Structure and types of the eukaryotic chromosomes WikiLectures
Structure and types of the eukaryotic chromosomes WikiLectures
Figure 1 Construction of the CRISPR/Cas9 imaging system for fluorescent labeling of a particular chromosome in live cells. (A) Scatter plot for numbers of sgRNA-binding sites in each cluster of.
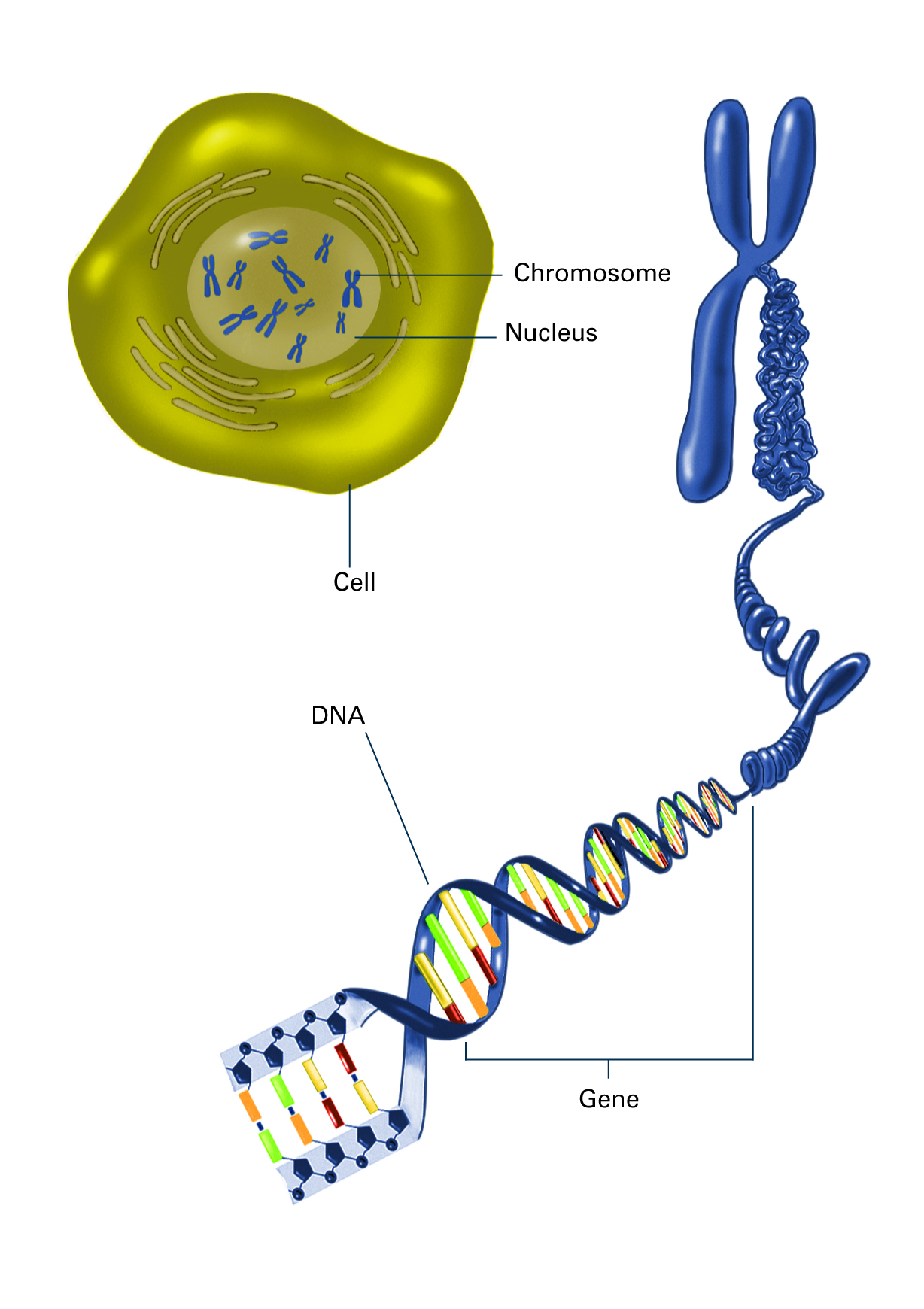
Image and Video Gallery National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Chromosome Structure - A Simple Labeling Exercise Chromosome Structure This simple worksheet shows a diagram of a chromosome and where it is located in the nucleus of the cell. Students use a word bank to label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus.

Assignment of a Novel Locus for Autosomal Recessive Congenital
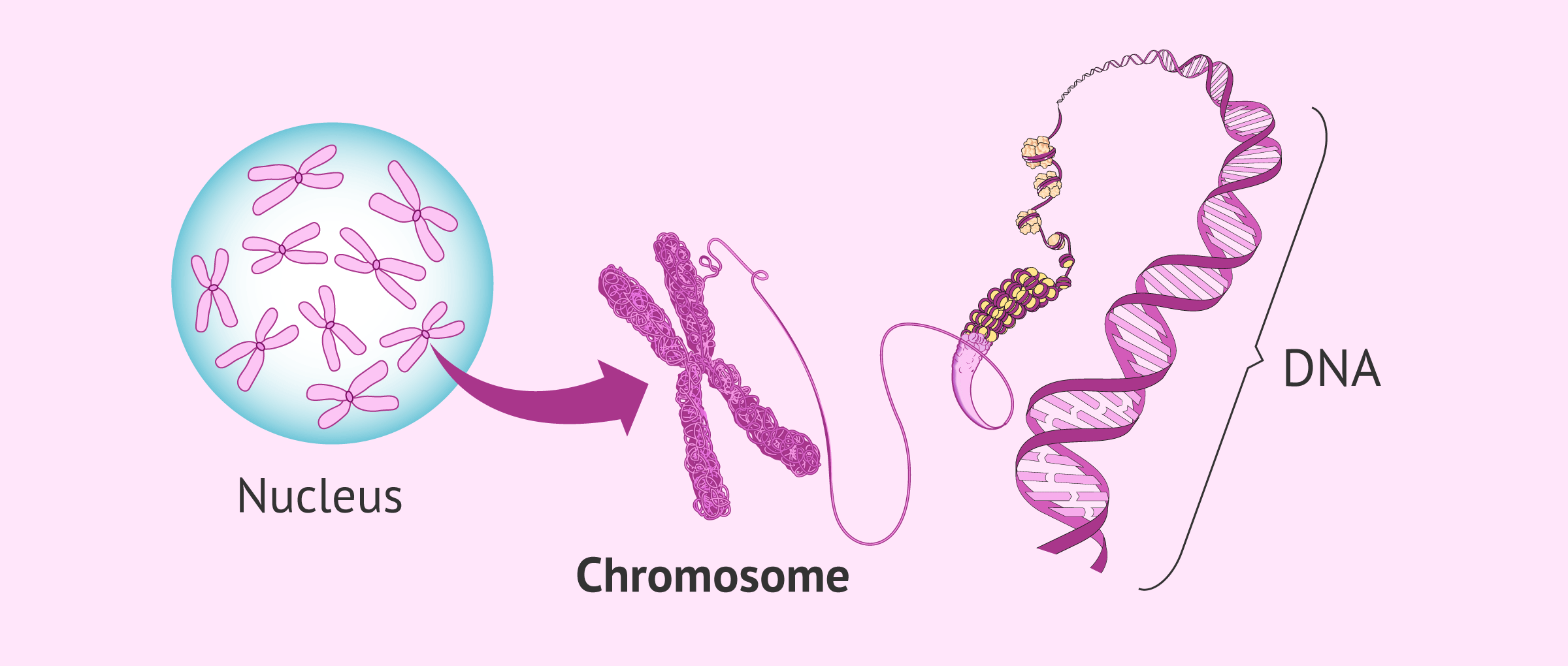
A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes. To obtain a view of an individual's karyotype, cytologists photograph the chromosomes and then cut and paste each chromosome into a chart, or karyogram, also known as an ideogram. In a given species, chromosomes can be identified by their number, size, centromere position, and banding.
What are Chromosomes?
In one application, by labeling and tracking the broken ends of chromosomal fragments, CRISPR FISHer enables real-time visualization of the entire process of chromosome breakage, separation, and.
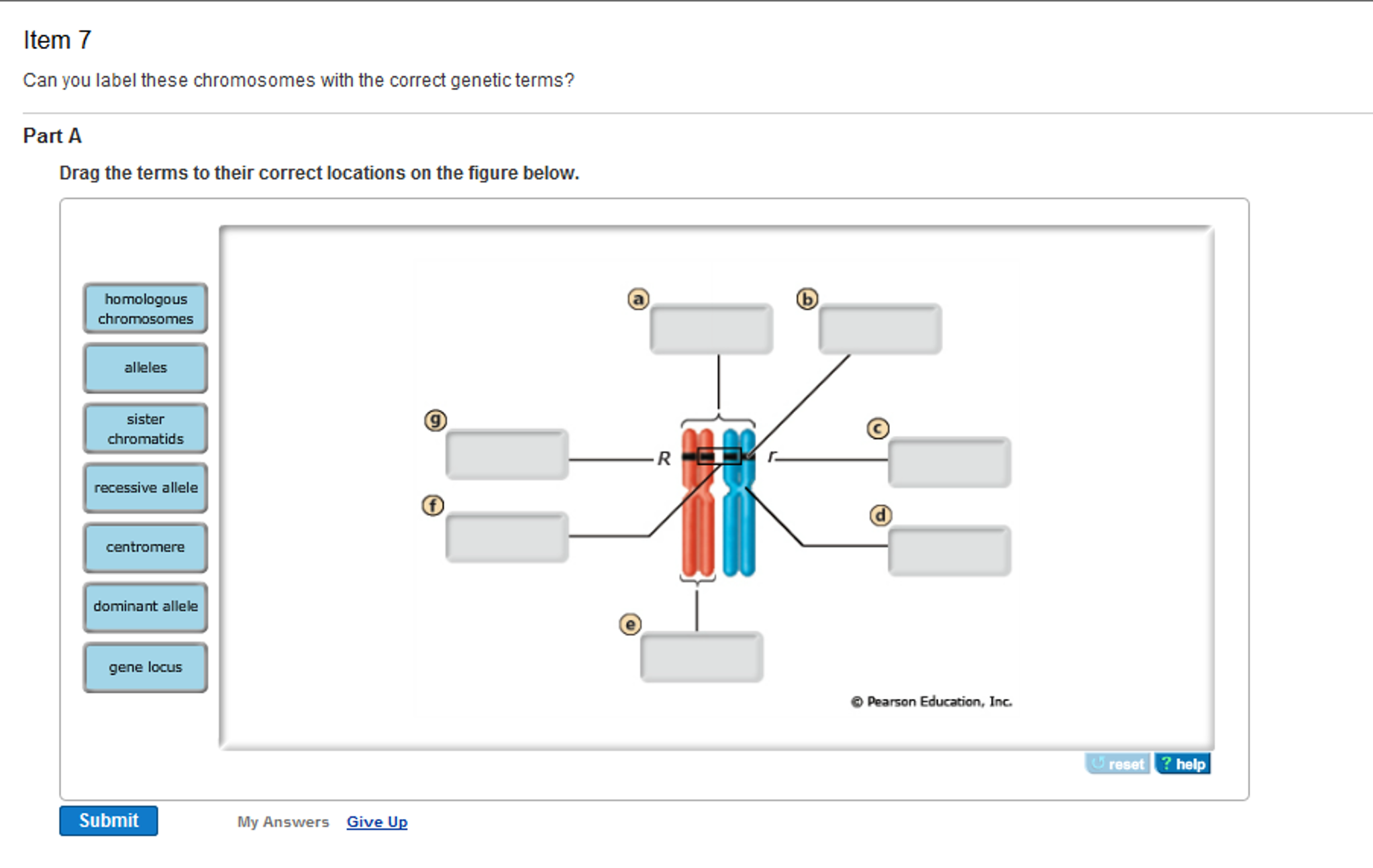
Solved Can you label these chromosomes with the correct
How to draw and label structure of chromosome by Bio simplified

Life Science News, November 4th 2013 Life Science Blog
1. INTRODUCTION Studies initiated during the last quarter of the nineteenth century gradually revealed the key roles of chromosomes in storing and transmitting hereditary information and in generating genetic variation. The most frequent method to study chromosome organization and behavior had been optical microscopy.
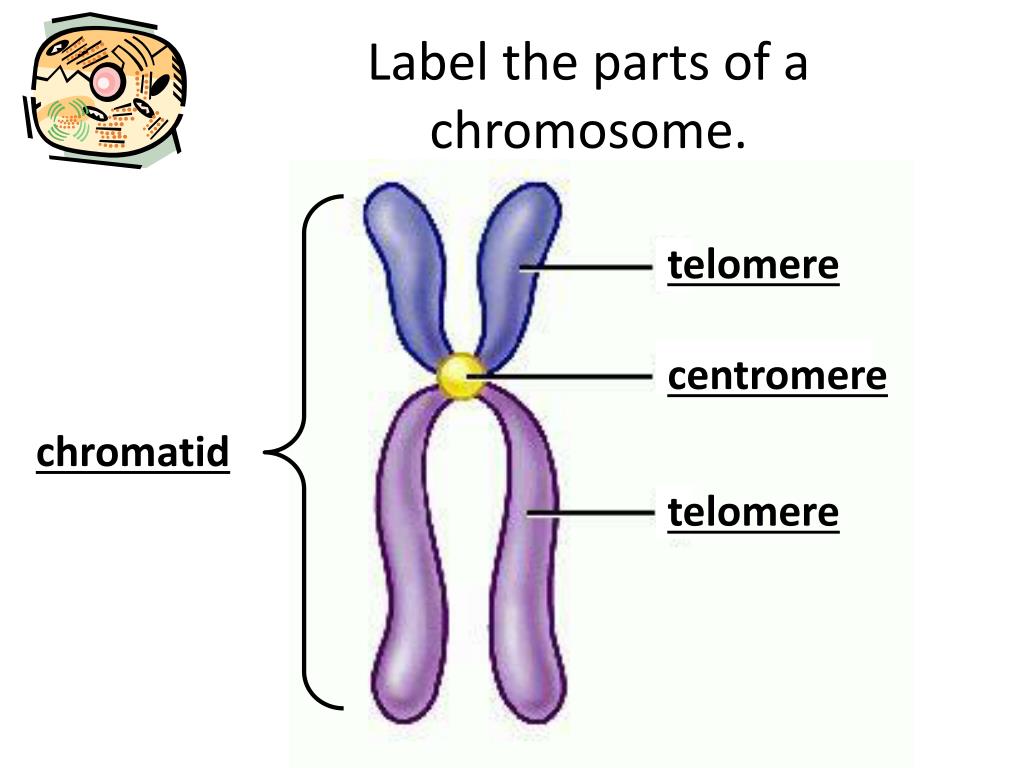
31 Label The Parts Of The Chromosome Labels Design Ideas 2020
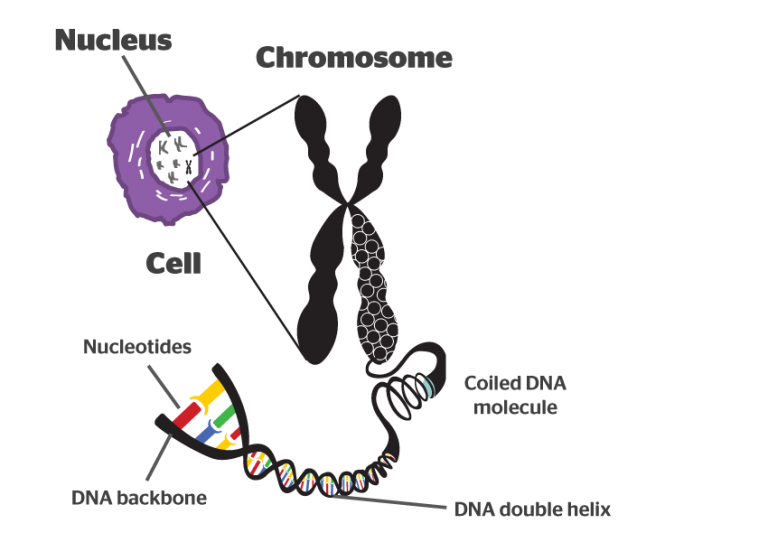
Diagram of Chromosome Structure. A chromosome is a physically discrete portion of the genome, which carries many individual genes. Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of chromatin, which is a mixture of DNA and protein.The protein, primarily histones, acts as a scaffold organizing the structure of the DNA, which is a long string (polymer) of nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.

Chromosome Structure (labeling) Free Worksheets Samples
The process of differentiating between cells is expressed by labeling the developmental tree. Tracing a path from the root to a specific cell in the tree reveals the history of its divisions. Normal human fetal cells will divide approximately 40 to 60 times before cell division halts as demonstrated by Hayflick [ 1 ].

Labeled Chromosome Structure Diagram imgprobe
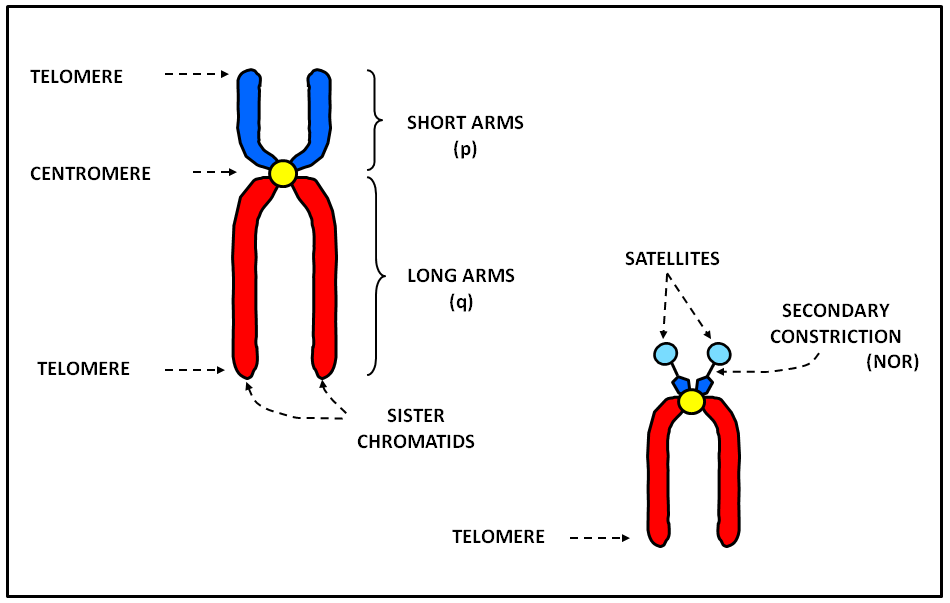
A chromosome has generally 8 parts; Centromere or primary constriction or kinetochore, chromatids, chromatin, secondary constriction, telomere, chromomere, chromonema, and matrix. Centromere or Kinetochore: It is the primary constriction at the center to which the chromatids or spindle fibers are attached.

DIP4FISH Labelling chromosomelike shapes using watershed effect of
< Prev Next > Chromosome Map Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.
What is a Chromosome Definition, Structure and Evolution
Thoru Pederson Nature Biotechnology 34 , 528-530 ( 2016) Cite this article 35k Accesses 296 Citations 168 Altmetric Metrics Abstract A lack of techniques to image multiple genomic loci in living.

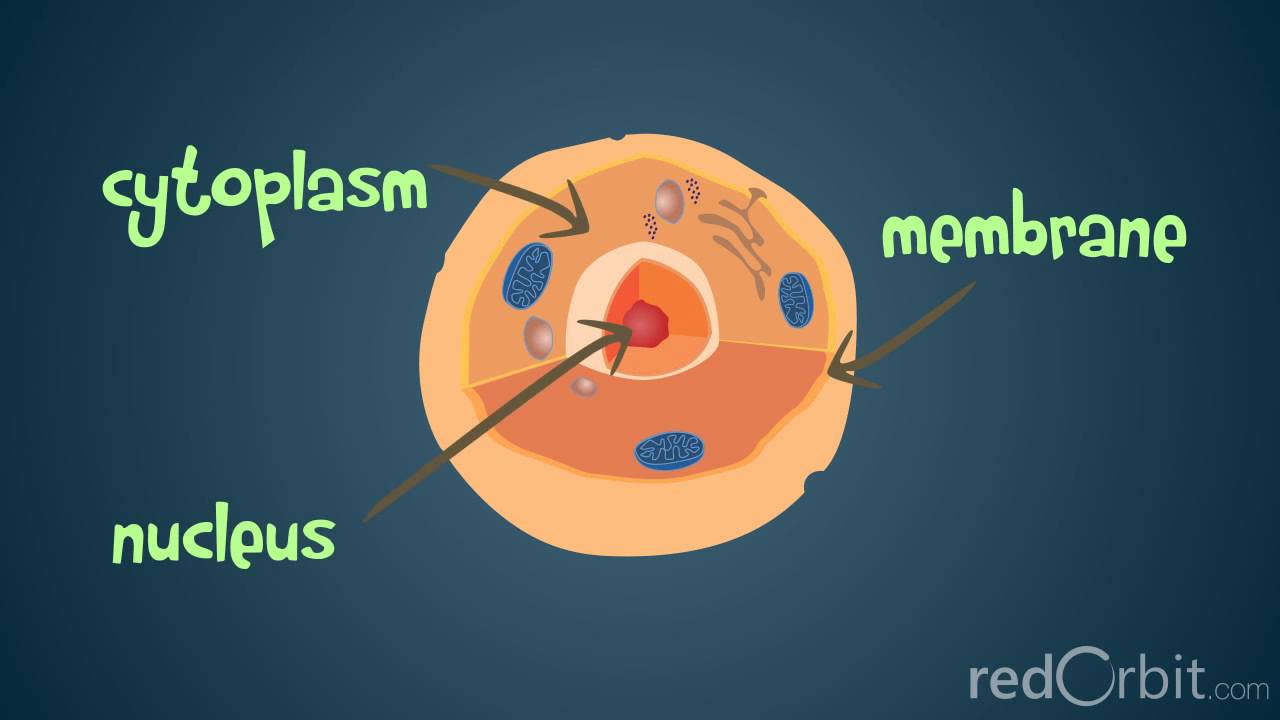
Biotechnology Basics of Cell, Nucleus, Chromosomes, DNA, RNA, Genes
chromosome, the microscopic threadlike part of the cell that carries hereditary information in the form of genes.A defining feature of any chromosome is its compactness. For instance, the 46 chromosomes found in human cells have a combined length of 200 nm (1 nm = 10 − 9 metre); if the chromosomes were to be unraveled, the genetic material they contain would measure roughly 2 metres (about 6.
What is a Chromosome? YouTube
Introduction When a cell divides, one of its main jobs is to make sure that each of the two new cells gets a full, perfect copy of genetic material. Mistakes during copying, or unequal division of the genetic material between cells, can lead to cells that are unhealthy or dysfunctional (and may lead to diseases such as cancer).

Chromosome Structure
In this paper, we describe the labeling of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR/Cas9 components, allowing multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.

Chromosomes Fact Sheet NHGRI Inherited Traits, Background For
Chromosomes are a key part of the process that ensures DNA is accurately copied and distributed in the vast majority of cell divisions. Still, mistakes do occur on rare occasions. Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes in new cells may lead to serious problems.

Image result for structure of chromosome Chromosome, Chromosome
Chromosome Definition. A chromosome is a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure. During interphase of the cell cycle, the chromosome exists in a loose structure, so proteins can be translated from the DNA and the DNA can be replicated. During mitosis and meiosis, the chromosome.