Human eye Extraocular Muscles Britannica
eye anatomy Optometrist in Petaling Jaya Optical Shop Promotion Malaya Optical
There are six extraocular muscles that attach to the outside of the eye from the bone in the eye's socket. These muscles work to rotate the eye, and move the eye up, down, and from side to side. When they work together, these muscles can move the eye in any direction. Medial Rectus (MR) - Moves the eye inward, towards the nose.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/eye-conjunctiva-871453538-5a26c6ad22fa3a0037d5edad.jpg)
How the Human Eye Works (Structure and Function)
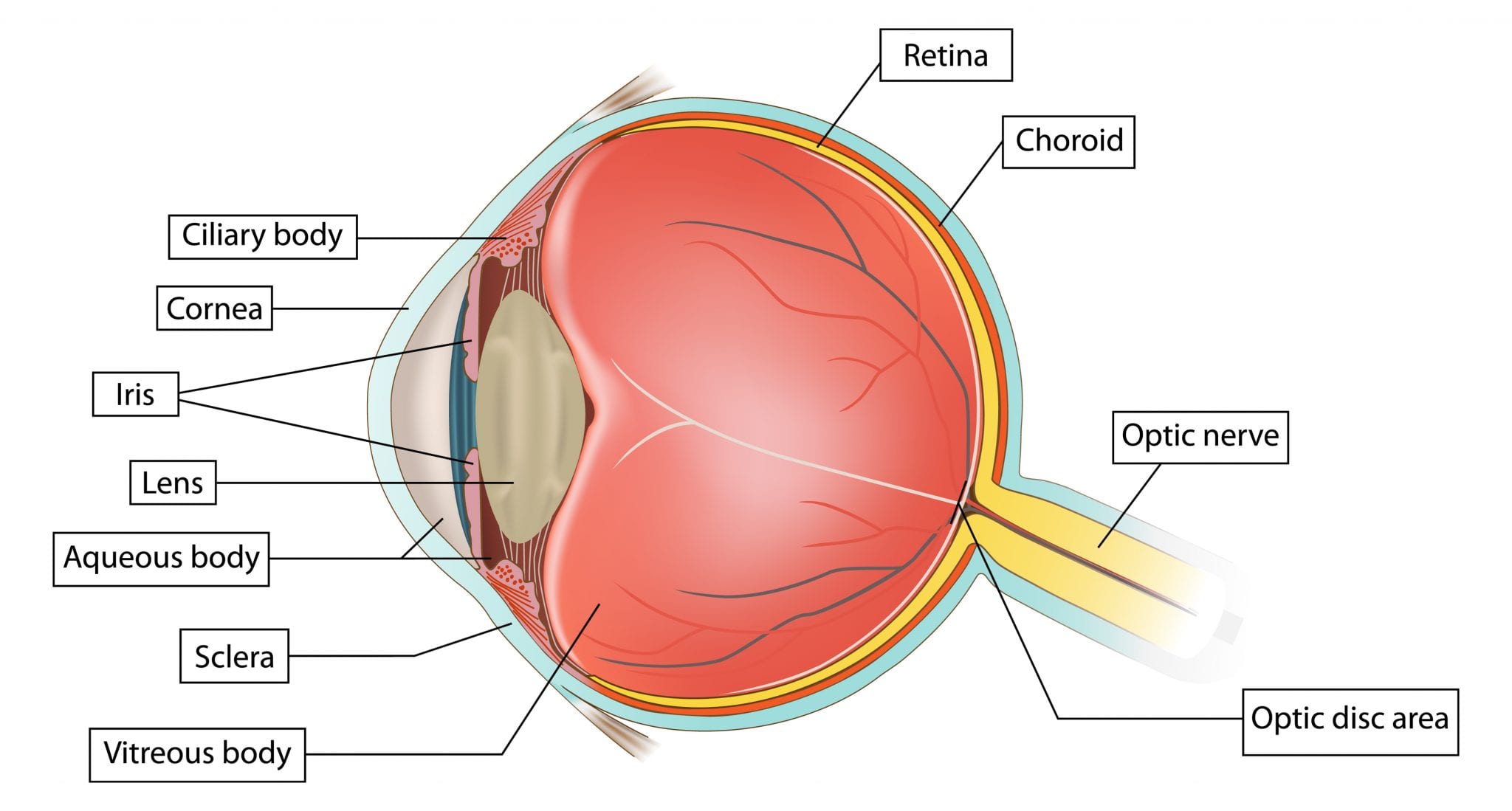
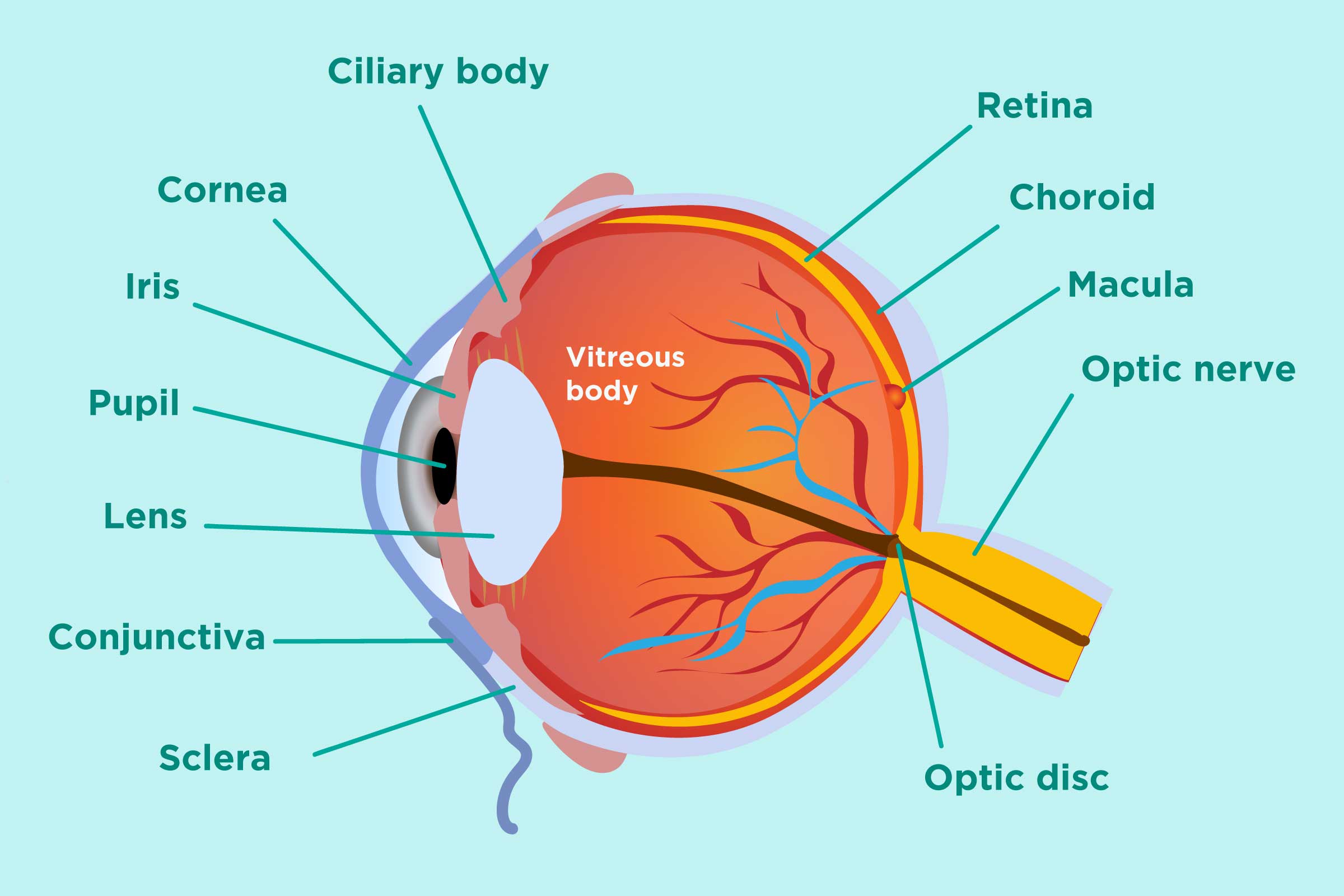
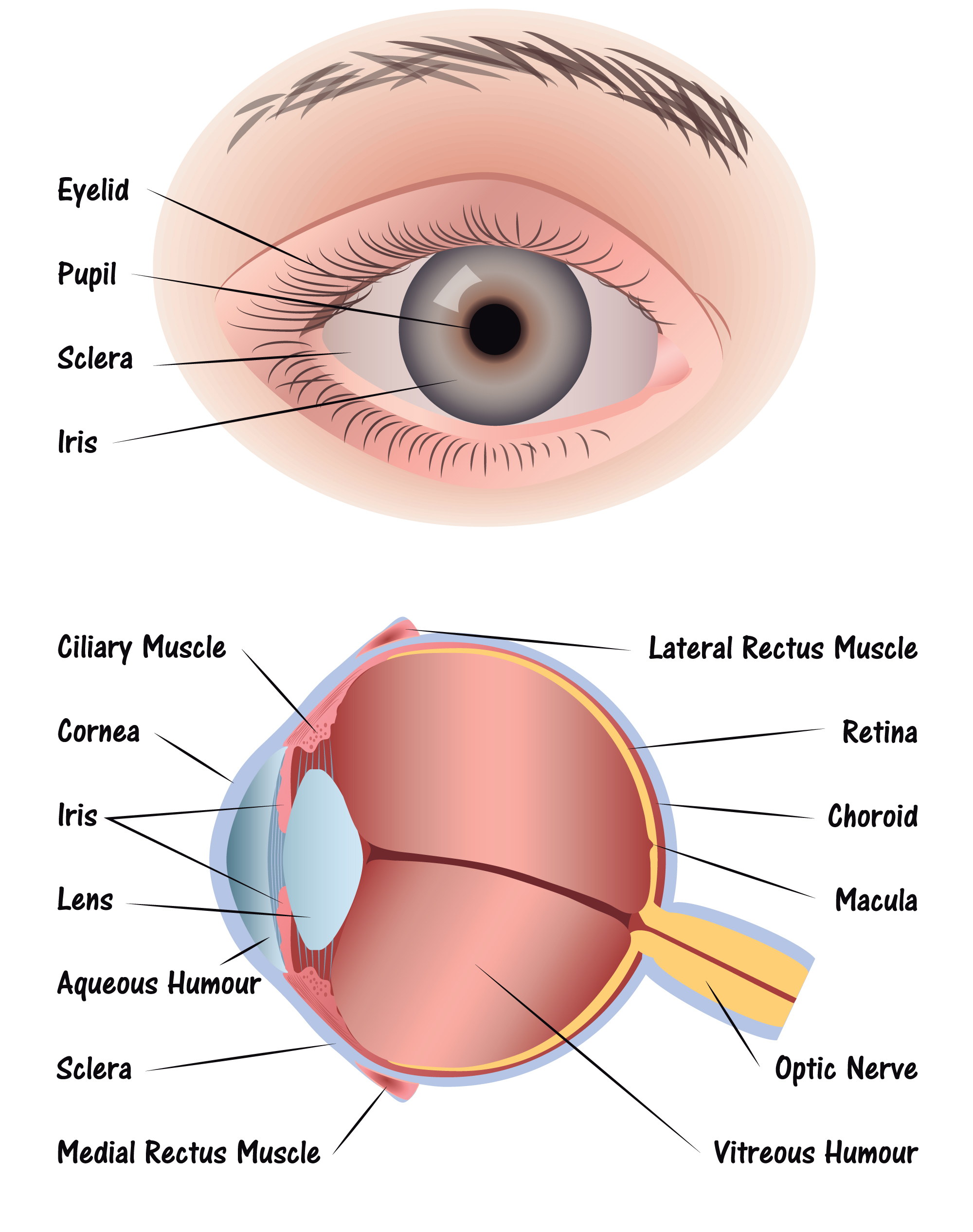
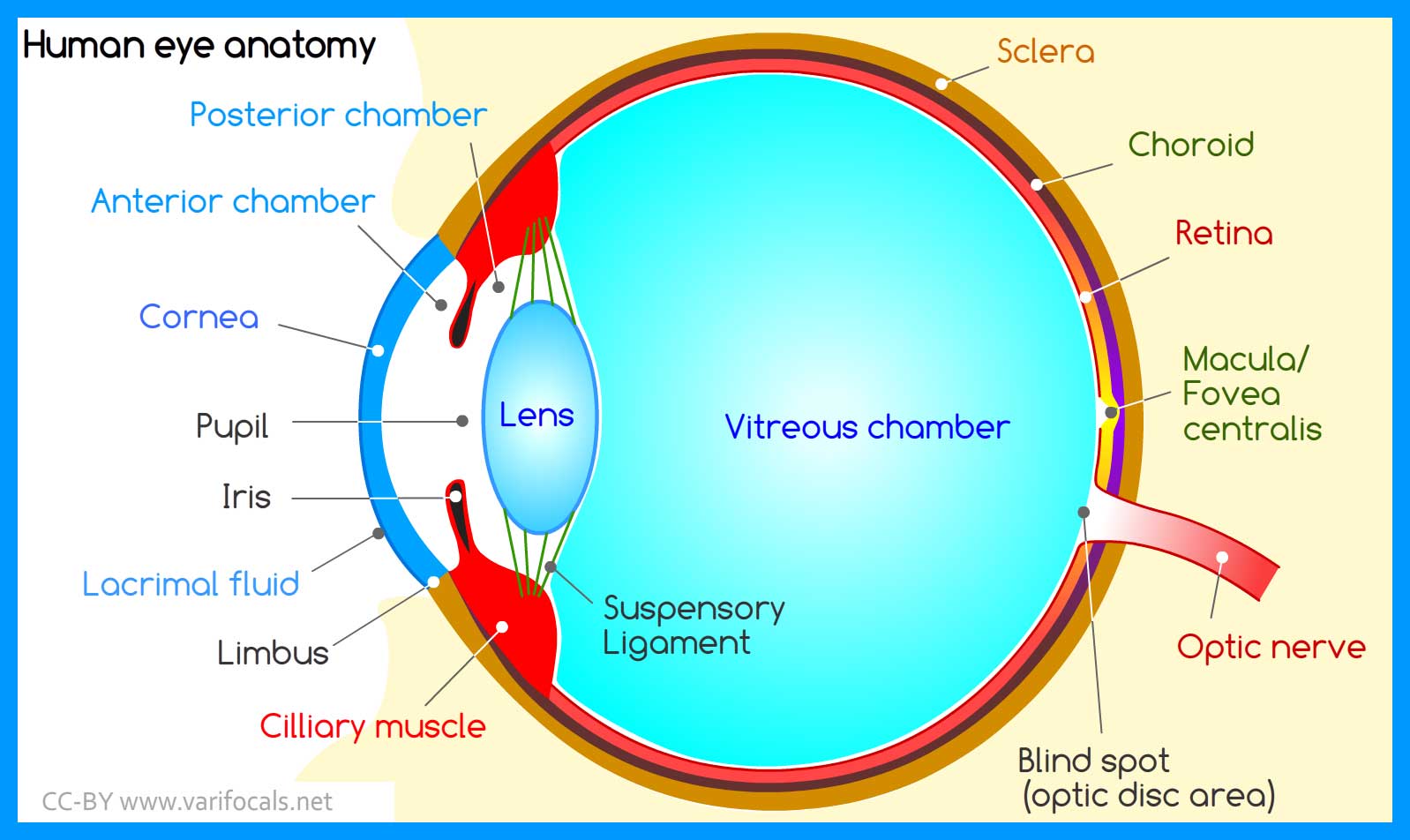
The iris (colored part) of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera, controlling the amount of light reaching the retina by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil (aperture). The eye's crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light rays.

Internal Anatomy Of The Eye Labeled Life Educations
The iris controls widening and narrowing (dilation and constriction) of the pupil. Cornea: the transparent circular part of the front of the eyeball. It refracts the light entering the eye onto the lens, which then focuses it onto the retina. The cornea contains no blood vessels and is extremely sensitive to pain.
ARCHIVE FileAnatomy of the eye.jpg Comparative Physiology of Vision
The retina is the innermost layer lining the back of the eyeball and the light-sensitive part of the eye. The retina contains photoreceptors that detect light. These photoreceptors are known as cones and rods. Cones enable us to detect colours, while rods help us to see in poor light. The retina contains nerve cells that transmit signals from.
Inflammatory Arthritis and Eye Health Prevention, Symptoms, Treatment
Download. English: Parts of the Eye (PDF 603.5 KB) Spanish: Las partes del ojo (PDF 897.7 KB) Check out this fact sheet to see a labeled diagram of the eye and learn about the different parts of the eye.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure and Function of the Human Eye
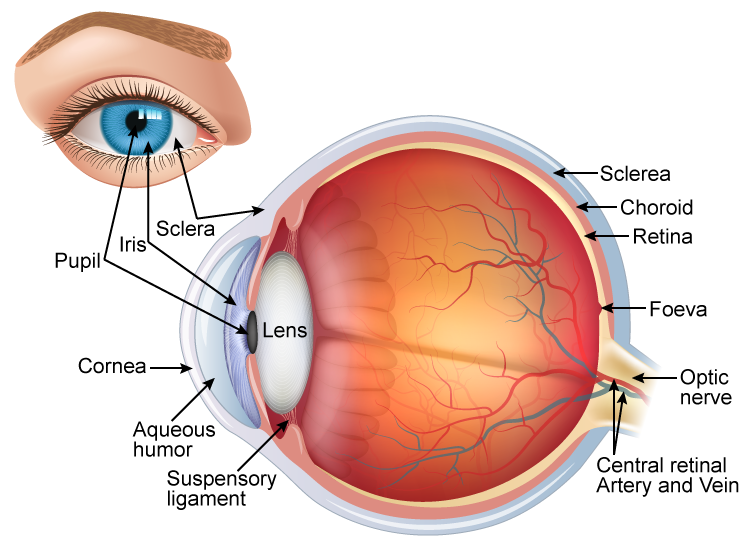
Iris. The colored part of the eye. The iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. Lens (also called crystalline lens). The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. Lower eyelid. Skin that covers the lower part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed.

3 Anatomy Surrounding the Eye OpticianWorks Online Optician Training Human anatomy and
Structure and Functions of Human Eye with labelled Diagram Biology Biology Article Structure Of Eye Structure of the Eye The eye is one of the sensory organs of the body. In this article, we shall explore the anatomy of the eye The structure of the eye is an important topic to understand as it one of the important sensory organs in the human body.
OUR EYES WORK LIKE CAMERA’S! Discovery Eye Foundation
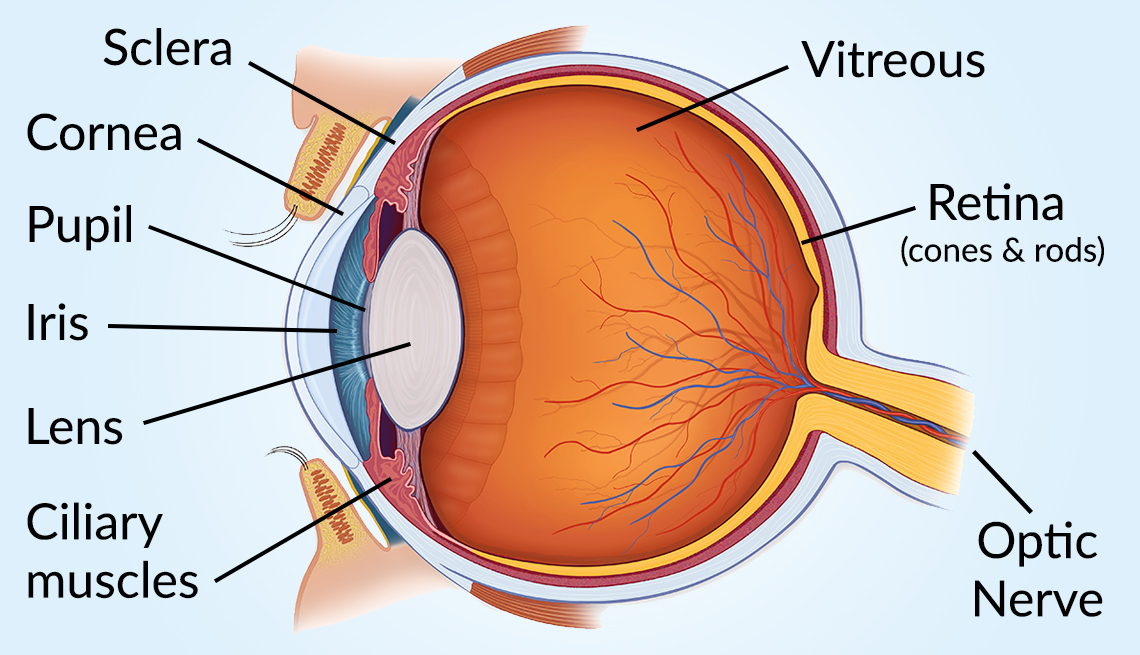
Eye Diagram Handout Parts of the Eye To understand eye problems, it helps to know the different parts that make up the eye and the functions of these parts. Here are descriptions of some of the main parts of the eye: Cornea: The cornea is the clear outer part of the eye's focusing system located at the front of the eye.

Blind Spot Eye Anatomy ANATOMY
Diabetes Healthy ANATOMY and Eyes OF THE AND ITS FUNCTION Toolkit Parts of the Eye Vision is wonderful, but you could lose To understand it if you eye have problems, diabetes. it is helpful to know the different parts of the eye. Please refer to the back of this handout for descriptions of their functions. The main parts of the eye— Optic 3

Human Eye Anatomy Parts of the Eye and Structure of the Human Eye
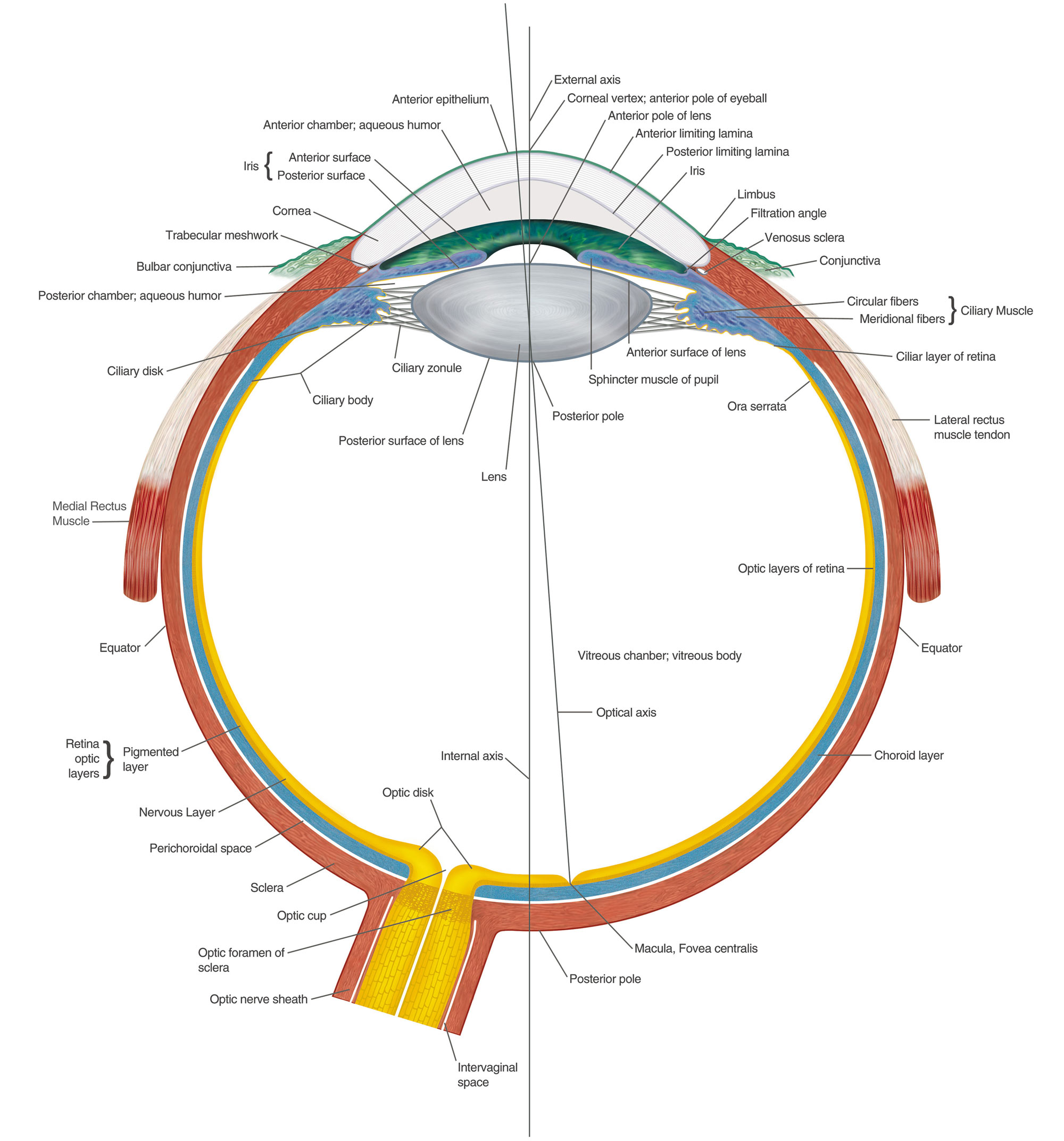
A brief description of the eye along with a well-labelled diagram is given below for reference. Well-Labelled Diagram of Eye The anterior chamber of the eye is the space between the cornea and the iris and is filled with a lubricating fluid, aqueous humour. The vascular layer of the eye, known as the choroid contains the connective tissue.

Human eye Extraocular Muscles Britannica
Eyelid anatomy Lacrimal gland Eye muscles Eyeball Outer layer Middle layer Inner layer Blood supply of the eye Nerves of the eye Sources + Show all Bones of the orbit The bony orbit is made out of seven bones, which include the maxilla, zygomatic bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, sphenoid bone and palatine bone.

Eye Anatomy
Diagram of the Eye Posted in Eye Health, Uncategorized | August 5, 2018 Even though the eye is small, only about 1 inch in diameter, it serves a very important function - the sense of sight.
Labeled Simple Labeled Human Eye Diagram
The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. Each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in, focuses on objects near and far, and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain. The orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the structures that.
Vision and Eye Diagram How We See
Apr. 29, 2023 To understand the diseases and conditions that can affect the eye, it helps to understand basic eye anatomy. Here is a tour of the eye starting from the outside, going in through the front and working to the back. Eye Anatomy: Parts of the Eye Outside the Eyeball The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit.

Anatomy of the Eye Human eye diagram, Eye anatomy diagram, Eye anatomy
1. Conjunctiva The conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). The conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. Conjunctivitis, often known as pink eye, occurs when this thin membrane becomes inflamed or swollen. Other eye disorders that affect the conjunctiva include:
draw a neat and labelled diagram of structure of the human eye slwbyx77 Science
The eye is protected from mechanical injury by being enclosed in a socket, or orbit, which is made up of portions of several of the bones of the skull to form a four-sided pyramid, the apex of which points back into the head.