How to use the VLOOKUP function

Vlookup function with 'false' YouTube
Vlookup is a crucial function for working with data in spreadsheets. Understanding true and false in vlookup is essential for accurate results. Using true in vlookup allows for an approximate match, while false requires an exact match. Common mistakes include mixing up true and false and not understanding the difference.
Google Sheet Tutorial VLOOKUP TRUE & FALSE Function YouTube
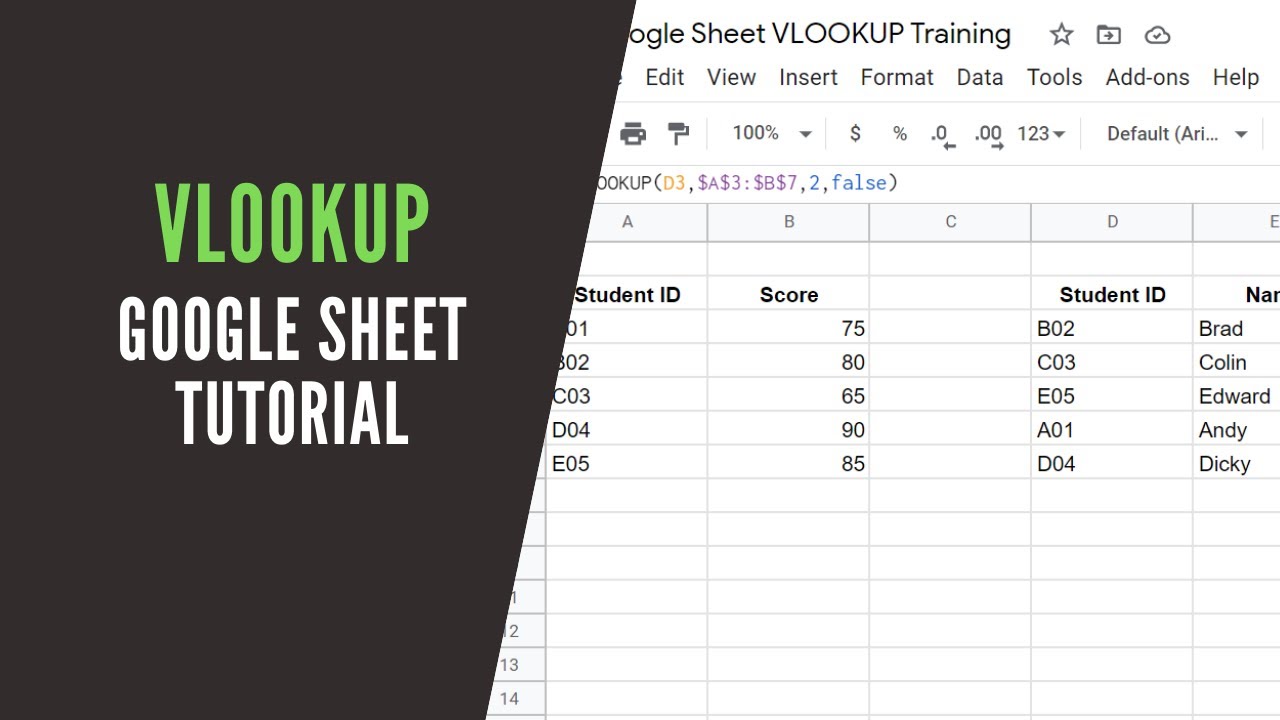
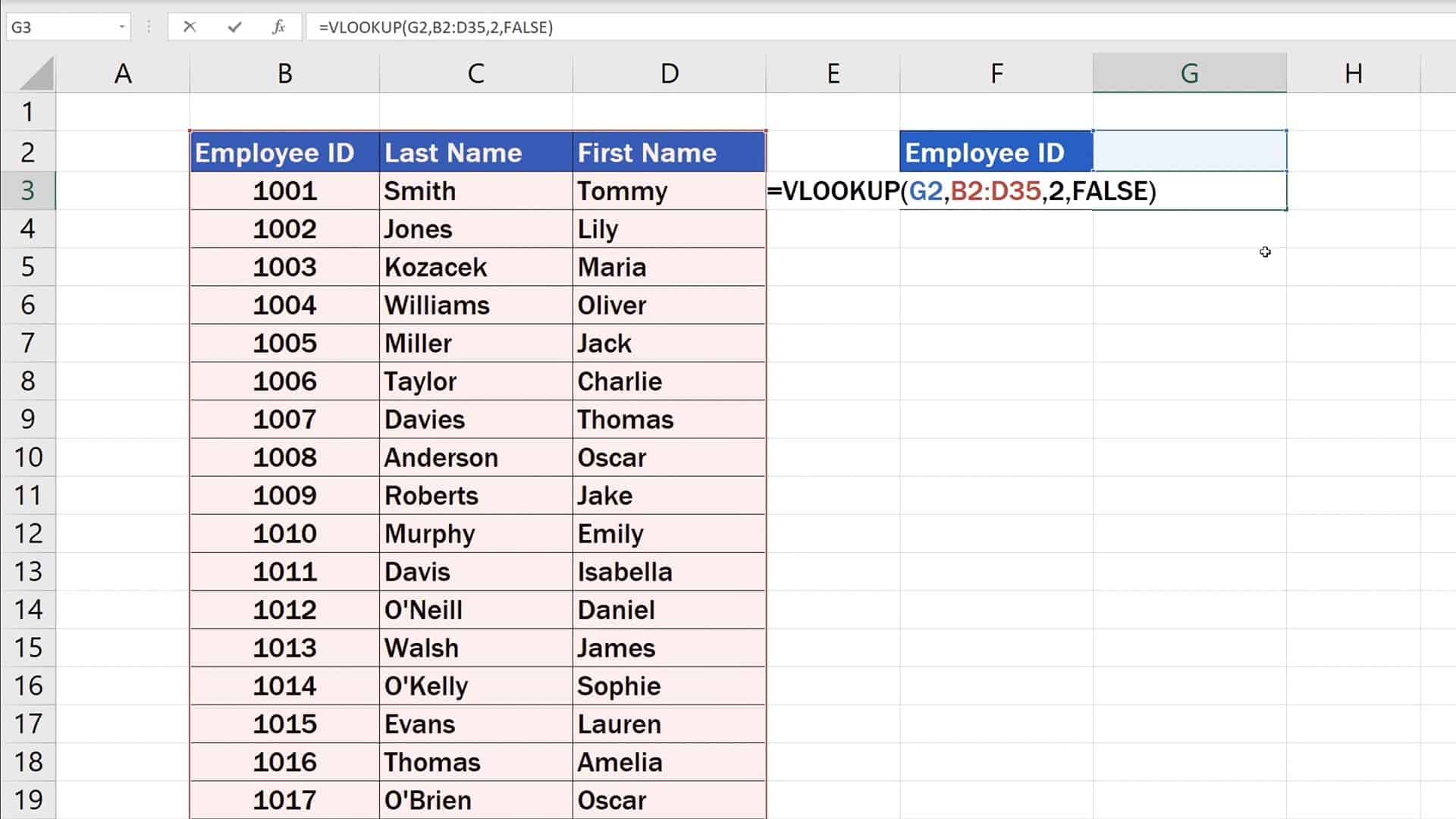
VLOOKUP(E1, A5:B11, 2, FALSE) How to Vlookup and return multiple values in Excel. The Excel VLOOKUP function is designed to return just one match. Is there a way to Vlookup multiple instances? Yes, there is, though not an easy one. This requires a combined use of several functions such as INDEX, SMALL and ROW is an array formula.

Vlookup (with True/False Example) YouTube
The column index number is the number of columns Excel must count over to find the matching value. The VLOOKUP function also has an optional fourth argument: range lookup. This can be either TRUE or FALSE. If the range lookup argument is FALSE, VLOOKUP will find only exact matches. If the range lookup argument is TRUE, or if a range lookup.

Vlookup TRUE or FALSE? YouTube
Follow the steps to use FALSE in Excel VLOOKUP. Open the VLOOKUP function in the F3 cell. Choose the Lookup Value as an E3 cell. Next, choose the VLOOKUP table array as the Table 1 range. Column Index Number as 2. The last argument is [Range Lookup]. Mention it as TRUE or 1 in the first attempt.
How to use the VLOOKUP function
The function looks like this: =VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]) The first three parameters are required, but the fourth is optional and will default to TRUE if left alone. Let's explore these a bit in more detail: Lookup Value: the value that you're asking Excel to search for in the your lookup table.

Perbedaan True dan False Pada Fungsi Vlookup di Excel Tutorial Excel Pemula YouTube
IF (VLOOKUP (…) = value, TRUE, FALSE) Translated in plain English, the formula instructs Excel to return True if Vlookup is true (i.e. equal to the specified value). If Vlookup is false (not equal to the specified value), the formula returns False. Below you will a find a few real-life uses of this IF Vlookup formula. Example 1.

Chapter 3 Vlookup exact match TRUE FALSE 1 0 2019 02 27S YouTube
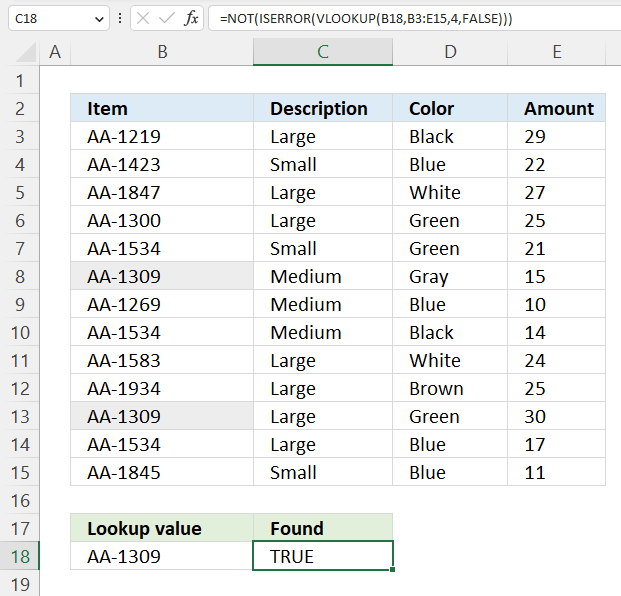
1. After installing Kutools for Excel, click Kutools > Select > Select Same & Different Cells to enable the utility. 2. In the Select Same & Different Cells dialog box, please configure as follows. 2.1) In the Find values in box, select the range which you will highlight values in; 2.2) In the According to box, select the range you will.
如何在Excel 2007和2010中正确使用VLOOKUP和True和False值 TurboFuture爱游戏客服中心 爱游戏 入口
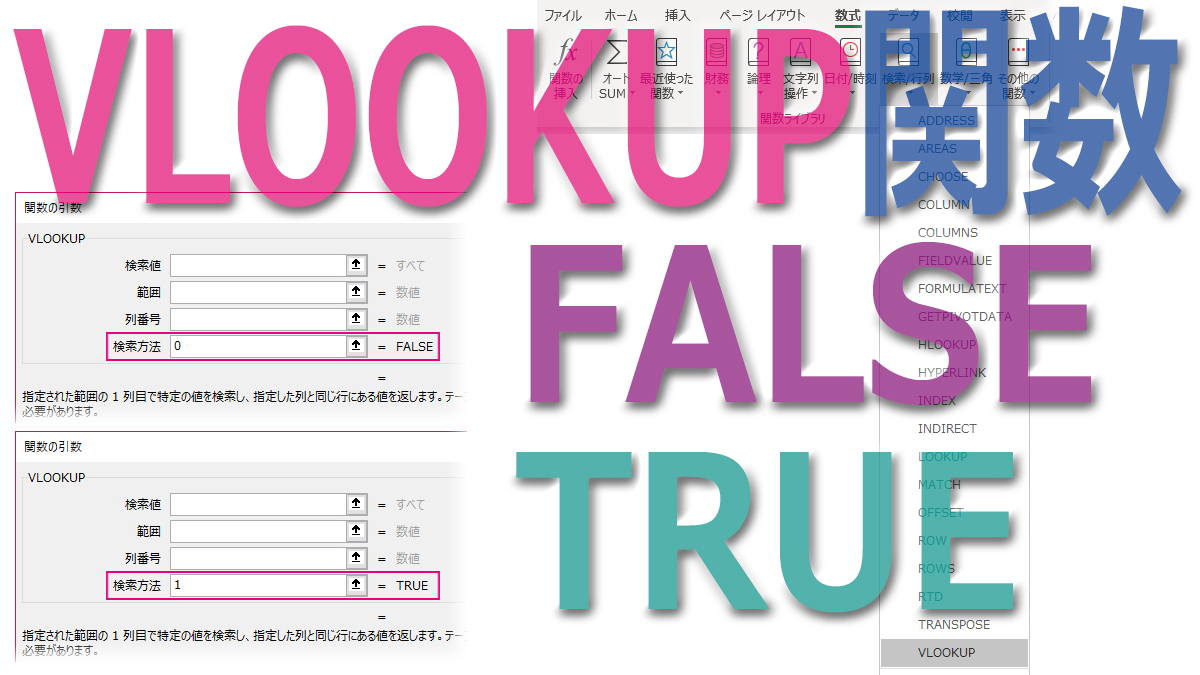
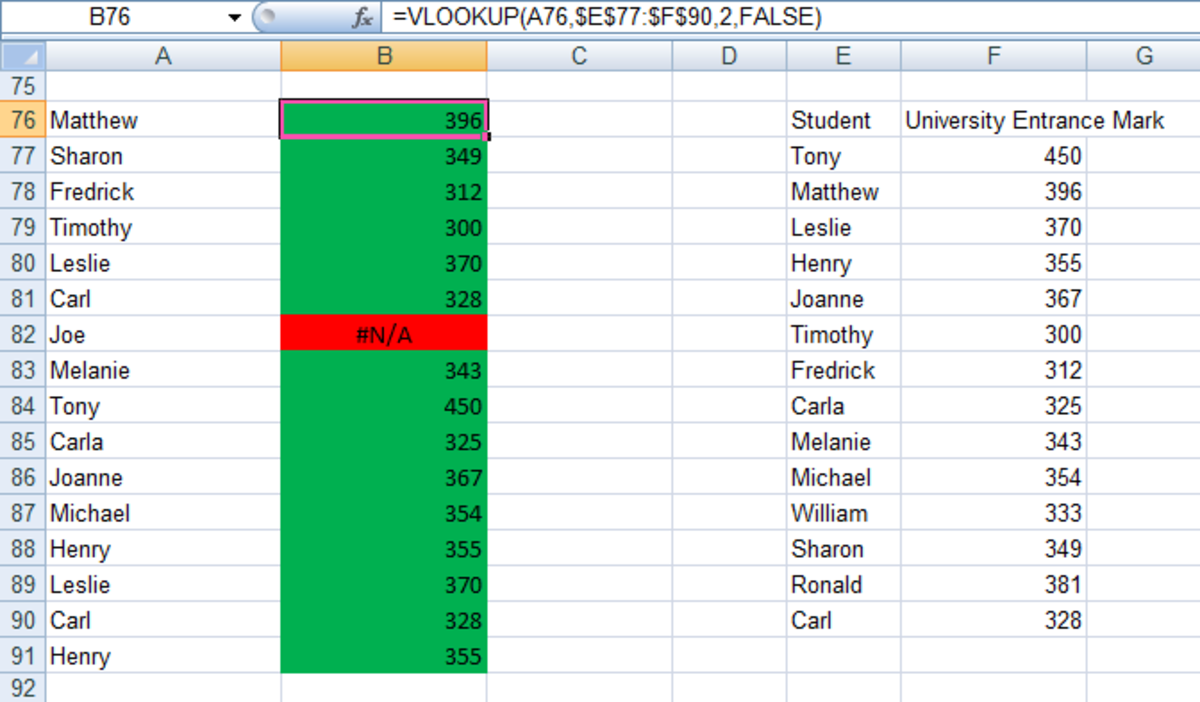
Excel Returns. TRUE. An exact, or approximate match. If Excel is unable to find an exact match, the next value that is less than the value you are interested in is returned. FALSE. An exact match. If Excel is unable to find a match, it returns #N/A. As you can see from the above table, Excel will return an approximate value if you choose TRUE.
VLOOKUP関数で「FALSE」と「TRUE」をどう使い分けるか TschoolBANK 作~るバンク
These two formulas are equivalent: = VLOOKUP ( value, data, column, FALSE) = VLOOKUP ( value, data, column, 0) In exact match mode, when VLOOKUP can't find a value, it will return #N/A. This a clear indication that the value isn't found in the table. 8. You can tell VLOOKUP to do an approximate match.

Excel How to Use TRUE or FALSE in VLOOKUP Statology
'FALSE' tells the VLOOKUP function to find an exact match, 'TRUE' tells the VLOOKUP function to find the nearest value that is still less than the lookup_value. Where the value is omitted the function will default to 'TRUE'. Until you understand how to use this correctly, it is best to use FALSE. In our example, our formula would be.

Difference of true and false in vlookup, usage of true and false in vlookup, learn with Hany
Returns. The VLOOKUP function returns any datatype such as a string, numeric, date, etc. If you specify FALSE for the approximate_match parameter and no exact match is found, then the VLOOKUP function will return #N/A. If you specify TRUE for the approximate_match parameter and no exact match is found, then the next smaller value is returned. If index_number is less than 1, the VLOOKUP.
How to Use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel (Step by Step)
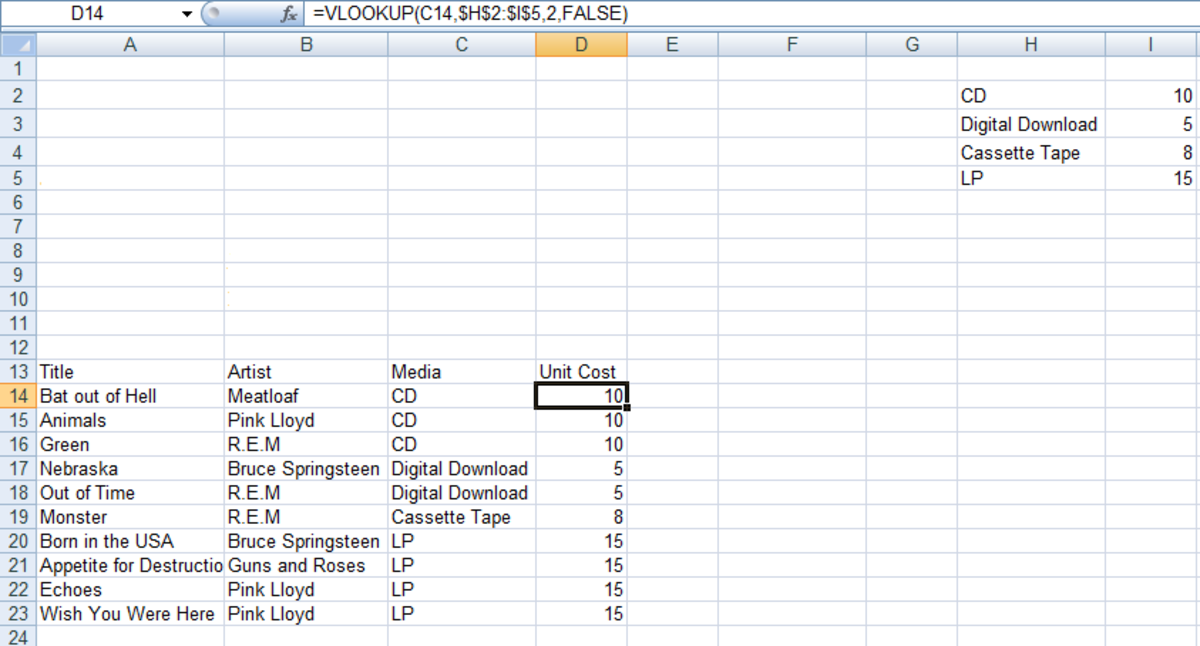
VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]) table_array: The range of cells to search for the lookup value. col_index_num: The column number that contains the return value. range_lookup: TRUE = approximate match, FALSE = exact match. Notice that the last argument allows you to specify TRUE to look for an approximate match.
How to Use VLOOKUP and the TRUE and FALSE Value Correctly in Excel 2007 and 2010 TurboFuture
Here's an example of how to use VLOOKUP. =VLOOKUP(B2,C2:E7,3,TRUE) In this example,. Enter either TRUE or FALSE. If you enter TRUE, or leave the argument blank, the function returns an approximate match of the value you specify in the first argument. If you enter FALSE, the function will match the value provide by the first argument.

Excel Vlookup False (lesson 1) YouTube
When using the VLOOKUP function in Excel, you can have multiple lookup tables. You can use the IF function to check whether a condition is met, and return one lookup table if TRUE and another lookup table if FALSE. 1. Create two named ranges: Table1 and Table2. 2. Select cell E4 and enter the VLOOKUP function shown below.

VLOOKUP Function Is Sorted (TRUE/FALSE) Google Sheets Formulas 8 YouTube
Depending on whether you choose TRUE or FALSE, your formula may yield different results. Excel VLOOKUP exact match (FALSE) If range_lookup is set to FALSE, a Vlookup formula searches for a value that is exactly equal to the lookup value. If two or more matches are found, the 1st one is returned.
Excel Vlookup showing false and true arguments YouTube
VLOOKUP False. We will look at False first because it is easier to understand. When using "False" or "0", the function returns an exact match. Effectively, Excel starts at the top of the list and works down item by item. If the lookup value exists in the list, it returns a value; if it does not, it returns #N/A.