23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy & Physiology

AN3 08 Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, Swallowing StudyBlue
The mouth, also called the oral cavity, is the opening in the human skull that allows food, liquids, and air to enter the body. The oral cavity begins at the lips and ends at the throat..

Diagram of the oral cavity Telegraph
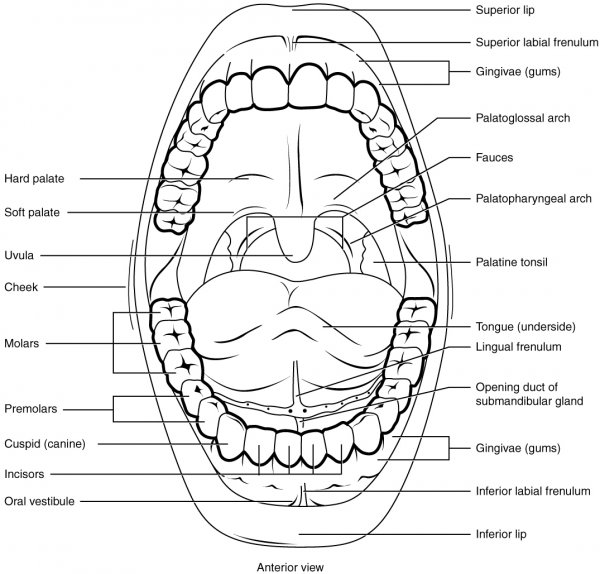
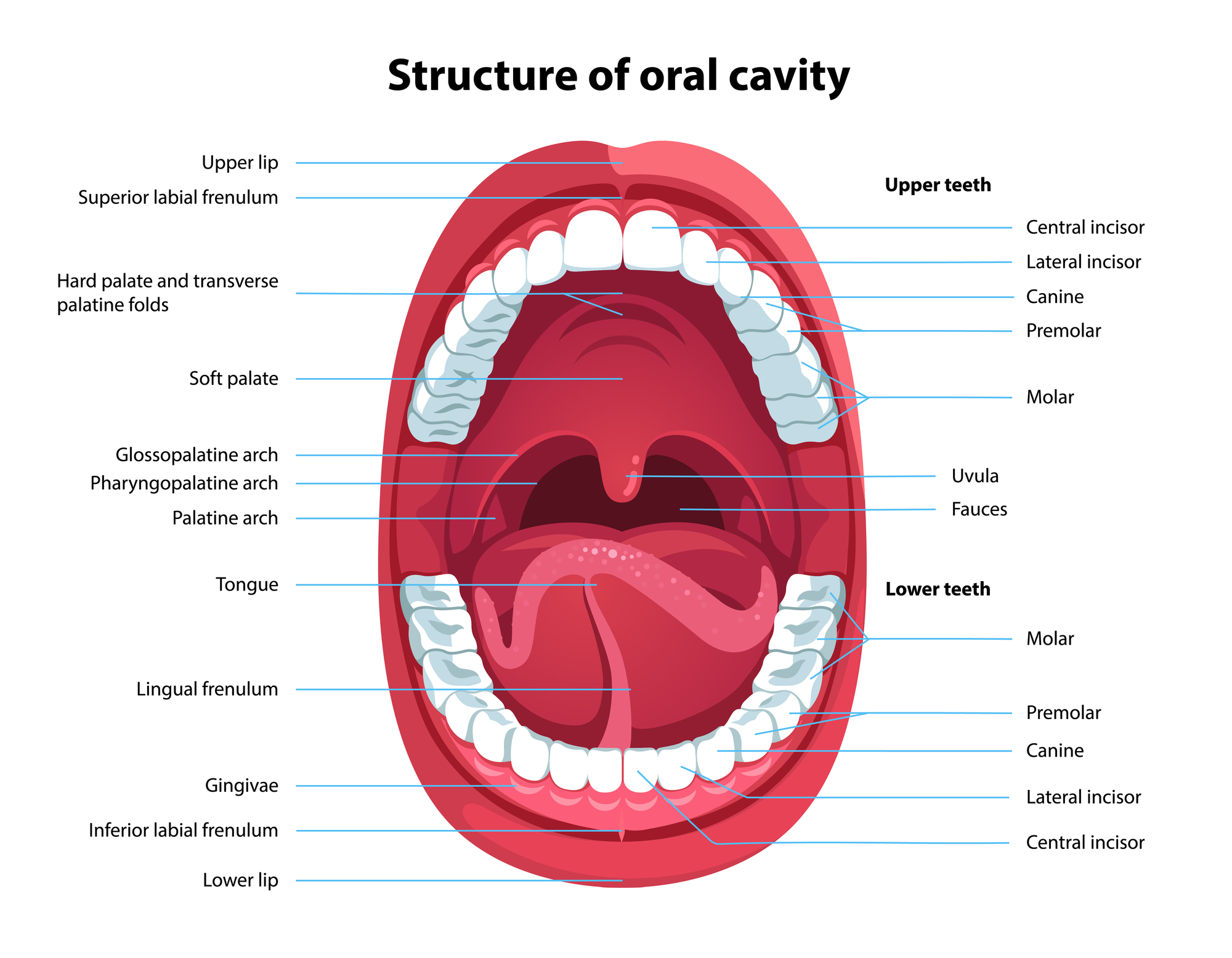
The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). The structures of the mouth are illustrated in Figure 23.3.1. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper.
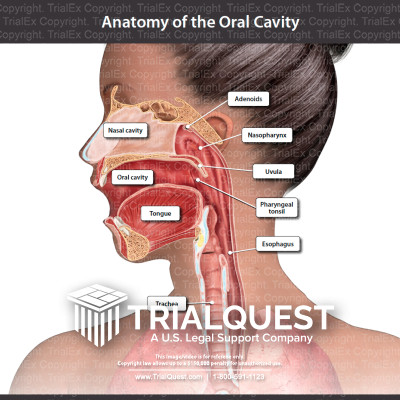
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity TrialExhibits Inc.
The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). The structures of the mouth are illustrated in. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper.

Diagram Of The Oral Cavity Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
The oral cavity, also known as the mouth, is the most proximal portion of the aerodigestive tract, and is continuous posteriorly with the oropharynx . Gross anatomy Boundaries The oral cavity includes the lips anteriorly.

Schematic drawing of the oral cavity [97]. Download Scientific Diagram
Oral Cavity. Above: Anatomy of the oral cavity. The oral cavity is the entry point into the digestive system. It is equipped with teeth and a tongue to grind up and break apart foodstuffs to begin physical digestion. Chemical digestion also begins in the mouth with enzymes produced and secreted by three pairs (right and left) of salivary glands.
Oral Cavity Anatomy, Functions, and Diseases Medical Library
oral cavity or buccal cavity Key People: Johann Christian Fabricius Related Topics: tooth tongue salivary gland palate lips mouth, in human anatomy, orifice through which food and air enter the body.

THE ORAL CAVITY PRESENTATION by Dee Geezy
Oral cavity Anatomy of the mouth. Floor of the mouth with lingual frenum and sublingual fold The mouth consists of two regions: the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks. [3]

23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction. This e-Anatomy module contains 110 illustrations on the oral cavity, the mouth, the tongue and the salivary glands. These fully annotated anatomical illustrations are presented as a comprehensive atlas of the oral cavity, specially designed for medical students, medicine residents and healthcare professionals.

Other articles where Soft palate is discussed palate The soft palate
Mouth Mouth Your mouth is part of your digestive and respiratory systems. It helps you with daily functions like eating, speaking and breathing. Taking care of your mouth can keep you healthy and reduce your risk for a wide range of dental and medical conditions.

DIAGRAM General Structures of the Oral Cavity Diagram Quizlet
The oral cavity, better known as the mouth, is the start of the alimentary canal. It has three major functions: Digestion - receives food, preparing it for digestion in the stomach and small intestine. Communication - modifies the sound produced in the larynx to create a range of sounds.
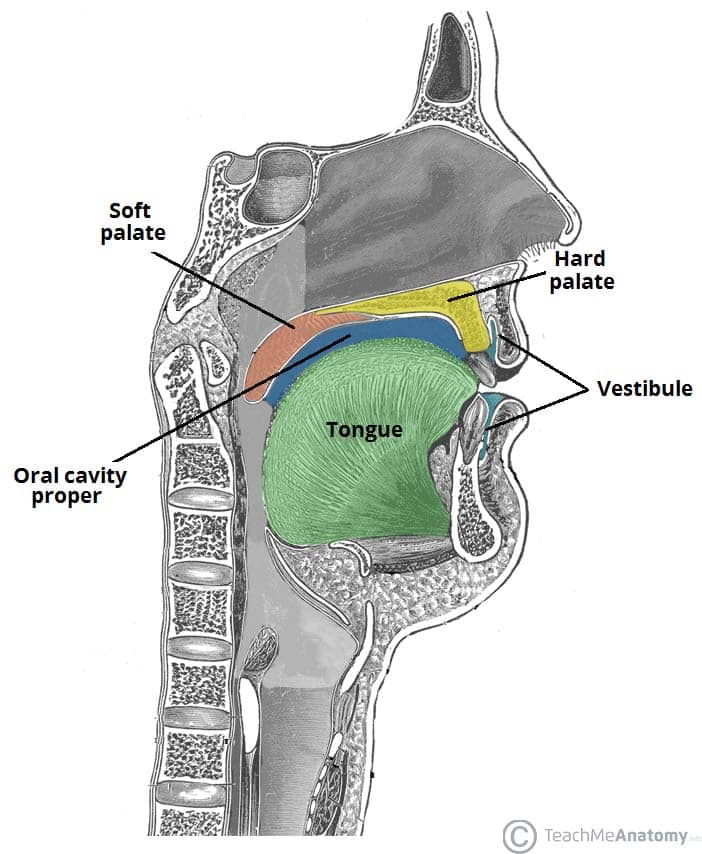
The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation TeachMeAnatomy
Figure 1.1 Diagram illustrating the anatomy and main structures of the oral cavity. (Modified from Tortora, G.J. & Grabowski, S.R. 2000. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 9 th edition, Wiley, New York. Reproduced by permission of John Wiley & Sons.)

Detailed mouth anatomy
Mouth Diagram The mouth is also known as the buccal cavity or oral cavity. It includes the lips, cheeks and palate. It also encloses the tongue, teeth and salivary glands. The mouth anteriorly opens outside via the lips and posteriorly opens via the fauces (throat) into the pharynx.
PPT Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx & Oesophagus PowerPoint
Anatomy. Under normal circumstances, the tongue is a pink, muscular organ located within the oral cavity proper. It is kept moist by the products of the major and minor salivary glands, which aids the organ as it facilitates deglutition, speech, and gustatory perception.While there is significant variability in the length of the tongue among individuals, on average, the organ is roughly 10 cm.
What Are the 3 Key Functions of the Teeth? Vancouver Centre for
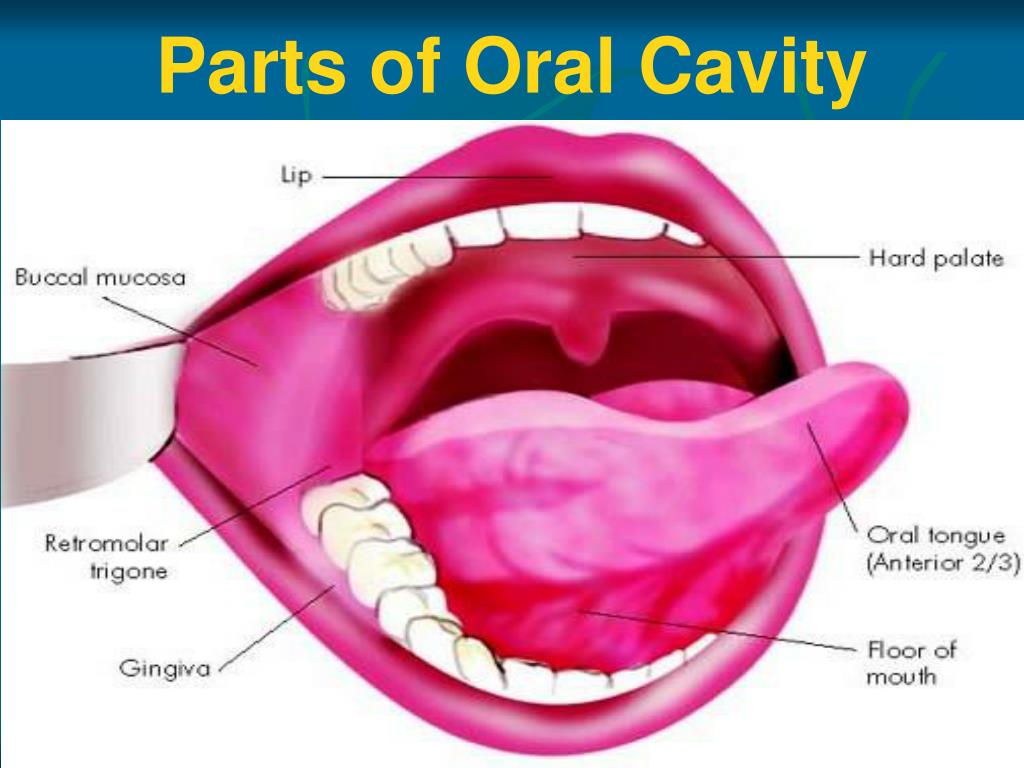
The oral cavity encompasses several relatively discrete regions. These include the hard palate, floor of the mouth, buccal mucosa including the upper and lower gingivobuccal sulci, retromolar trigone, and anterior two thirds or oral portion of the tongue and lips ( Figs. 190.2 - 190.5 and 196.1 ).

Pin on Anatomy
The mouth is made up of the teeth, tongue, hard palate, and soft palate. The oral cavity is bounded by the teeth, tongue, hard palate, and soft palate. These structures make up the mouth and play a key role in the first step of digestion: ingestion. This is where the teeth and tongue work with salivary glands to break down food into small.

What is the Oral Cavity
Salivary Glands There are three major paired salivary glands: the parotid, submandibular (submaxillary), and sublingual glands [5]. The vestibule area receives the secretion from the parotid glands [7], while the submandibular and sublingual glands open into the oral cavity proper [10].