Learn German German Grammar Modalverben Modal verbs A1 YouTube
German Modal Verbs (die Modalverben) learn German,modals,german,conjugation,verbs
What are modal verbs in German? The six modal verbs in German are: dürfen, können, mögen, müssen, sollen, wollen. As mentioned, these verbs are "assisting" another verb in a sentence. Modal verbs are verbs which express a mood like "want to" or "like to".

Learn German Modale Verben YouTube
German Modal verbs modify the content of the main verb of the sentence (i.e. the way or how something is done). The conjugated modal verb is in the second position of the sentence, the verb in the infinitive is at the end of the sentence. In the example below, the modal verb "wollen" (to want) changes the meaning of the sentence and is conjugated and placed in second position.

Modalverben German Wortschatz Vocabulario Deutsch Alemán Aprender alemán, Estudia alemán
Grammatical terms in German: das Modalverb: Modal verbs are verbs that usually relate to a second verb, defining it more precisely. They make clear, for example, whether something is possible or necessary. In a sentence in the present tense, the modal verb is conjugated, while the second verb is used in the infinitive.

Learn about German Modal Verbs
What are modal verbs? Modal verbs, also called modal auxiliaries (in German: Modalverben), are verbs that modify the relationship between subject and predicate and, thus, determine the grammatical mood.In the vast majority of cases, they cannot stand alone (as the only verb) in a sentence and form a multi-part predicate together with the respective main verb.

Modal Verbs in German Modal Verbs in German on
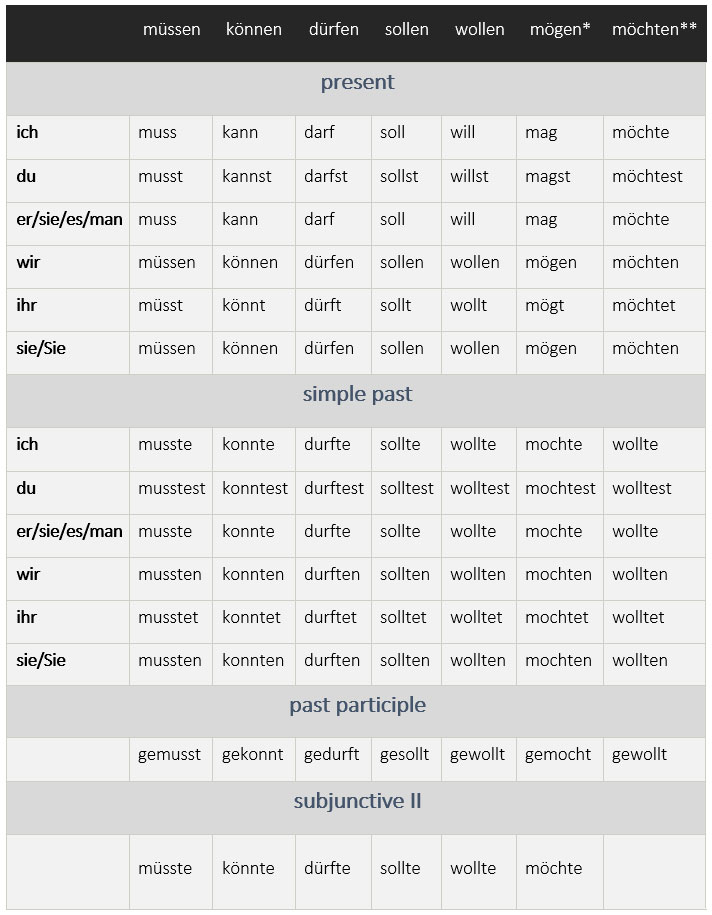
German has six modal verbs. Modal verbs are usually accompanied by another verb that expresses the action. In the present and simple past tenses, this other verb is an infinitive at the end of the sentence. Modal verbs: Finite tenses Present tense of modal verbs The present tense conjugation of modal verbs is irregular.

Modalverben Learn german, Study german, German language
Modal Verbs - Free Exercise show special characters display incorrect answers Exercises A1 Type in the modal verbs in the present tense. Ich (können) dir helfen. Ihr (müssen) noch viel lernen. Du (dürfen) heute früher nach Hause gehen. Er (wollen) nachher einkaufen gehen. Ihr (sollen) eure Hausaufgaben machen.

How to Use German Modal Verbs Learn German with Herr Antrim
Modal verbs, or modale Verben in German, are a special category of verbs that modify or indicate the mood of the main verb in a sentence. These verbs are essential for expressing abilities, permissions, obligations, and necessity in both written and spoken German. There are six modal verbs in the German language: müssen - must, have to

Introduction to German Modal Verbs & How to Use Them Learn German with Herr Antrim
What's a Modal Verb? Modal verbs are special verbs that allow us to talk about probabilities, obligations, abilities, or make requests. There are six of them in German: They are mostly used in conjunction with another verb, putting a spin on said verb. If I say "I can ride a bike," is telling you I've mastered the art of balancing and pedaling.

Modalverben Konjugation Learn german, Study german, Worksheets
Conjugating the German modal verbs is an important part of learning the language. The tables below show how to conjugate three modal verbs, dürfen, können, and mögen, including examples of how they are used in sample modal sentences and expressions. There are actually six modal verbs in German: Dürfen> may, be permitted Können > can, be able

German modal verbs Past, present, & future The German Professor
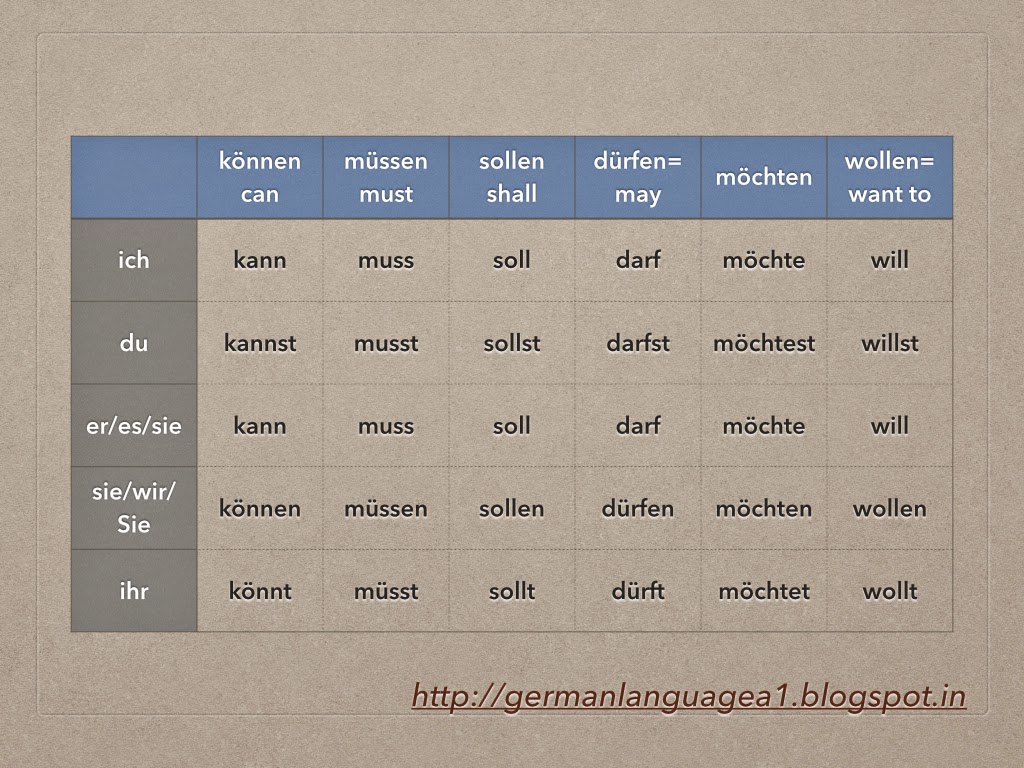
There are 6 modal verbs in German and they express different conditions: Modal verbs that express capacity/ability/permission: dürfen and können Dürfen is the modal verb that is used to signify authorisation. If it is used with a negative sentence then it indicates prohibition. Können does not serve to express permission and prohibition.

Modal Verbs in German Modal Verbs in German on
What's so great about German modal verbs? They're super versatile. You can use them to express commands, politeness, even probability! In German, there are six modal verbs: können, müssen, sollen, dürfen, möchten and wollen. Let's take a look at their conjugation and a few sample sentences. But first, we put together a quick guide to the top five.

German Modal Verbs Explained I Will Teach You A Language
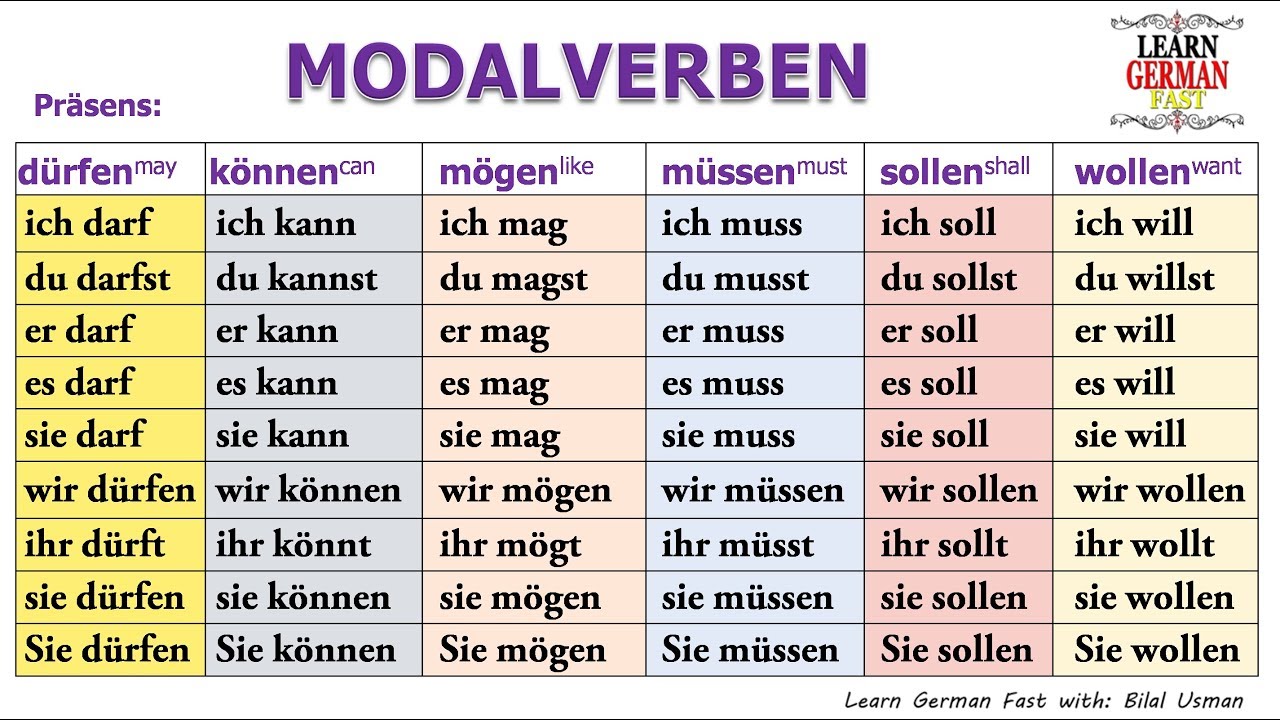
What is a modal verb in German? The modal verbs in German are dürfen (be allowed to/may), können (be able to/can), mögen (to like/may), müssen (to have to/must), sollen (to ought to/should) and wollen (to want to). Modal verbs express ability, necessity, obligation, permission or possibility.

Modal Verbs in German Rules worth noting
In general, the verbs "müssen" (to have to) and "sollen" (to ought to) follow more or less the regular rules of the simple past tense in German. To the first-person singular "muss" or "soll," you add a , which then stays for all other persons. For example, the past conjugation of "müssen" looks like this: er, sie, es musste\t.
Learn German MODALVERBEN Präsens dürfen können mögen müssen sollen wollen YouTube
Learn all German Modal Verbs in 8 Minutes | Super Easy German (91) - YouTube © 2023 Google LLC LEARN MORE WITH OUR APP: https://www.seedlang.com?pr=modCORRECTION: 3:11 Du musst schlafen.FOLLOW.

Modal verbs Modalverben Learn German (Lesson 9) Complete A1B1 Course Deutsch lernen
Modal Verbs in German Modale Verben im Deutschen Modal Verbs in German - Summary Summary Modal verbs always connect with the infinitive of another verb in present and past tense. In the perfect tense, they always come the auxiliary verb "haben" and are put at the end of the phrase. "Das Mädchen will den Freund besuchen."
German Language A1 Modal verben
There are 6 modal verbs in German: „ können ", „ wollen ", „ möchten ", „ sollen ", „ müssen ", „ dürfen ". Modal verbs express whether you can, want to, must, should, or are allowed to do something. Modal verbs are usually combined with a second verb ("main verb") and must be conjugated.