Science of vision How do our eyes enable us to see? How It Works Magazine
The Lens Of The Eye YouTube
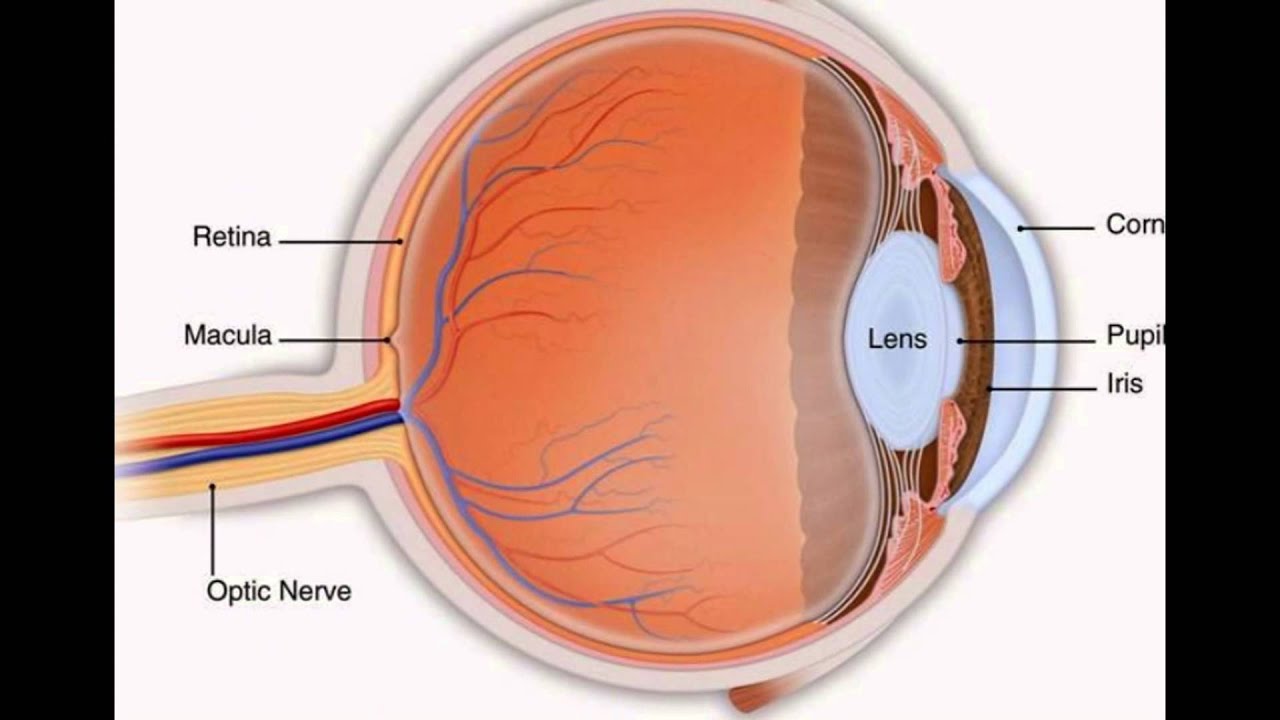
Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Iris. The colored part of the eye. The iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. Lens (also called crystalline lens). The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. Lower eyelid.
FileThe human eye.JPG Wikimedia Commons
Browse 6,269 back of the eye photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more photos and images. NEXT Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Back Of The Eye stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Back Of The Eye stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs.
How Do We See Light? Ask A Biologist
Browse 9,400+ human eye anatomy stock photos and images available, or search for vision or retina to find more great stock photos and pictures. vision retina human eye structure eye chart human eyeball eye doctor eye diagram cataract retinopathy pancreas Sort by: Most popular Anatomy of human eye and descriptions. Components of human eye.
What is the Optic Disc? (with pictures)
The iris (colored part) of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera, controlling the amount of light reaching the retina by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil (aperture). The eye's crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light rays.
Inflammatory Arthritis and Eye Health Prevention, Symptoms, Treatment
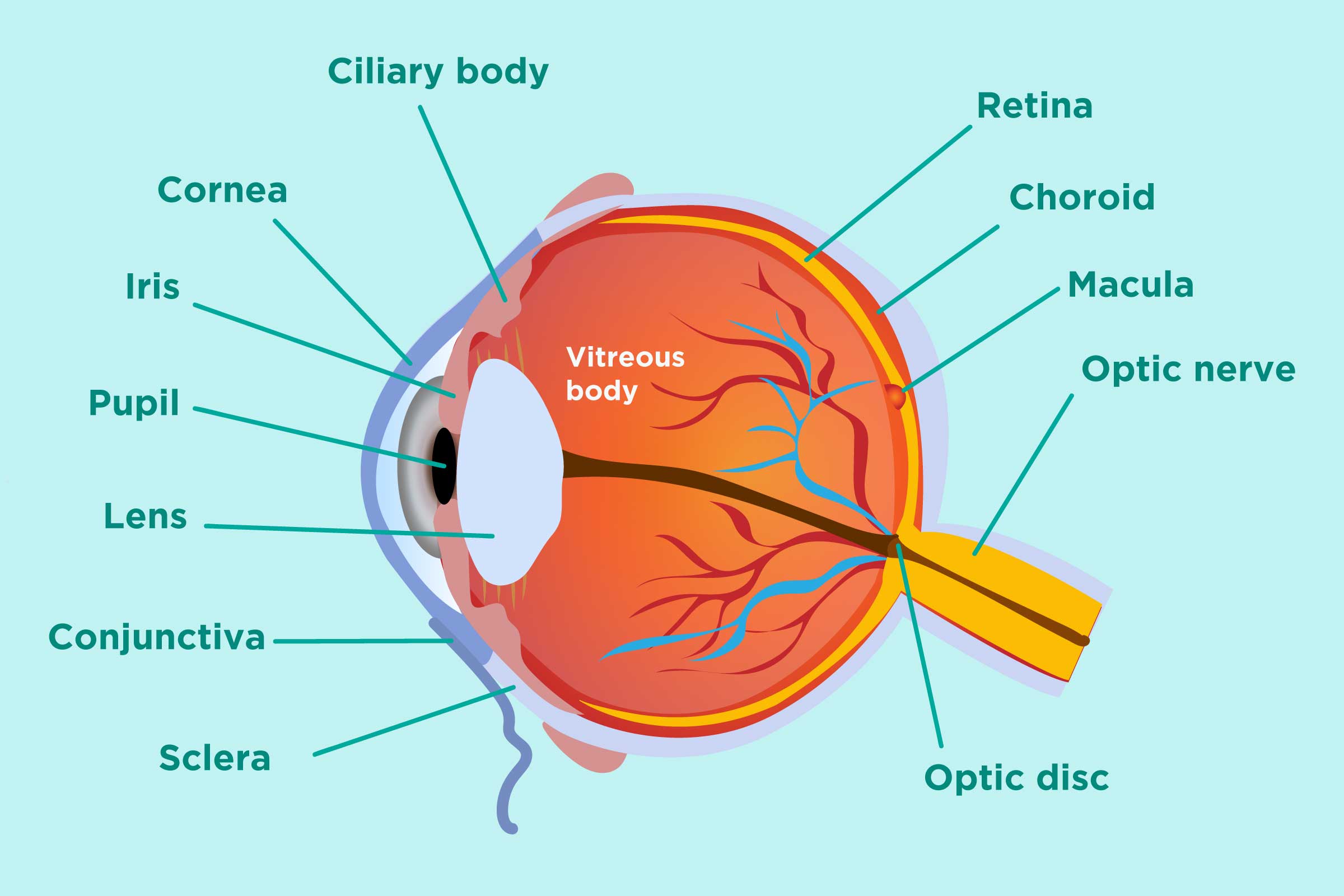
1. Conjunctiva The conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). The conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. Conjunctivitis, often known as pink eye, occurs when this thin membrane becomes inflamed or swollen. Other eye disorders that affect the conjunctiva include:
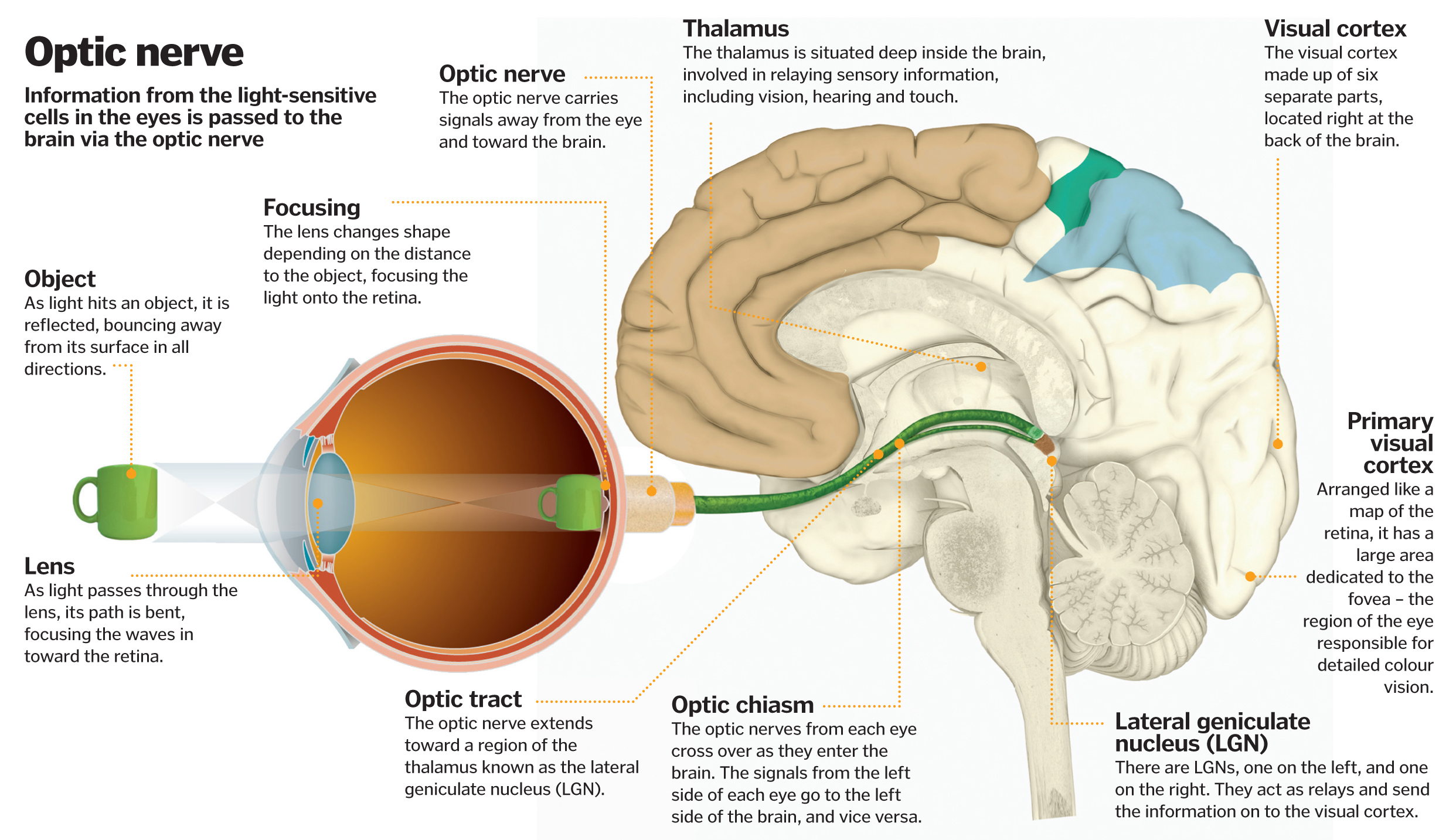
Science of vision How do our eyes enable us to see? How It Works Magazine
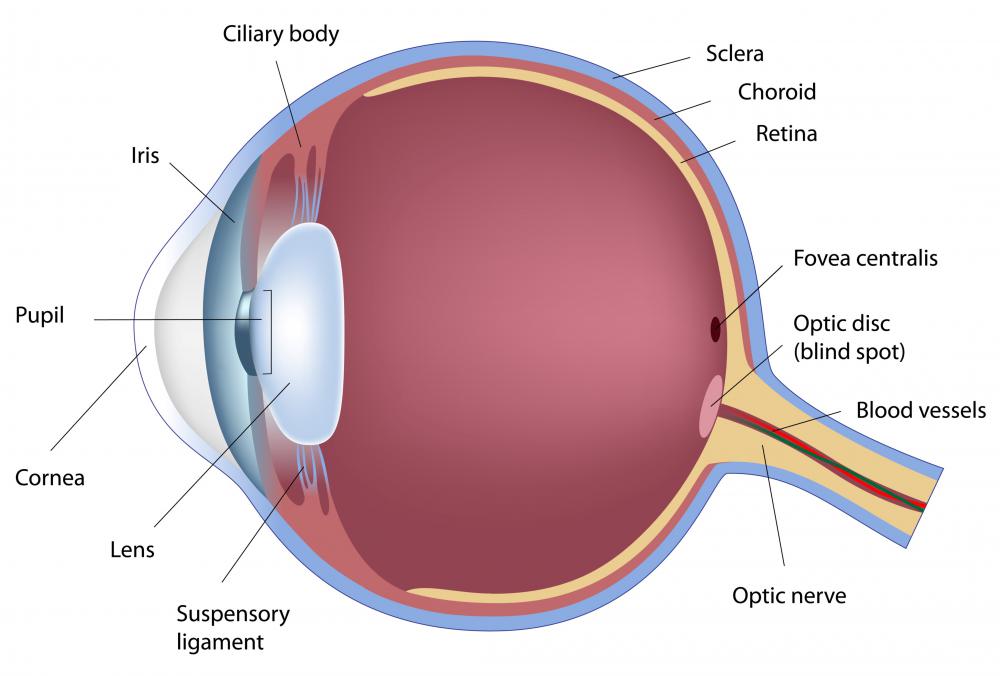
Mayo Clinic Overview Parts of the eye Enlarge image Retinal diseases vary widely, but most of them cause visual symptoms. Retinal diseases can affect any part of your retina, a thin layer of tissue on the inside back wall of your eye.

Eye Rolled Back Stock by HaleyOfTheFlame on DeviantArt
A choroidal nevus is a freckle located on the back or inner part of your eye. The choroid is part of the uvea, which is the pigmented part of your eye and includes the iris. The choroid falls between the sclera and the cornea. There's such a thing as an amelanotic choroidal nevus, which simply means that the spot is very light in color.
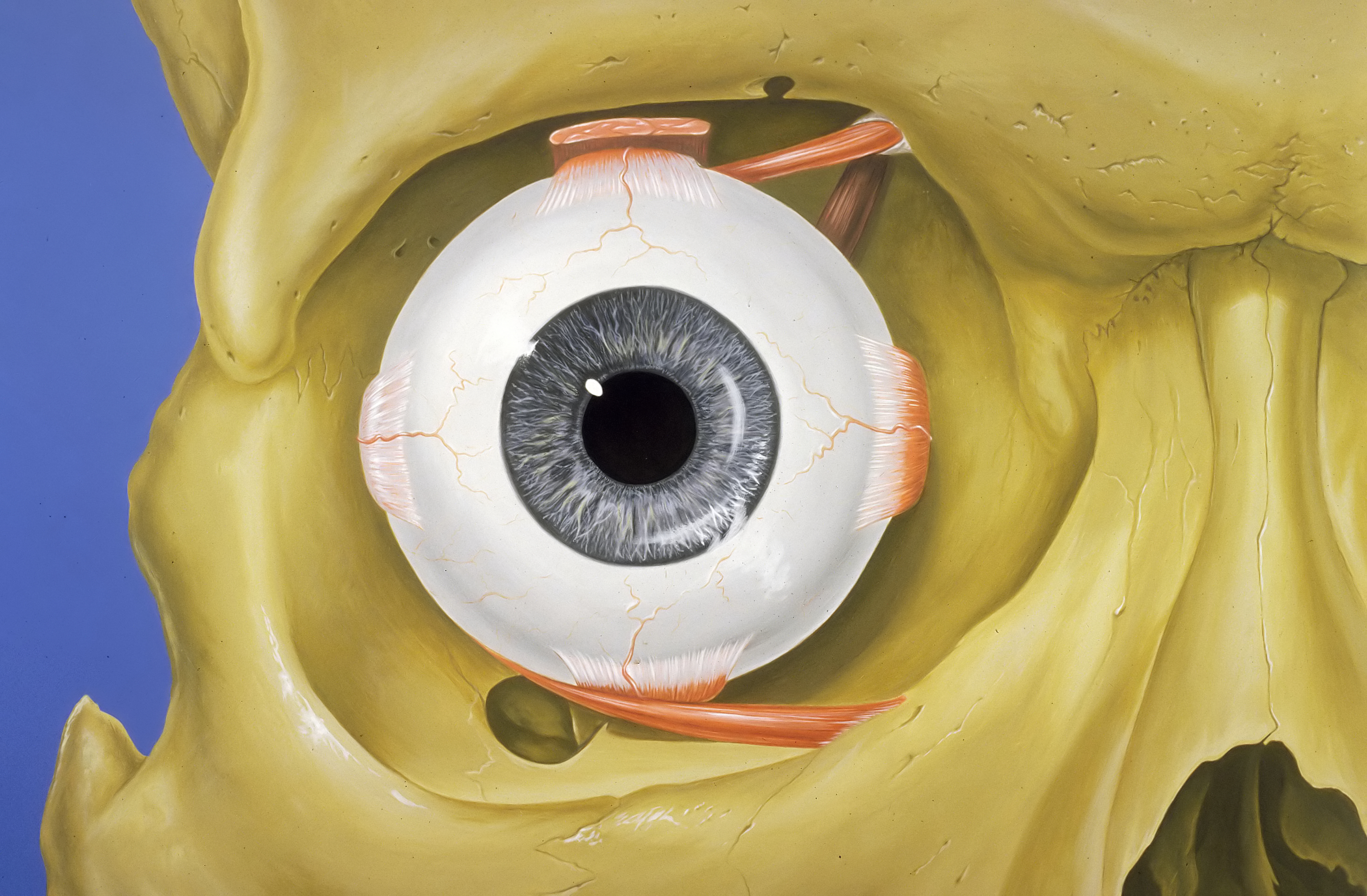
FileEye orbit anatomy anterior2.jpg Wikimedia Commons
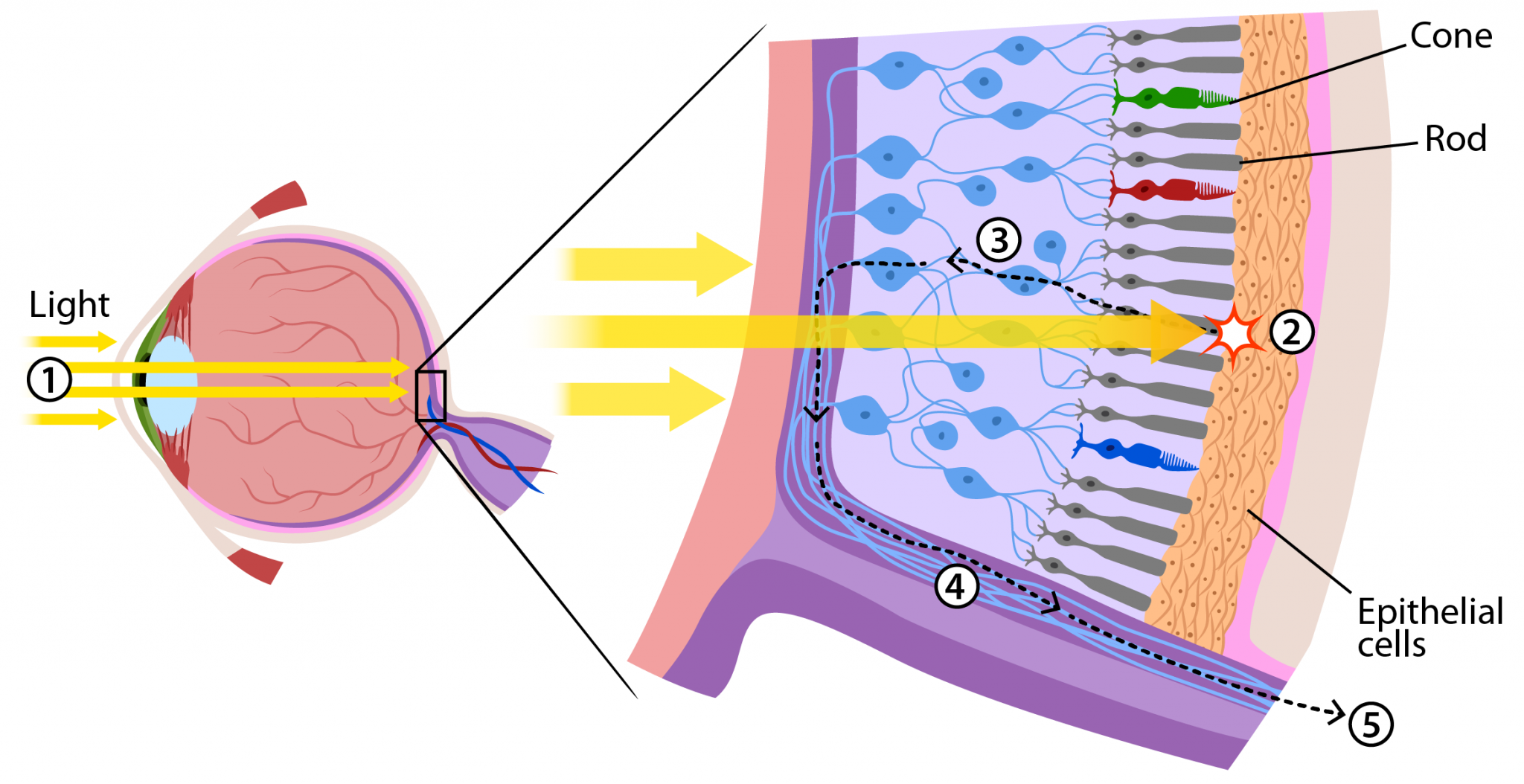
Eye Anatomy: The Back of the Eye Dr. Russel Lazarus, October 11, 2020 Did you know that the back of the eye is responsible for transferring visual information from the eye to the brain? In order to see clearly, light is focused onto the back of your eye where it is transformed into electrical impulses.

How Your Eye Works Optometry in Denver Optical Masters
3 min read Retinal imaging takes a digital picture of the back of your eye. It shows the retina (where light and images hit), the optic disc (a spot on the retina that holds the optic nerve,.
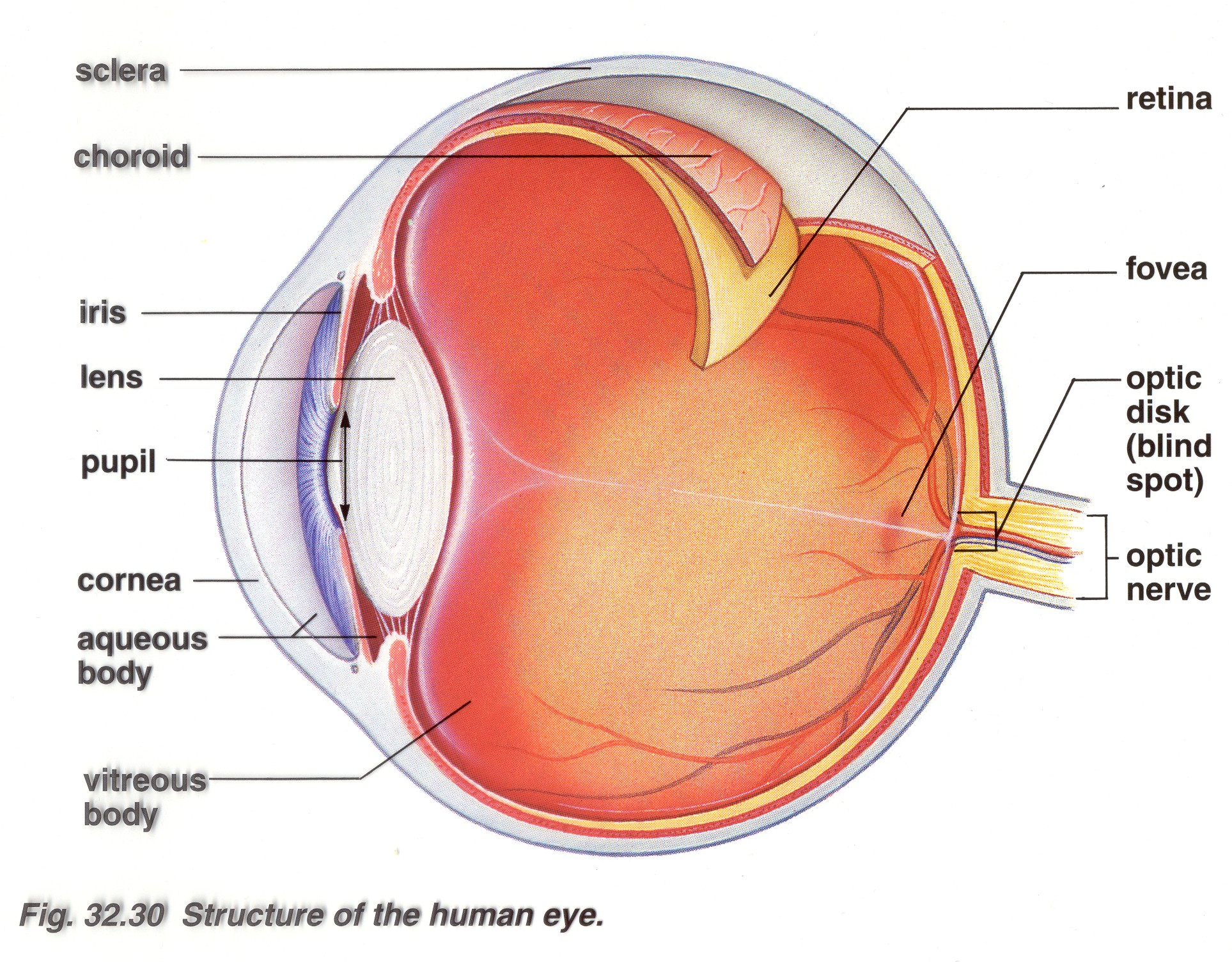
Brain Post How Big is Your Blind Spot? SnowBrains
Search from Back Of The Eye stock photos, pictures and royalty-free images from iStock. Find high-quality stock photos that you won't find anywhere else.
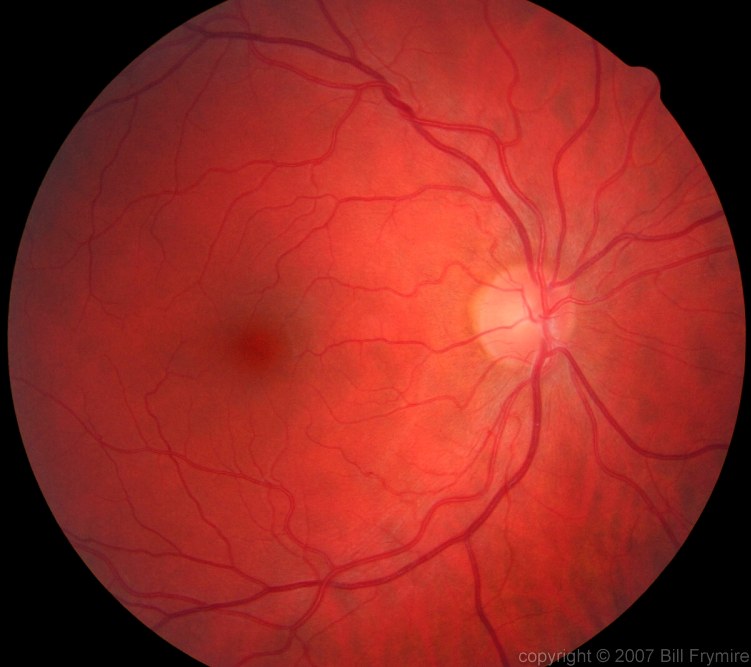
Looking at the back of a retina Image of the Week Bill FrymireBill Frymire
With OCT, a machine scans the back of your eye. This provides very detailed pictures of the retina and macula. Your ophthalmologist studies these pictures to check for problems.
ArtStation Eye anatomy photorealistic eyeball Resources
Muscles in the iris dilate (widen) or constrict (narrow) the pupil to control the amount of light reaching the back of the eye. Directly behind the pupil sits the lens. The lens focuses light toward the back of the eye. The lens changes shape to help the eye focus on objects up close.
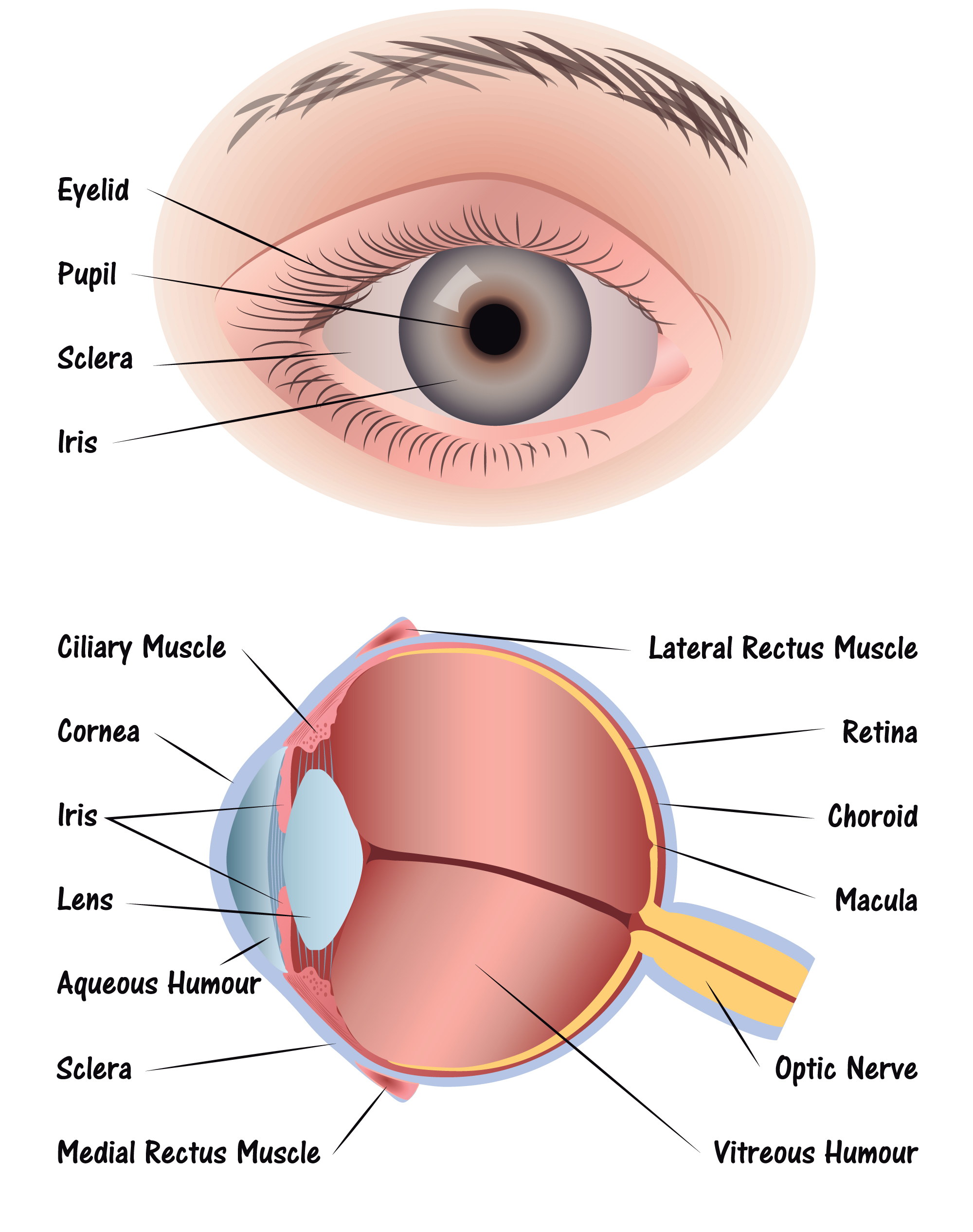
eye diagram Discovery Eye Foundation
Optical coherence tomography, or OCT, is an imaging method used to generate a picture of the back of your eye, called your retina. The noninvasive method produces an image by measuring the amount of a dim red light that reflects off of your retina and optic nerve.

Eye Anatomy
The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. Located near the optic nerve, it receives light and sends pictures to the brain of what the eye sees. As we age, the vitreous gel, a clear jelly-like substance that fills most of the eye's interior, begins to break down, shrink, and pull away from the retina..

Internal Anatomy Of The Eye Labeled Life Educations
Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a thin layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from its normal position. Retinal detachment separates the retinal cells from the layer of blood vessels that provides oxygen and nourishment to the eye. The longer retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater.
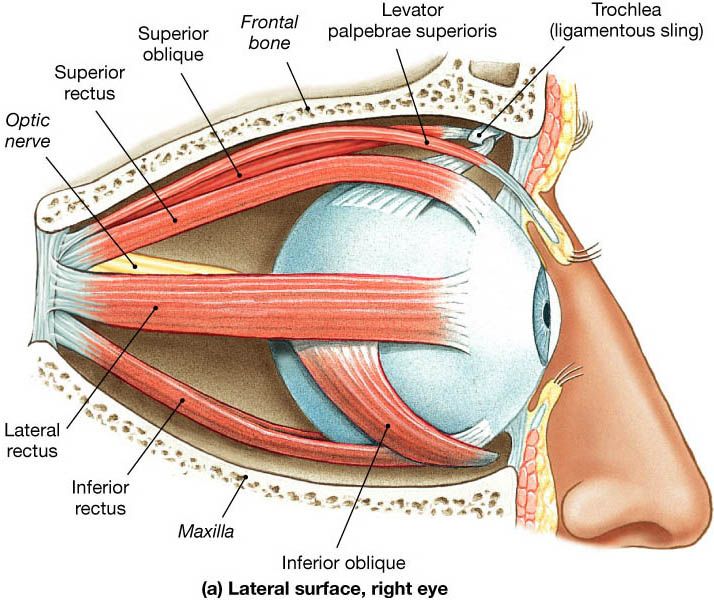
=== Vision disorders
Symptoms. Eye melanoma may not cause signs and symptoms. When they do occur, signs and symptoms of eye melanoma can include: A sensation of flashes or specks of dust in your vision (floaters) A growing dark spot on the iris. A change in the shape of the dark circle (pupil) at the center of your eye. Poor or blurry vision in one eye.