The Radiology Assistant Pancreatic cystic Lesions
microcystic serous cystadenoma: usually head; 30% have a central scar cystic with a solid component macrocystic tumors can have a solid component as well pancreatic adenocarcinoma may undergo cystic degeneration (8%) 6 generally solid

MR Imaging of Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas RadioGraphics
The purpose of this review is to outline the management guidelines for the care of patients with cystic pancreatic lesions. CONCLUSION. The guidelines are as follows: Annual imaging surveillance is generally sufficient for benign serous cystadenomas smaller than 4 cm and for asymptomatic lesions.

Cystic Pancreatic Lesions A Simple Imagingbased Classification System for Guiding Management
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this review is to outline the management guidelines for the care of patients with cystic pancreatic lesions. CONCLUSION. The guidelines are as follows: Annual imaging surveillance is gener-ally sufficient for benign serous cystadenomas smaller than 4 cm and for asymptomatic le-sions.
Cystic pancreatic lesions Radiology Key
The core objectives of the Incidental Findings Project are to (1) develop consensus on patient characteristics and imaging features that are required to characterize an incidental finding; (2) provide guidance to manage such findings in ways that balance the risks and bene fits to patients; (3) recommend reporting terms that re flect the level o.

MR Imaging of Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas RadioGraphics
Publicationdate 2021-08-01. This is the second version of the role of CT in staging pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer is the fourth largest cause of cancer death in the United States and Europe with over 100,000 deaths per year in Europe alone. The overall 5-year survival ranges from 2-7 % and has hardly improved over the last two decades.
The Radiology Assistant Pancreatic cystic Lesions
CME Tools Share Abstract The widespread use of high-spatial-resolution cross-sectional imaging has led to an increase in detection of incidental pancreatic cystic lesions. These lesions are a diverse group, ranging from indolent and premalignant lesions to invasive cancers.
Cystic pancreatic lesions Radiology Key
Pancreatic cystic lesions are frequently identified on cross-sectional imaging. As many of these are presumed branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, these lesions generate much anxiety for the patients and clinicians, often necessitating long-term follow-up imaging and even unnecessary surgical resections.

MR Imaging of Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas RadioGraphics
Introduction Classification Pancreatic cysts can be categorized into the following groups: Pseudocysts Common cystic neoplasms: IPMN - intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm SCN - Serous cystic neoplasm MCN - Mucinous cystic neoplasm Uncommon cystic neoplasms: SPEN (solid pseudopapillary epithelial neoplasm) Tumors with cystic degeneration:

The Radiology Assistant Pancreatic cystic Lesions
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are excellent modalities for both initial detection and characterization of cystic pancreatic lesions. An imaging classification system for these lesions has been proposed that is based on the morphologic features of the lesion.
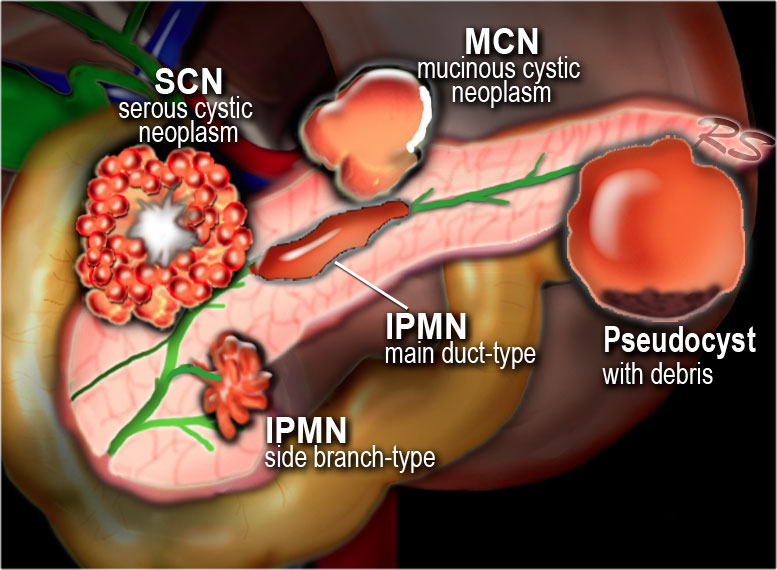
The Radiology Assistant Pancreas Cystic Lesions
The purpose of this review is to outline the management guidelines for the care of patients with cystic pancreatic lesions. CONCLUSION. The guidelines are as follows: Annual imaging surveillance is generally sufficient for benign serous cystadenomas smaller than 4 cm and for asymptomatic lesions.
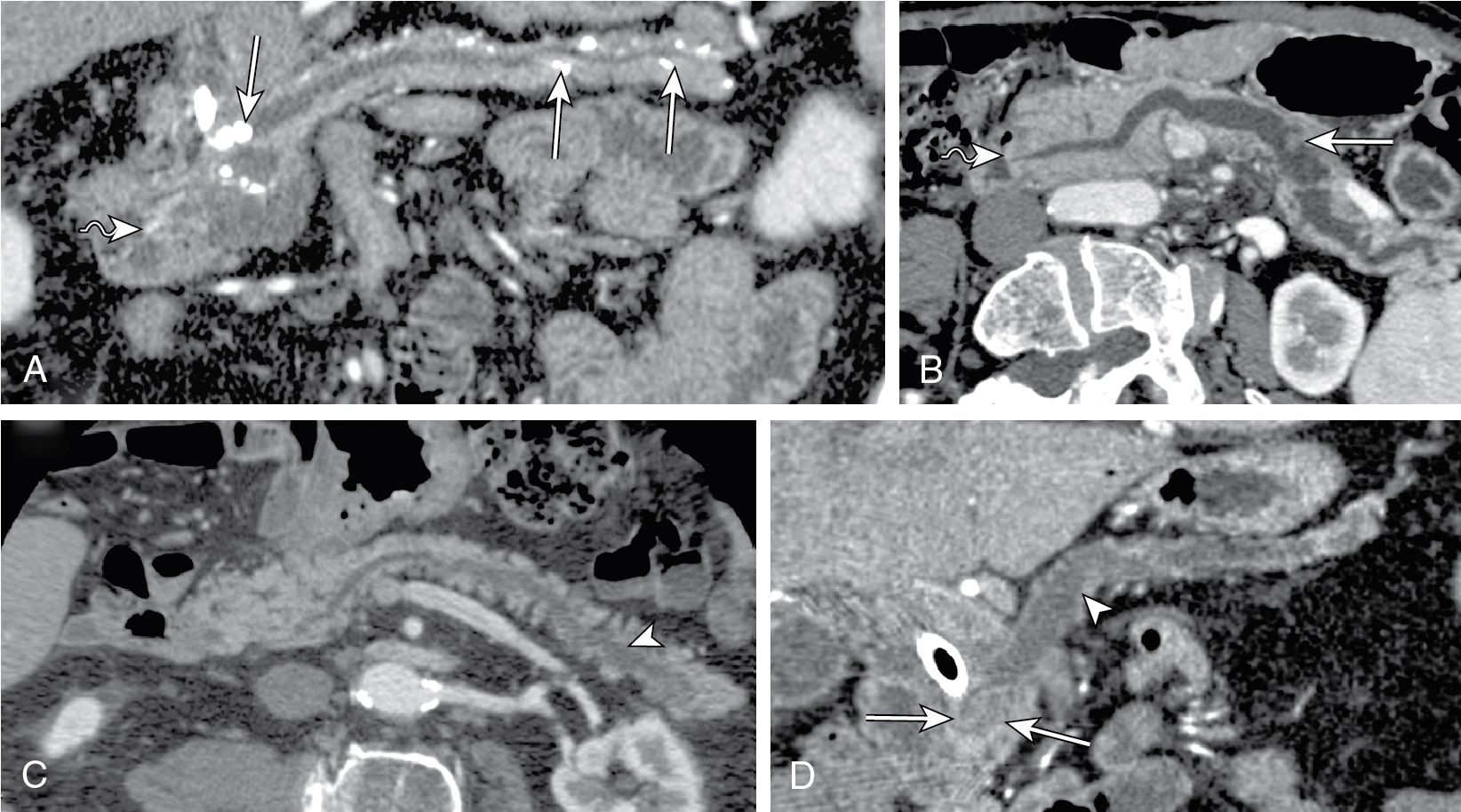
Cystic pancreatic lesions Radiology Key
Pancreatic cystic lesions are relatively common imaging findings and may be secondary to both benign and malignant disease processes. Accurate characterization of the internal features of a cyst—including fluid, hemorrhage, septa, and enhancing soft-tissue components—is important to guide the differential diagnosis, and cross-sectional magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the optimal.
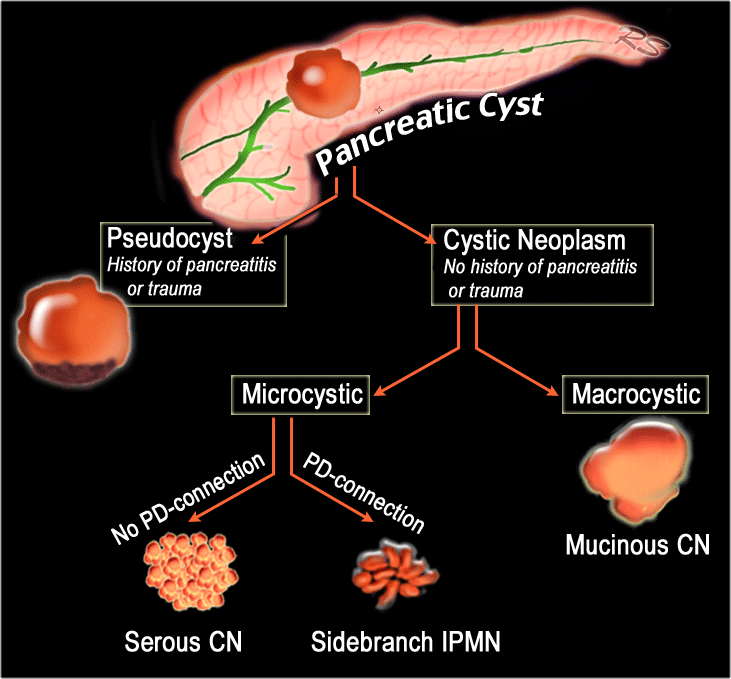
The Radiology Assistant Pancreas Cystic Lesions
Pancreatic cystic Lesions. Radiology department of the Academical Medical Centre, Amsterdam and the Alrijne hospital in Leiderdorp, the Netherlands. Cystic pancreatic lesions are increasingly identified due to the widespread use of CT and MRI. Certain pancreatic cysts represent premalignant lesions and may transform into mucin-producing.
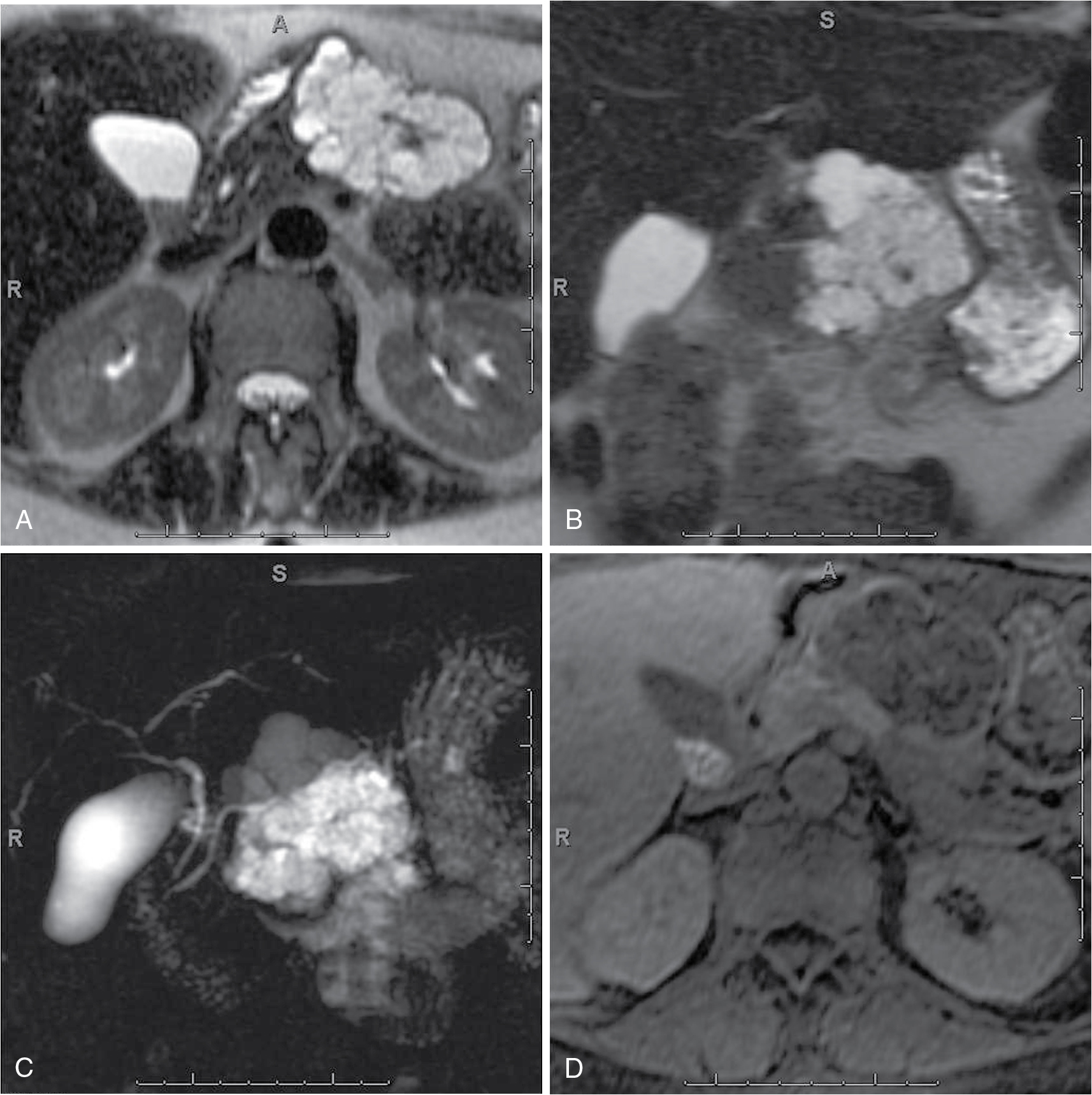
Cystic pancreatic lesions Radiology Key
Pancreatic cystic neoplasms (PCN) comprise of a diverse array of pancreatic cysts, including intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN), mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCN), serous cystic neoplasms (SCN), cystic neuroendocrine tumors (cNET), and many others. Increasing use of cross-sectional imaging has resulted in greater numbers of PCNs discovered incidentally. The overall risk of.

MR Imaging of Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas RadioGraphics
Introduction Temporally, two phases of acute pancreatitis are identified in the Revised Atlanta Classification: Early - first week Only clinical parameters are important for treatment planning and are determined by the systemic inflammatory response syndrome - SIRS, which can lead to organ failure. Late - after the first week
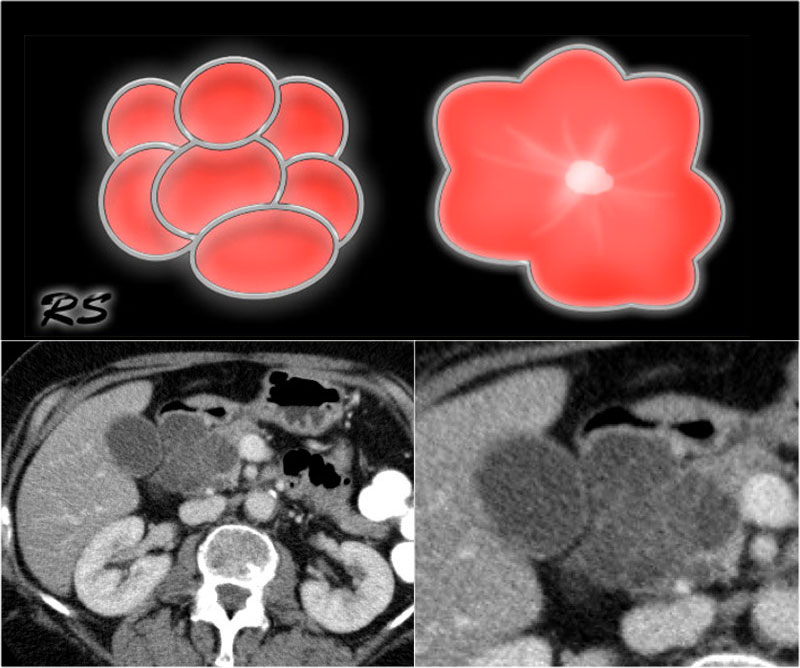
The Radiology Assistant Pancreas Cystic Lesions
Introduction. Cystic pancreatic lesions (CPLs) are quite common: Their frequency of detection ranges from 2.4 to 19.6%, and their prevalence as well as size and number increases with age (from 7.9 below 70 years to 40.2 over 70 years) [1-5].A precise characterization is fundamental for the correct management of these lesions, as they have heterogeneous biological behavior and different.

The Radiology Assistant Pancreas Cystic Lesions
Pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) are present on up to 49% of abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams making these a common incidental finding, one that likely increases with age. 1 Definitions vary but a PCL is generally considered to be any closed sac-like structure with fluid or semi-fluid content within the pancreas on imaging, with or without communication with the main pancreatic.