Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology

Brain and face CT interactive anatomy atlas eAnatomy
e-Anatomy is a high-quality anatomy and imaging content atlas.It is the most complete reference of human anatomy available on the Web, iPad, iPhone and Android devices. Explore detailed anatomical views and multiple modalities (over 8,900 anatomic structures and more than 870,000 translated medical labels) with images in CT, MRI, radiographs, anatomical diagrams and nuclear images.

Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
CT head (sometimes termed CT brain ), refers to a computed tomography examination of the brain and surrounding cranial structures. It is most commonly performed as a non-contrast study, but the addition of a contrast-enhanced phase is performed for some indications. This article covers non-contrast and delayed post-contrast imaging.
The Radiology Assistant Brain Anatomy
CT Brain AnatomyGrey matter structures. The cortex, insula, basal ganglia and thalamus are the important grey matter structures. Important grey matter structures visible on CT images of the brain include the cortex, insula, basal ganglia, and thalamus.

Approach to CT head
Key points. White matter of the brain lies deep to the cortical grey matter. The internal capsules are white matter tracts which connect with the corona radiata and white matter of the cerebral hemispheres superiorly, and with the brain stem inferiorly. The corpus callosum is a white matter tract located in the midline.

Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
Last updated: 29 June 2022. Basic radiological anatomy of the brain and spine with annotated CT and MRI images covering the brain, including the brainstem structures and ventricles, and whole spine.

Ct Scan Brain Anatomy Anatomy Of Head Ct Scan Normal The Brain On Ct And Mri / Frontal
CT Brain Anatomy Skull bones and sutures Key points Main skull bones - frontal, parietal, occipital, ethmoid, sphenoid and squamous temporal Main sutures - coronal, sagittal, lambdoid and squamosal Injury to the pterion area may lead to formation of extradural haematoma due to injury of the middle meningeal artery

MRI anatomy brain axial image 18 Brain anatomy, Mri brain, Ct brain anatomy
ANATOMICAL PARTS Ala of nose Alveolar process Ambient cistern Angular gyrus Anterior arch of atlas Anterior cerebral artery: Postcommunicating part; A2 segment Anterior cerebral artery: Precommunicating part; A1 segment Anterior chamber Anterior clinoid process Anterior commissure Anterior communicating artery

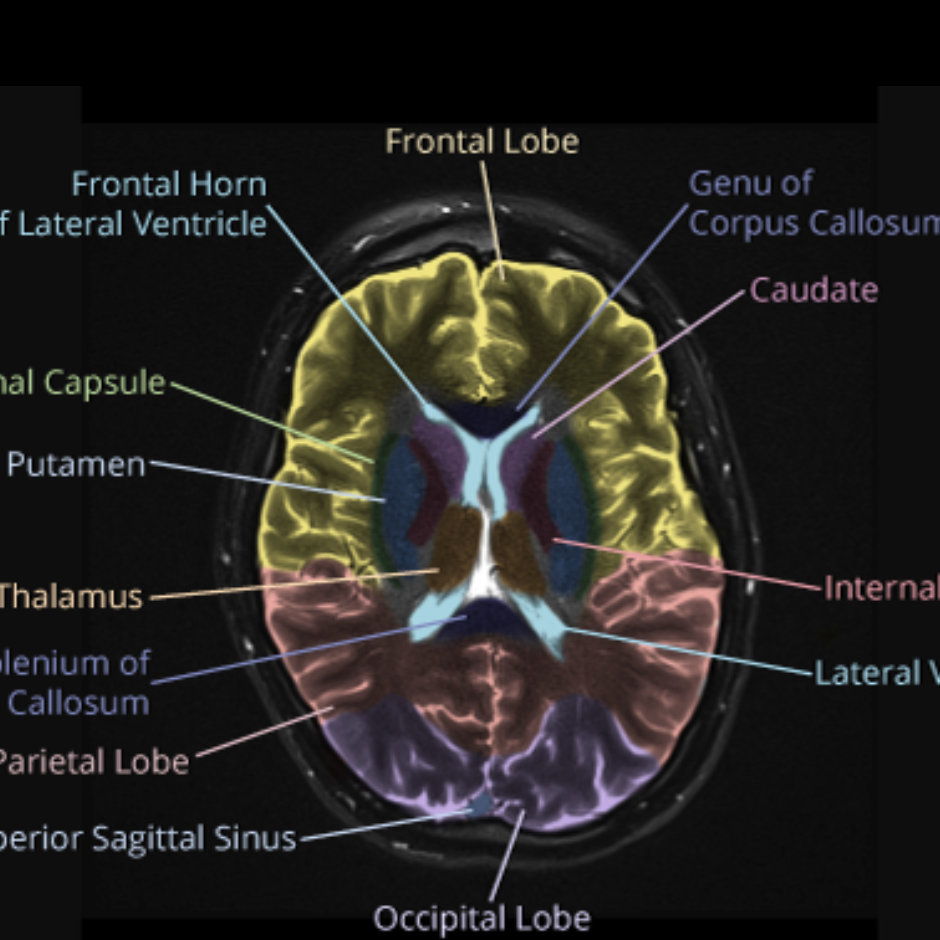
Brain lobes annotated MRI Image
Key points Grey matter appears grey White matter appears blacker The brain consists of grey and white matter structures which are differentiated on CT by differences in density. White matter has a high content of myelinated axons. Grey matter contains relatively few axons and a higher number of cell bodies.
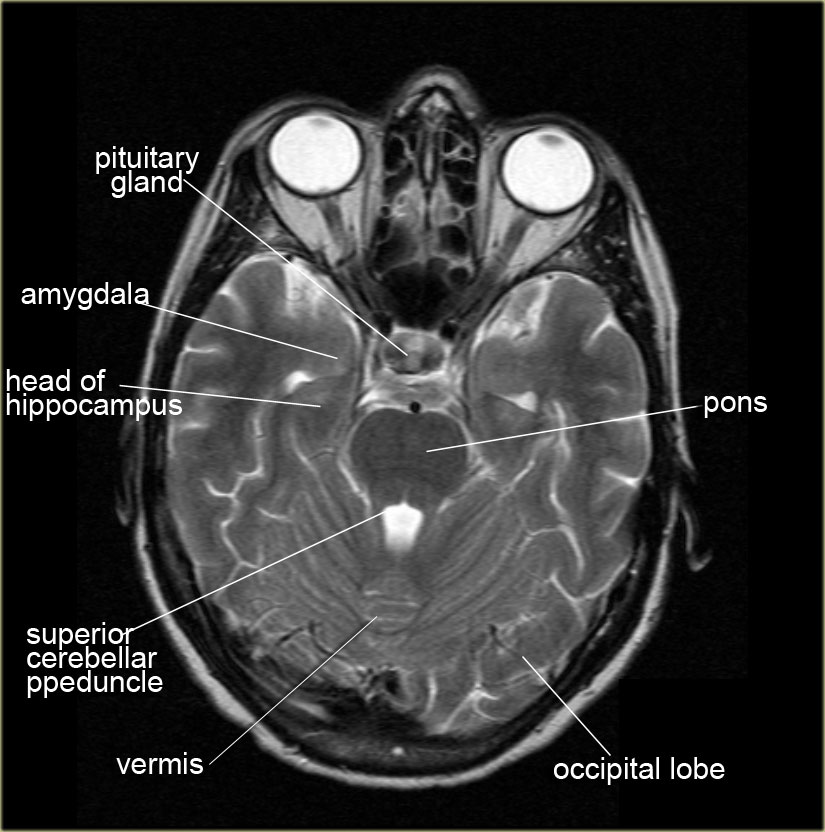
MRI Brain Anatomy
CT images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. This means that the right side of the brain is on the.
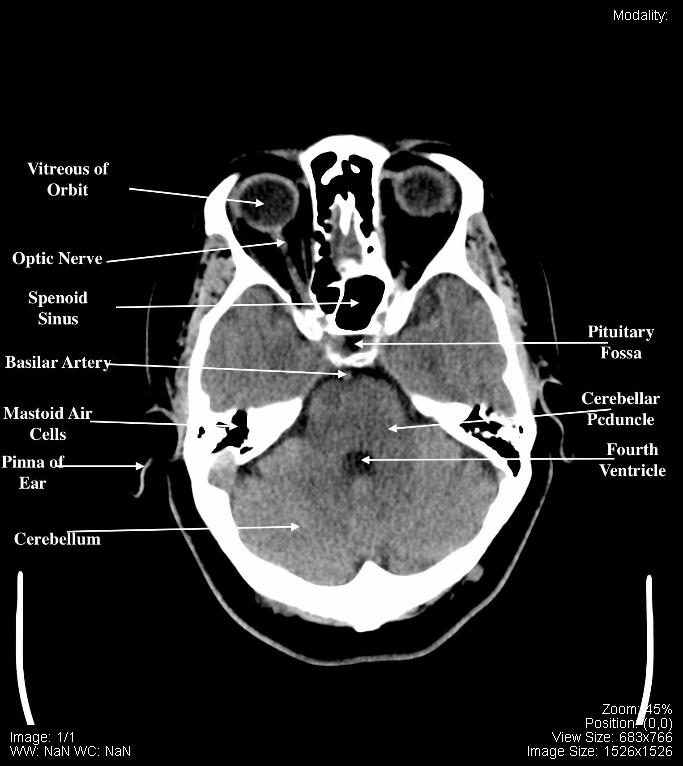
CT Scan Tips & Protocols CT BRAIN ANATOMY
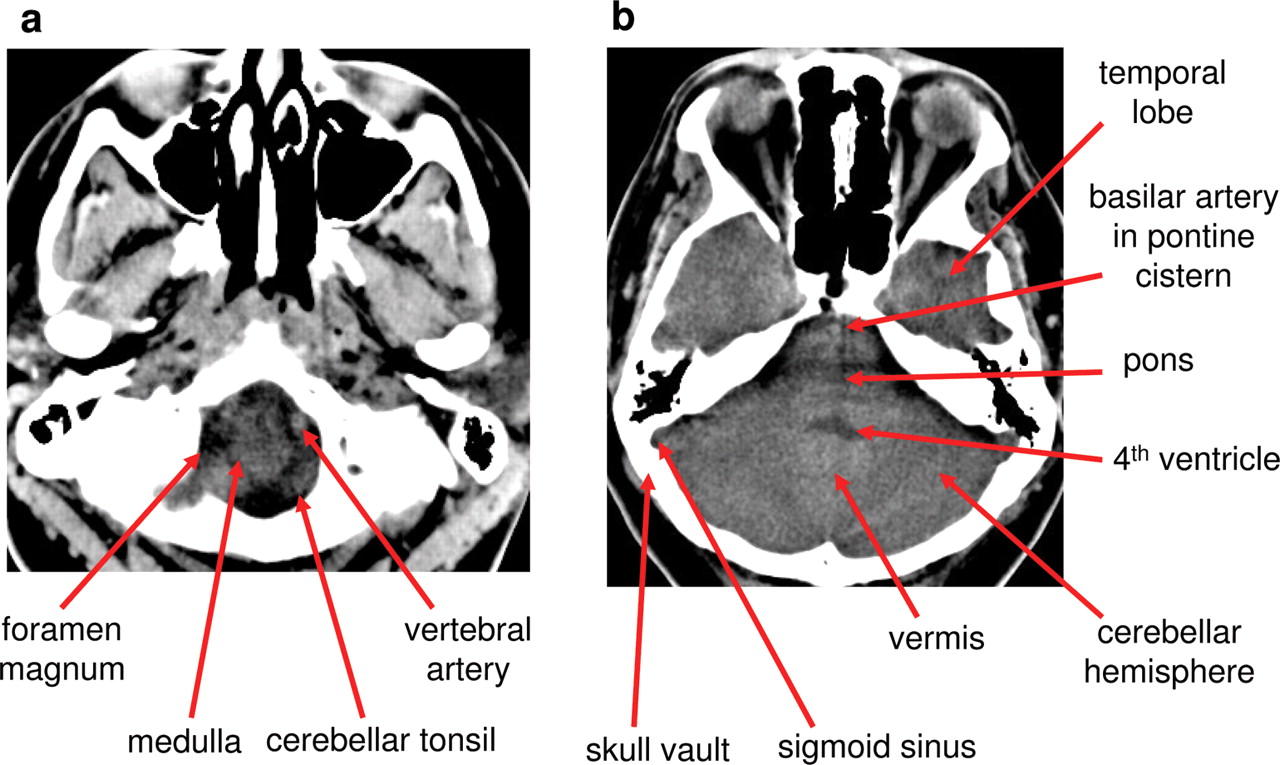
Normal CT head (with labels) Annotated image The labeled structures are (excluding the correct side): foramen magnum medulla oblongata vertebral artery cerebellar tonsil premedullary cistern internal jugular vein basilar artery sigmoid sinus petrous internal carotid artery in the carotid canal cerebellar hemisphere external auditory canal

Brain and face CT interactive anatomy atlas eAnatomy
CT images of the brain are conventionally viewed from below, as if looking up into the top of the head. This means that the right side of the brain is on the left side of the viewer. The anterior part of the head is at the top of the image. CT brain - image orientation Hover on/off image to show/hide findings Click image to align with top of page

Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by body region and modality. Brain CT head: non-contrast axial CT head: non-contrast coronal CT head: non-contrast sagittal CT head: non-contrast axial with clinical questions CT head: angiogram axial CT head: angiogram coronal
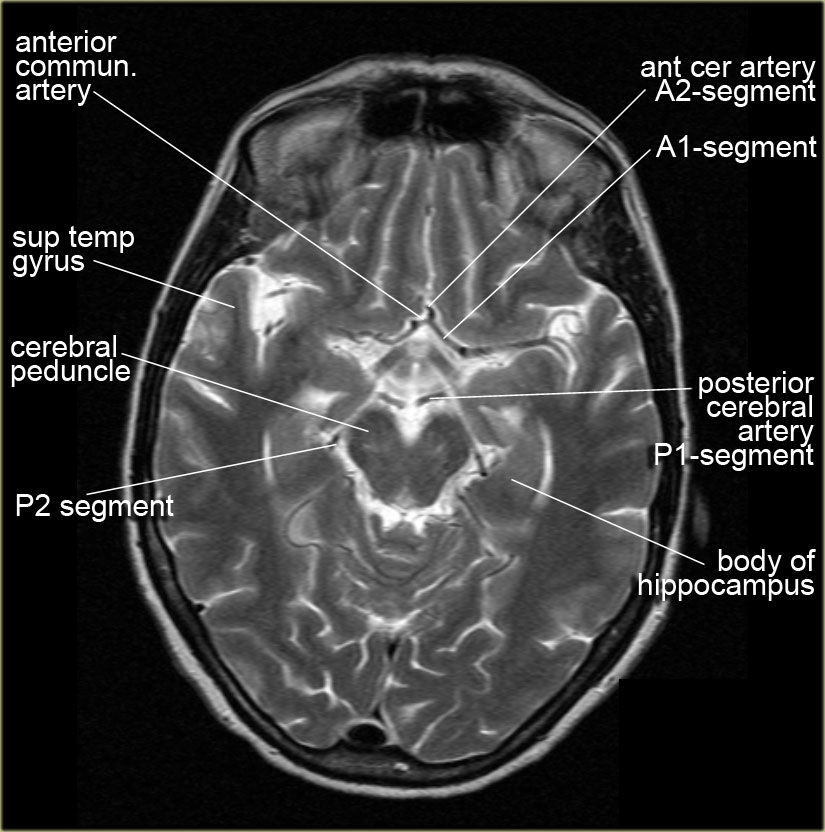
The Radiology Assistant Brain Anatomy
The video shows the basic CT anatomy of the brain.For each slice we have highlighted. This video is a part of basic radiologic head CT SCAN anatomy series. The video shows the basic CT anatomy.

The Radiology Assistant Brain Anatomy
The brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the sulci, fissures and basal cisterns.CSF is also found centrally within the ventricles.The sulci, fissures, basal cisterns and ventricles together form the 'CSF spaces', also known as the 'extra-axial spaces'. CSF is of lower density than the grey or white matter of the brain, and therefore appears darker on CT images.
CT Brain Anatomy Tutorial introduction
CT Brain ct Axial non-contrast C+ delayed C+ delayed C+ delayed Brainstem and cerebellum without evidence of focal lesions. Lateral ventricles of normal volume. Third and fourth ventricles in midline. Basal subarachnoid cisterns normal configuration. Focal abnormalities are not observed in the brain parenchyma.
Normal anatomy of the brain on CT and MRI with a few normal variants Practical Neurology
ct Normal CT head with annotated and original images. Case Discussion Annotated teaching CT head in standard and bone windows. 62 public playlists include this case (advertising)