r u {\displaystyle \mathbf {r} _{u}} and r v . {\displaystyle \mathbf {r} _{v}.}

Alphabet 01 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V Free Download Nude Photo Gallery
#ThorMotorCoach #VegasRV #RUVGreat adventures all start somewhere. Why not start yours in a Thor Vegas R.U.V. It's fully equipped and easy to drive. If a C.

ENGLISHU.K.G., Chapter 1 Letters of the Alphabet Nischal's Blog
derivations of such models for constant-velocity problems in a variety of 2D polar and r-u coordinates systems and in 3D spherical and r-u-v coordinate systems, sparing tedious derivations for simple tracking problems. The conversions for r-u and r-u-v coordinate systems do not appear to have been previously published.

Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz Alphabet Letters Alphabet Letter Road With White And Yellow Line
De nition: If the rst parameter uis kept constant, then v7!~r(u;v) is a curve on the surface. Similarly, if vis constant, then u7!~r(u;v) traces a curve the surface. These curves are called grid curves.
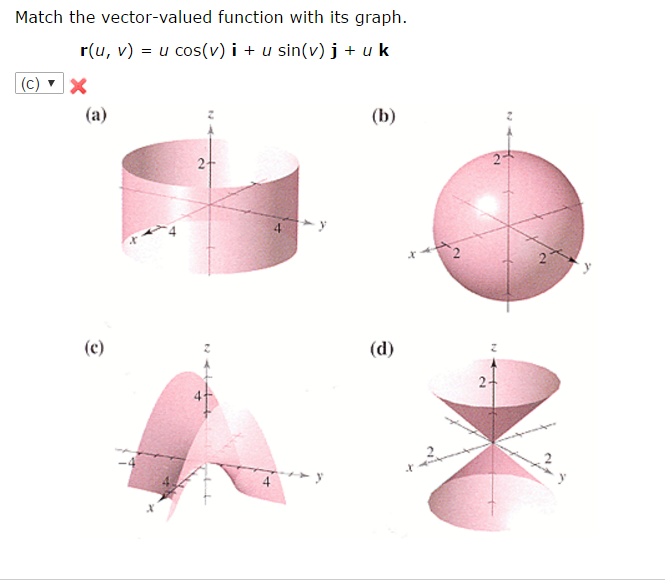
Solved Match the vectorvalued function with its graph. r(u,
Electric power can be expressed as P = electrical power (watts, W) The power consumed in the electrical circuit above can be calculated as P = (12 volts) / (18 ohm) electric light bulb is connected to a supply. The current flowing can be calculated by reorganizing I = P / U = (100 W) / (230 V) 0.43 The resistance can be calculated by reorganizing
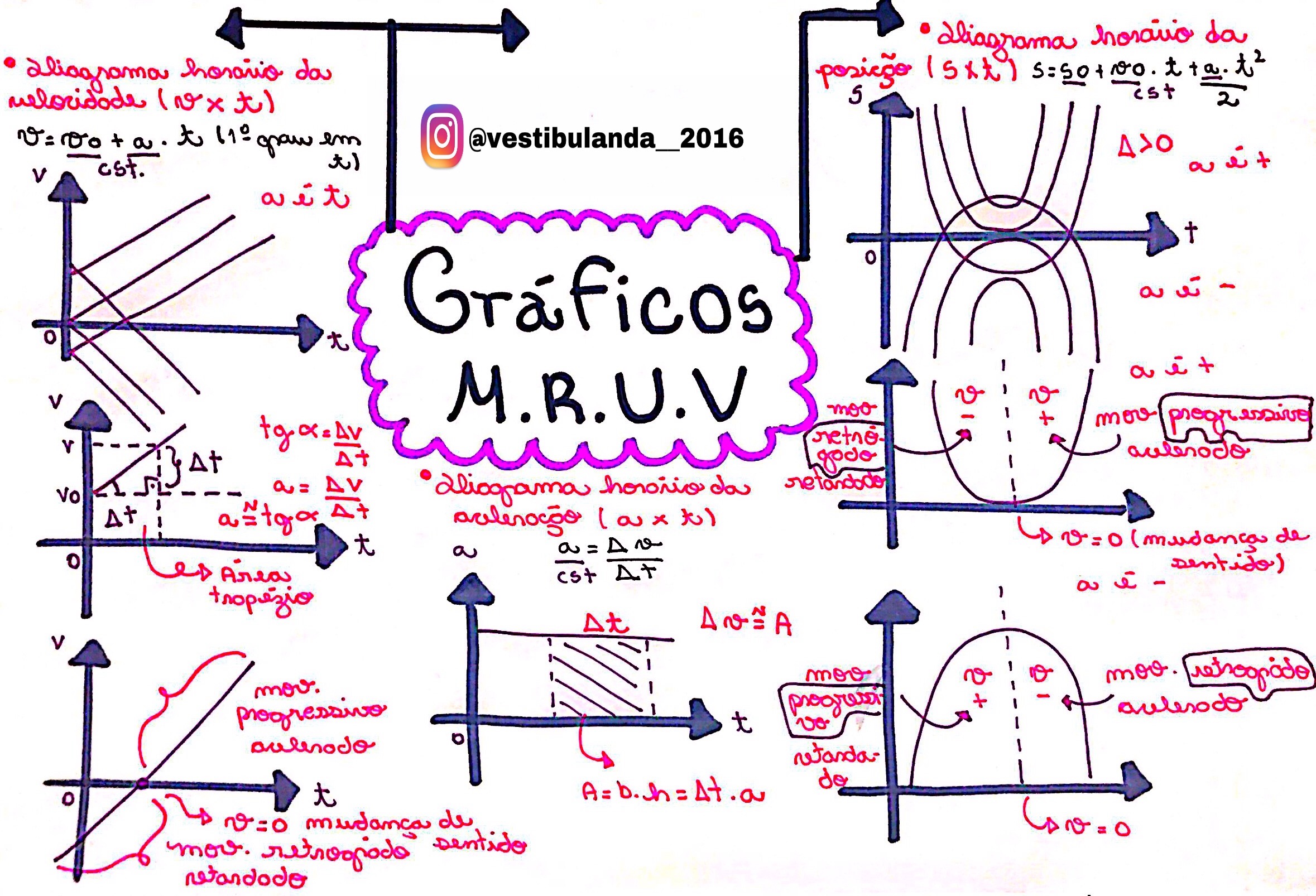
ENEM Mapa Mental Gráficos M R U V Física
The normal unit vector will be n^(x, y, z) =n^(φ(u, v)) = φu(u, v) ×φv(u, v) ∥φu(u, v) ×φv(u, v)∥ n ^ ( x, y, z) = n ^ ( φ ( u, v)) = φ u ( u, v) × φ v ( u, v) ‖ φ u ( u, v) × φ v ( u, v) ‖ but if you use the same parameterization to transform the surface integral to a 2d integral you get
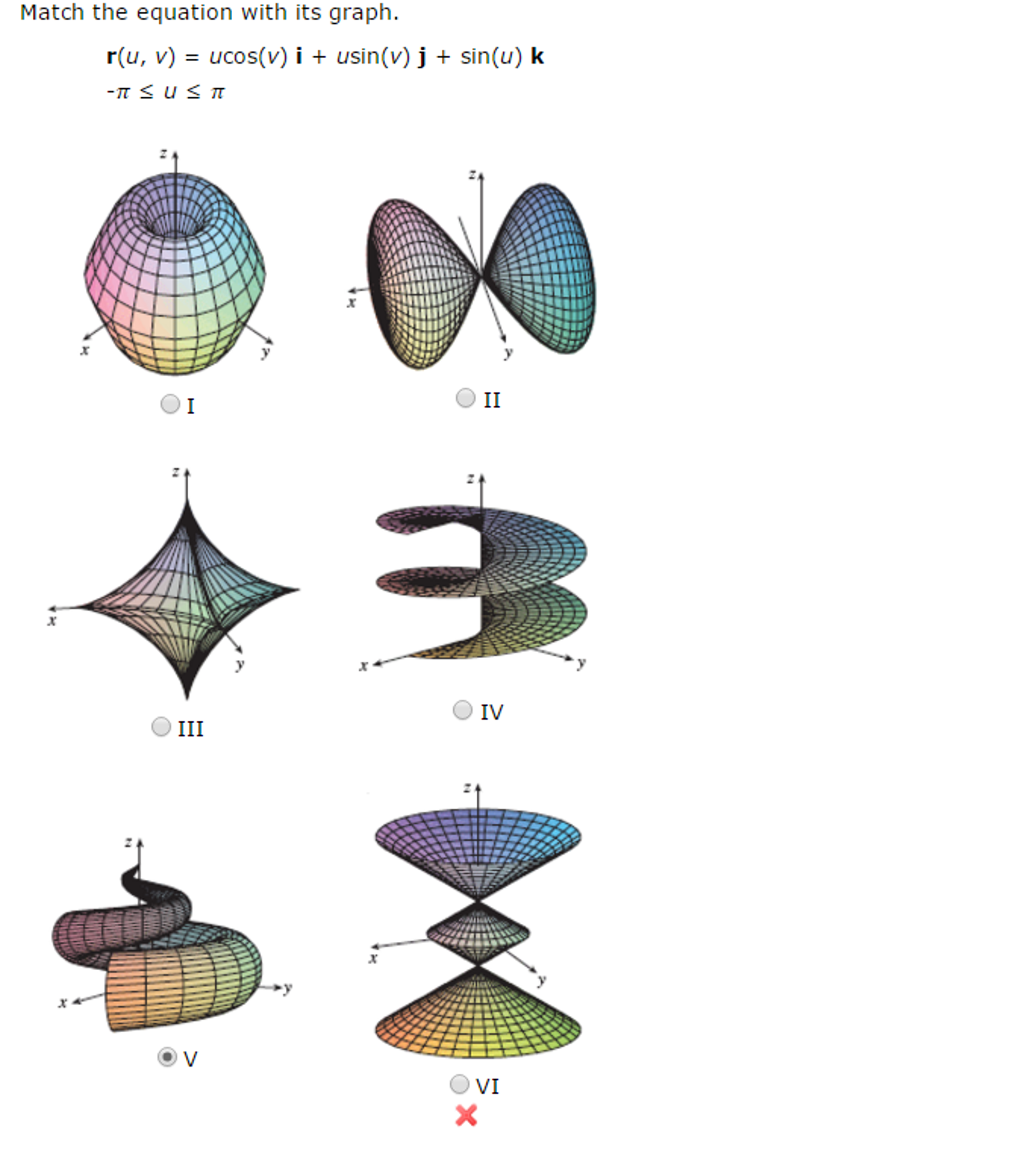
Solved Match the equation with its graph. r(u, v) = u
Suppose that r( u,v) is a regular parametrization of a surface. Since the crossproduct r u ×r v is orthogonal to both r u and r v, the vector r u ×r v is normal to the surface at r( u,v) . It follows that the unit vector

M.R.U.V / PARTE 2 YouTube
The parameterized surface is a vector valued function r ( u, v) of two variables, whether written in ijk vector notation or as an ordered triple of functions of u and v. Since each of the variables u and v ranges over an interval, the domain for r ( u, v) is a coordinate rectangle, say [ a, b ] x [ c, d ], in the uv -plane.
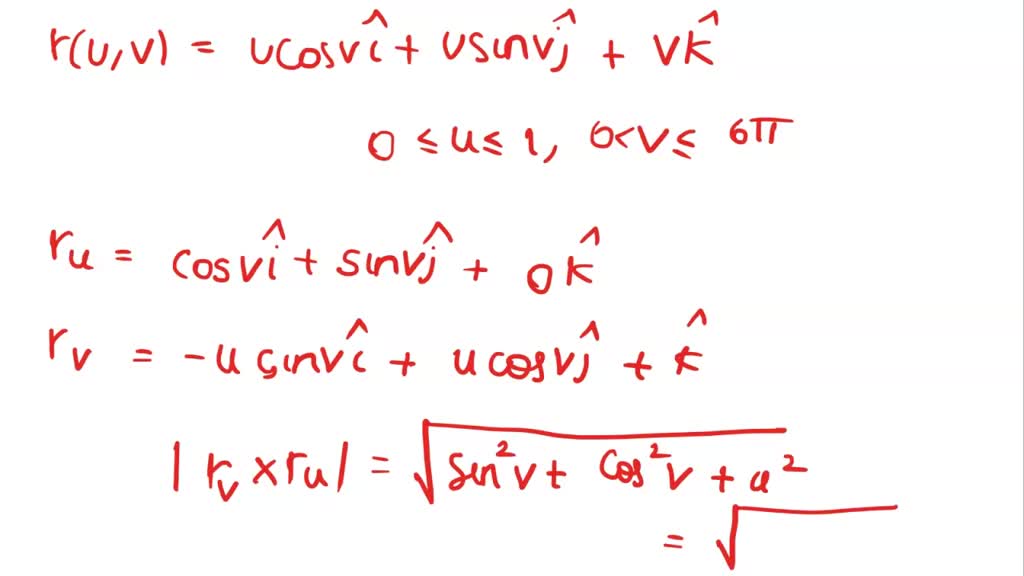
SOLVED point) The vector equation r (u, v) u COS vi + usin vj + vk; 0
Standard Parameterized Surfaces Planes The plane through a point with has parametric equation r(u, v) = r0 + uu + vv, u, v 2 R The grid lines are parallel to u, v. Equivalent vector. The blue lines in the picture are the grid lines with u = 0, u = 1 and u = 2 respectively. The orange lines are v = 0, v = 1 and v = 2.
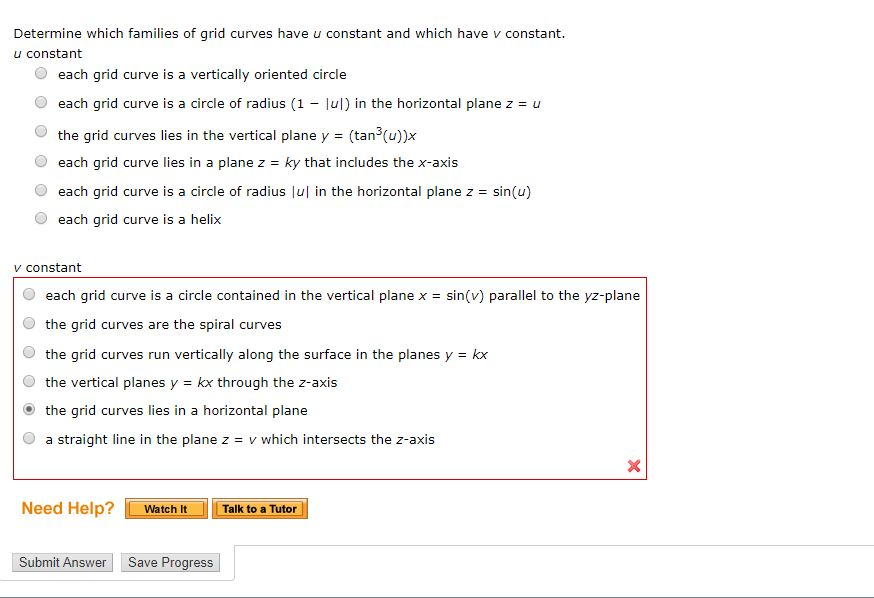
Solved Match the equation with its graph r(u, v) = sin(v) i
RÚV.is - RÚV okkar allra. Efstaleiti 1. 103 Reykjavík. Sími: 515-3000
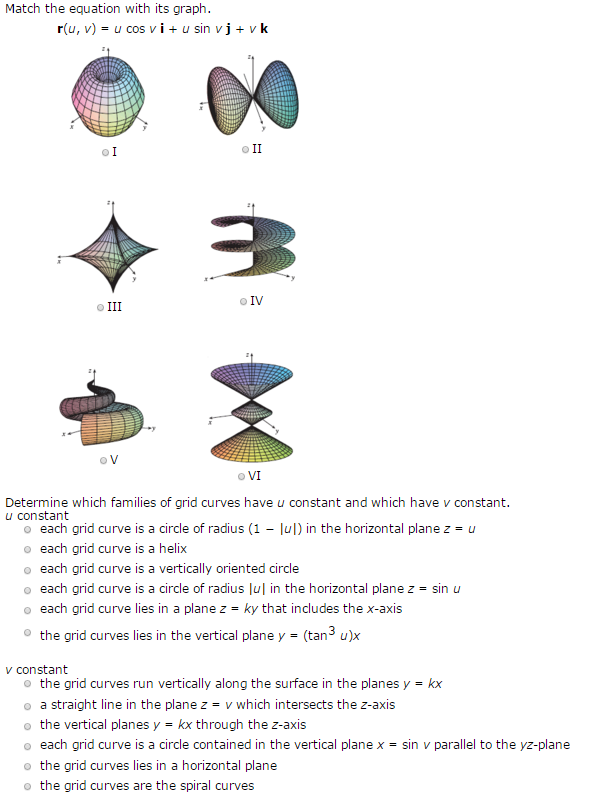
Match The Equation With Its Graph. R(u, V) = U Cos...
Summary. This update automatically applies Safe OS Dynamic Update to the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) on a running PC to address a security vulnerability that could allow attackers to bypass BitLocker encryption by using WinRE. For more information, see CVE-2024-20666.