Megakaryocyte number and myeloid erythroid ratio in intact control... Download Table
Acute myeloid leukemia with expanded erythropoiesis Haematologica
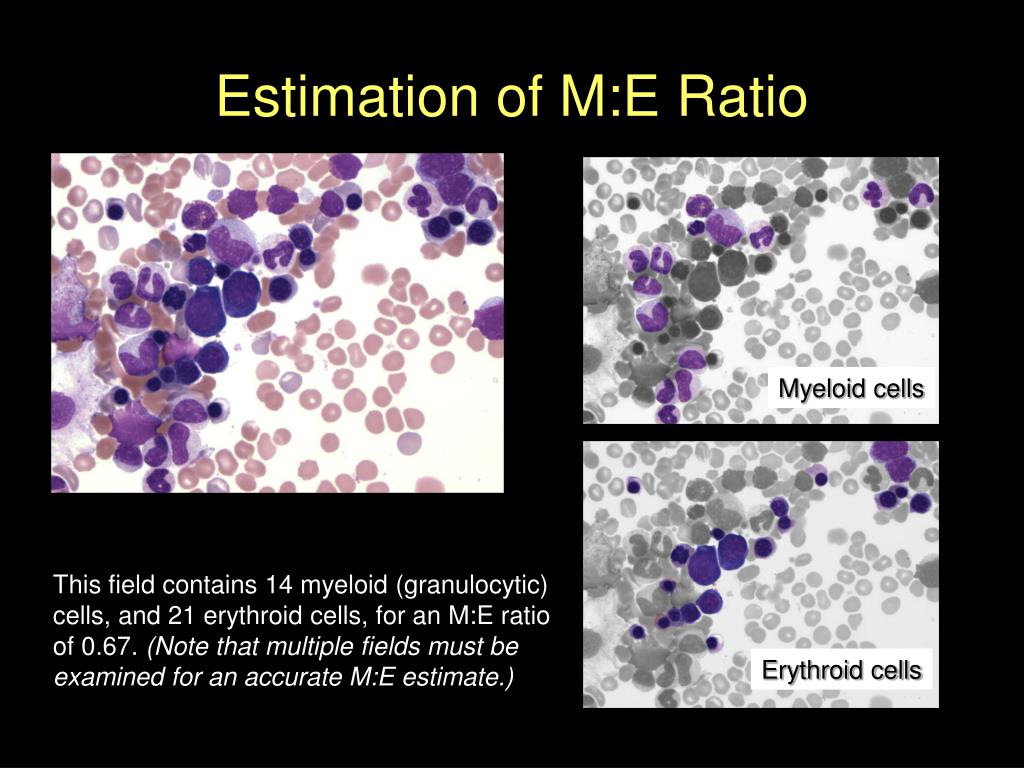
7 Estimation of myeloid:erythroid ratio comparing granulocytes and erythroid precursors.. Erythroid, myeloid, and/or megakaryocytic hypoplasia are terms applied to the situation in which there are fewer precursor cells than appropriate for the number of mature cells in peripheral blood. For example, the absence of erythroid hyperplasia in an.

Myeloid to erythroid ratio (ME ratio) presented as mean and... Download Scientific Diagram
Hematopoietic components Bone marrow aspirate showing normal "trilineage hematopoiesis": myelomonocytic cells (an eosinophil myelocyte marked), erythroid cells (an orthochromatic erythroblast marked), and megakaryocytic cells
Dentistry and Medicine CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA
Summary Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (aCML) is a blood and bone marrow cancer. A person with aCML has a disorder in the bone marrow cells responsible for producing blood cells, but doctors.
PPT Bone Marrow Evaluation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID671342
An estimation of general hematopoietic activity and the myeloid/erythroid ratio can also be performed. The erythroid elements are smaller with round, dense, and deeply basophilic nuclei . The cytoplasm is basophilic in the blast forms with increasing eosinophilia as they mature.

Megakaryocyte number and myeloid erythroid ratio in intact control... Download Table
Normal M:E Ratio The normal M:E ratio in adults varies from 1.2:1 to 5:1 myeloid cells to nucleated erythroid cells. An increased M:E ratio (6:1) may be seen in infection, chronic myelogenous leukemia or erythroid hypoplasia. A decreased M:E ratio (<1.2-1) may mean a decrease in granulocytes or an increase in erythroid cells.

Fat , Myeloid , Erythroid cell ratio in bone marrow (*) FaME Bone Marrow Cells, Hematology
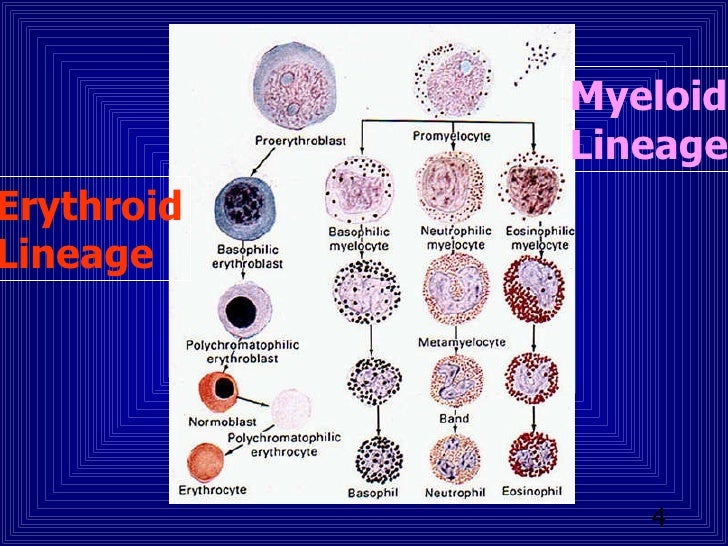
The normal myeloid:erythroid ratio in mice ranges from 0.8 to 2.8:1 (average, 1.5:1), 37 and age and strain must be considered during comparative analyses. The nuclei and cytoplasm should mature together, asynchronous maturation is abnormal, and cellular maturation should be complete and orderly for all lineages.
Rbc
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of myeloid neoplasms that are often difficult to diagnose due to their pathologic and clinical heterogeneity. The key features of MDS are peripheral blood cytopenias, ineffective hematopoiesis manifesting as morphologic dysplasia, and clonal genetic abnormalities.

PPT Myeloproliferative Disorder PowerPoint Presentation ID3066493
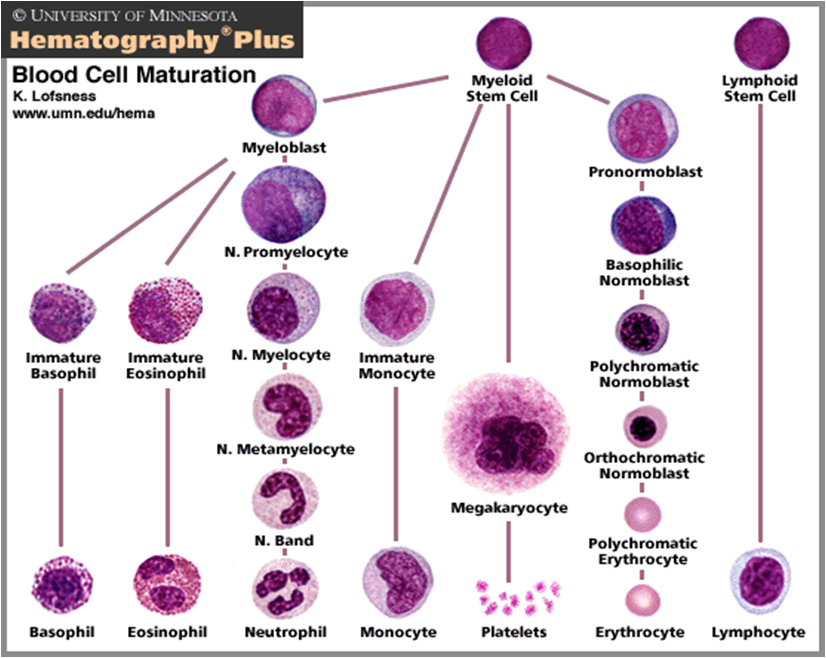
Myeloid cells: Normal or abnormal maturation Indicate if excess blasts Abnormal localization of immature precursors Erythroid cell: Normal or abnormal maturation Provide differential of myeloid and erythroid elements, based on counting 200 - 500 cells in aspirate smear Megakaryocytes: Normal or abnormal numbers and morphology Lymphocytes:

Advances in understanding erythropoiesis evolving perspectives Nandakumar 2016 British
What is being tested? Bone marrow is the soft and sponge-like tissue found inside the body's larger bones that produces blood cells. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are procedures used to collect and evaluate bone marrow cells and structure.

Thread by 4theLoveofPath Instead of my normal GTScase, I wanted to look at the morphology of
Introduction The bone marrow is the largest primary lymphoid organ and is one location of antigen-independent lymphocyte development. It is also a secondary lymphoid organ because terminal antigen-induced lymphoid cell differentiation occurs within its microenvironment ( Tavassoli and Yoffey, 1983 ).

Erythroid, myeloid, and lymphoid cells developed from EML C1. (A) EML... Download Scientific
Marrow aspirate specimen with a myeloid/erythroid ratio (M/E ratio) of 1:1-2, typical for a patient with a hemolytic anemia or one recovering from blood loss. View Full Size | | Download Slide (.ppt) + + FIGURE A6-6. Myeloid hyperplasia of the marrow. Marrow aspirate specimen showing a myeloid/erythroid ratio of ≥3:1, suggesting either a.

The Site of Bone Marrow Acquisition Affects the Myeloid to Erythroid Ratio in Apparently Healthy
Myeloid and erythroid cells: With myeloid and erythroid precursors, we do the following: 1) Assess for complete and balanced maturation, 2) Calculate a myeloid to erythroid ratio, 3) Evaluate morphologic features and 4) Look at cell proportions.

Erythroid Lineage Cells in the Liver Novel Immune Regulators and Beyond
Interestingly, a peculiarly normal cellularity and myeloid-to-erythroid (M:E) ratio was reported in seven (50%) and 11 (84.6%) out of the 14 and 13 patients with reported data, respectively. Moreover, megakaryocytes were small in 10 patients (71.4%), pleomorphic in three patients (21.4%), and dysplastic in a single patient (7.1%), respectively.

myeloid erythroid ratio Ratio, Image, Map
Myeloid:erythroid ratio | definition of myeloid:erythroid ratio by Medical dictionary Myeloid:erythroid ratio | definition of myeloid:erythroid ratio by Medical dictionary https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/myeloid%3aerythroid+ratio Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free Dictionary 13,715,621,931 visits served

Myeloid to erythroid ratio eClinpath
Myeloid to erythroid ratio By Tracy Stokol / January 1, 2019 In a normal bone marrow, there is an approximately 1:1 (ranging from 0.7:1 to 2:1) ratio of myeloid (M) to erythroid (E) progenitors in marrow (Wright's stain, 50x objective)

Myeloid to Erythroid ratio.... Normal is 31 Hematology, Pathology, Bone marrow
The early myeloid progenitors are localized in the paratrabecular areas close to the adventitia of the small arteries. Normally, the layer of immature granulocytes does not exceed 2-3 rows of maturing cells. With maturation, the cells migrate to the intertrabecular spaces.